-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Jul 22. 2025, 15:41:41
In the era of automotive electrification and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), automotive grade aluminum circuit boards have emerged as a critical technology, bridging the gap between thermal management, mechanical durability, and electrical performance. Unlike consumer electronics PCBs, which prioritize cost and miniaturization, automotive grade aluminum circuit boards are engineered to withstand the harshest vehicle environments—extreme temperatures, constant vibration, chemical exposure, and decades of operational stress. This article explores the unique characteristics, design considerations, application ecosystems, and quality standards of automotive grade aluminum circuit boards, highlighting their role in enabling next-generation automotive electronics.
Core Characteristics of Automotive Grade Aluminum Circuit Boards
Automotive grade aluminum circuit boards are distinguished by their specialized construction and material selection, optimized for vehicle-specific challenges:
Structural Composition
Aluminum Substrate: The base layer, chosen for its high thermal conductivity and lightweight properties. Unlike FR-4 or ceramic substrates, aluminum balances heat dissipation with structural rigidity, making it ideal for underhood and cabin applications alike.
Thermally Conductive Dielectric Layer: A thin, insulating layer composed of ceramic-reinforced polymers or high-performance polyimides. This layer electrically isolates the aluminum substrate from the copper circuit layer while enabling efficient heat transfer—critical for power-dense components like EV inverters or LED drivers.
High-Purity Copper Circuit Layer: Thin, uniform copper foil bonded to the dielectric via advanced lamination techniques. This layer forms conductive pathways for electrical signals, with designs optimized to minimize resistance and maximize heat spreading.
The integration of these layers creates a multi-functional platform that manages both electrical current and thermal energy, a duality essential for modern automotive systems.
Key Performance Traits
Thermal Stability: Aluminum’s ability to dissipate heat rapidly prevents component overheating, even in power-dense applications like battery management systems (BMS) or ADAS sensors. This stability extends component lifespans and maintains performance under continuous load.
Mechanical Robustness: The aluminum substrate resists warping, vibration, and shock—critical for components mounted in engine bays, door panels, or chassis, where mechanical stress is constant. Surface treatments like anodization further enhance resistance to corrosion and abrasion.
Electrical Insulation: The dielectric layer maintains high dielectric strength, ensuring reliable insulation between the aluminum substrate and copper traces, even in high-voltage systems (e.g., EV inverters operating at 400V+).
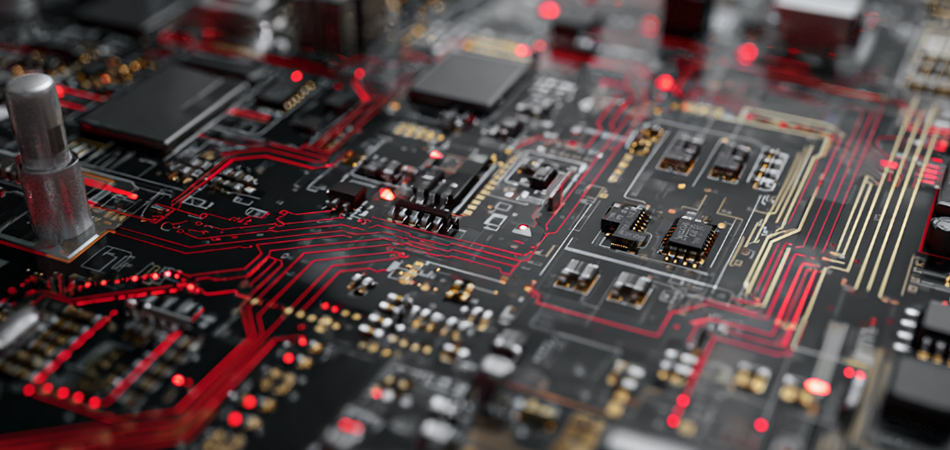
Design Considerations for Automotive Environments
Designing automotive grade aluminum circuit boards requires balancing multiple priorities, from thermal efficiency to regulatory compliance:
Thermal Management Optimization
Heat Path Engineering: PCB layouts are designed to create direct thermal pathways from high-power components (e.g., MOSFETs, LEDs) to the aluminum substrate. This may include large copper pads, thermal vias, or exposed heat sinks integrated into the aluminum layer.
Thermal Cycling Resilience: The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of the aluminum substrate is matched to copper and semiconductor materials to minimize stress during temperature fluctuations (from -40°C in cold climates to 150°C underhood). This reduces the risk of delamination or solder joint failure.
Vibration and Environmental Resistance
Structural Reinforcement: PCB designs include reinforced edges, thicker substrates, or stiffening ribs for components exposed to high vibration (e.g., sensors in suspension systems). Solder joints are optimized for mechanical strength, with techniques like solder mask-defined pads reducing stress concentration.
Environmental Sealing: Coatings such as conformal shielding or parylene protect against moisture, oils, and road salts, ensuring reliability in underhood or exterior applications (e.g., taillight PCBs exposed to rain and snow).
Compliance with Automotive Standards
Functional Safety: Designs align with ISO 26262, the global standard for automotive functional safety, ensuring PCBs in safety-critical systems (e.g., braking electronics) meet rigorous failure-rate requirements.
Material Regulations: Compliance with RoHS, REACH, and IATF 16949 ensures the use of halogen-free, lead-free materials, aligning with global environmental and quality standards.
Applications in Critical Automotive Systems
Automotive grade aluminum circuit boards are integral to nearly all advanced vehicle systems, enabling innovation in safety, efficiency, and connectivity:
Electric and Hybrid Vehicle (EV/HEV) Systems
Battery Management Systems (BMS): Monitor cell voltage, temperature, and state of charge (SOC) in EV batteries. Aluminum PCBs dissipate heat from sensing circuits and balancing resistors, preventing thermal runaway and ensuring battery longevity.
Inverters and Motor Controls: Convert DC power from batteries to AC for electric motors. The aluminum substrate manages heat from high-power transistors, maintaining efficiency and preventing overheating during acceleration or charging.
Onboard Chargers (OBCs): Regulate power flow from charging stations to batteries. Aluminum PCBs dissipate heat from transformers and rectifiers, ensuring safe, efficient charging even in high-ambient temperatures.
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Radar and LiDAR Modules: Detect obstacles and measure distances for features like adaptive cruise control and automatic emergency braking. Aluminum PCBs manage heat from high-frequency RF components, ensuring stable performance and accurate sensor data.
Camera Systems: Power and control front-facing, surround-view, or interior cameras. The aluminum substrate dissipates heat from image sensors and processing chips, preventing image degradation in hot or cold conditions.
Vehicle Lighting and Comfort Systems
LED Headlights and Taillights: Aluminum PCBs power high-output LEDs, dissipating heat to maintain brightness and prevent color shift over time. Their mechanical robustness ensures reliability in exterior lighting exposed to weather and road debris.
Infotainment and Climate Control: Support touchscreens, audio systems, and HVAC controls. Aluminum PCBs manage heat from processors and power amplifiers, ensuring quiet, reliable operation in cabin environments.

Manufacturing and Quality Assurance
Producing automotive grade aluminum circuit boards requires precision engineering and strict quality control to meet automotive standards:
Advanced Manufacturing Processes
Controlled Lamination: The aluminum substrate, dielectric layer, and copper foil are bonded under precise temperature and pressure conditions to ensure uniform adhesion, minimizing thermal resistance at layer interfaces.
Laser Etching and Drilling: High-precision laser techniques create fine circuit traces and micro-vias, enabling high-density designs for compact systems like ADAS sensors. This precision reduces signal loss and improves thermal conductivity.
Automated Assembly: Surface Mount Technology (SMT) with robotic placement ensures accurate component soldering, with vision systems inspecting for defects like cold solder joints or misalignment—critical for reliability in safety-critical applications.
Rigorous Testing Protocols
Thermal Performance Testing: Infrared (IR) imaging and thermal resistance analysis validate heat dissipation pathways, ensuring PCBs meet thermal requirements for their intended application.
Environmental Stress Testing: PCBs undergo thermal cycling (rapid temperature changes), vibration testing (simulating road conditions), and humidity testing to verify durability in real-world environments.
Electrical Testing: Continuity checks, insulation resistance measurements, and high-potential (hipot) tests ensure electrical performance meets specifications, with no short circuits or leakage.
Trends Shaping Automotive Grade Aluminum Circuit Boards
Electrification-Driven Innovation
As EV adoption accelerates, demand for high-voltage, high-power aluminum PCBs is rising:
High-Voltage Compatibility: Designs are evolving to support 800V architectures, requiring thicker dielectrics and enhanced insulation to manage higher voltages safely.
Integrated Cooling Solutions: Some PCBs integrate microfluidic channels or heat pipes within the aluminum substrate, enabling liquid cooling for extreme power densities in next-generation EVs.
ADAS and Autonomy Advancements
High-Frequency Optimization: PCBs for 77GHz radar and LiDAR are being engineered with low-loss dielectrics and precise trace geometries to minimize signal attenuation, critical for accurate object detection in autonomous vehicles.
Sensor Fusion: PCBs supporting multiple sensors (radar + camera + LiDAR) in a single module require compact, thermally efficient designs, with aluminum substrates managing heat from multiple high-power components.
Sustainability and Circular Design
Recyclable Materials: Manufacturers are exploring recycled aluminum substrates and bio-based dielectrics to reduce environmental impact, aligning with automotive OEMs’ carbon-neutral goals.
Longevity Engineering: Designs focus on extending PCB lifespans to match vehicle service lives (15+ years), reducing electronic waste and supporting circular economy initiatives.

Conclusion
Automotive grade aluminum circuit boards are indispensable to the evolution of modern vehicles, enabling the safety, efficiency, and connectivity that define next-generation mobility. By combining thermal management, mechanical durability, and electrical performance, these PCBs meet the unique demands of automotive environments, from underhood heat to cabin comfort systems. As vehicles become more electrified, autonomous, and connected, the role of automotive grade aluminum circuit boards will only grow—driving innovation in material science, design, and manufacturing. For engineers, manufacturers, and OEMs, these PCBs represent a critical investment in reliability, ensuring that automotive electronics perform flawlessly, mile after mile, for decades to come.
Keywords: Automotive Grade Aluminum Circuit Board, automotive electronics, thermal management, EV PCBs, ADAS, aluminum substrate, automotive reliability, PCB manufacturing.
This article provides a comprehensive, technically rigorous overview of automotive grade aluminum circuit boards, optimized for search engine visibility while emphasizing industry relevance and innovation. By focusing on application-specific challenges and future trends, it offers value to engineers, procurement professionals, and automotive technology enthusiasts alike.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
