-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Jun 26. 2025, 10:37:11
In the realm of modern electronics manufacturing, Aluminum Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) have carved out a significant niche due to their exceptional thermal conductivity and mechanical robustness. Among the various features that contribute to the functionality and reliability of these PCBs, countersink holes stand out as a critical element. These seemingly simple holes play a multifaceted role, influencing everything from component mounting and electrical performance to the overall durability and aesthetic appeal of the PCB assembly.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of countersink holes in aluminum PCBs. We will delve into their fundamental characteristics, explore the key considerations in their design and manufacturing, discuss quality control measures, and examine their diverse applications across different industries. Additionally, we will look at the emerging trends and challenges associated with these holes, offering insights into the future of their role in electronics manufacturing.
Understanding Countersink Holes in Aluminum PCBs
Definition and Basic Function
A countersink hole in an aluminum PCB is a conical - shaped depression that is created around a drilled hole. Its primary function is to allow for the use of flat - head screws or rivets, enabling these fasteners to sit flush with the surface of the PCB. This flush - mounting is not just about aesthetics; it serves several practical purposes.
Mechanically, it provides a more stable and secure connection when attaching components to the PCB. By ensuring that the fastener head lies flat against the board, the clamping force is evenly distributed, reducing the risk of stress concentrations that could lead to component failure over time. In dynamic environments where vibrations are common, such as in automotive or aerospace applications, this secure connection is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the electronic assembly.
From an electrical perspective, in some cases where the fastener also acts as an electrical conductor, a properly formed countersink hole ensures optimal contact with the PCB traces, minimizing electrical resistance and potential signal interference.
Types of Countersink Holes
There are two main types of countersink holes commonly used in aluminum PCBs: through - hole countersinks and blind countersinks.
Through - hole countersinks are created by first drilling a hole that passes completely through the PCB and then forming the conical depression on one or both sides. This type is suitable when the fastener needs to penetrate the entire thickness of the board, for example, when mounting the PCB to a chassis or when making connections between multiple PCBs.
Blind countersinks, on the other hand, are only formed on one side of the PCB, and the hole does not go all the way through. They are typically used when the component is mounted on only one side of the board, and a flush finish is desired on that surface without affecting the opposite side. Blind countersinks require more precise manufacturing techniques due to the need to control the depth of the countersinking process accurately.
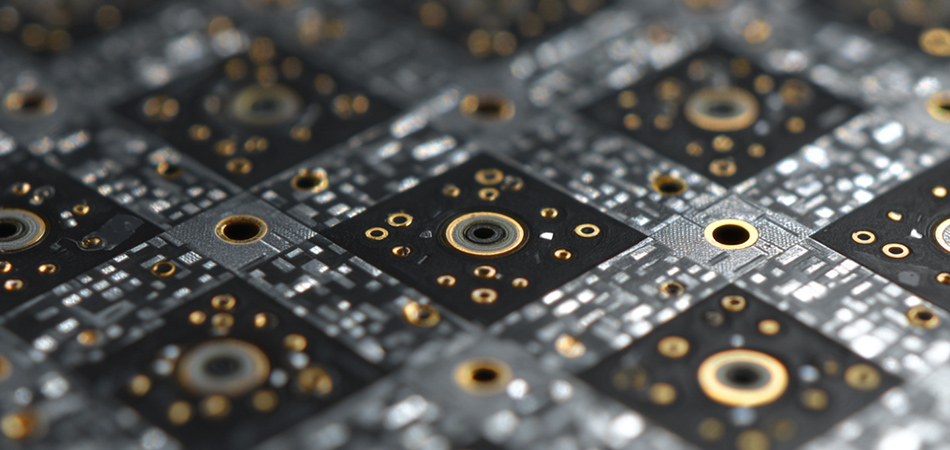
Design Considerations for Countersink Holes in Aluminum PCBs
Hole Dimensions and Specifications
The dimensions of countersink holes in aluminum PCBs are carefully determined based on the type and size of the fasteners to be used. The diameter of the drilled hole before countersinking must be precisely matched to the shank diameter of the screw or rivet. A hole that is too small can make insertion difficult and may cause damage to the PCB or the fastener, while a hole that is too large can result in a loose connection.
The depth of the countersink is equally important. It should be sufficient to accommodate the head of the flat - head fastener, ensuring that it sits flush with the PCB surface. However, excessive depth can weaken the structural integrity of the PCB, especially in thinner aluminum substrates. The angle of the countersink is also a critical parameter, with standard angles commonly used in the industry, but custom angles may be specified for specific applications.
Material Compatibility
Aluminum PCBs consist of an aluminum substrate, a dielectric layer, and copper traces. When designing countersink holes, it is essential to consider the compatibility of these materials with the fasteners and any additional materials used in the mounting process.
For instance, different metals used for fasteners can react with the aluminum substrate, leading to galvanic corrosion. To prevent this, designers may select fasteners made of corrosion - resistant materials or apply protective coatings. Additionally, the countersinking process should not damage the dielectric layer, as this could compromise the electrical insulation of the PCB. Special care must be taken to ensure that the mechanical stress generated during the creation of the countersink hole does not cause cracks or delamination in the PCB layers.
Placement and Layout
The placement of countersink holes on the PCB is a crucial aspect of the design process. From a mechanical standpoint, they should be located in areas that can withstand the forces exerted by the fasteners without causing excessive stress on the PCB or the mounted components. This may involve avoiding areas near sensitive electronic components or regions where the PCB is likely to experience high stress concentrations, such as near the edges or around cutouts.
For electrical performance, the layout of the countersink holes must be planned to avoid interfering with the copper traces and electrical pathways. Sufficient clearance needs to be maintained between the holes and the traces to prevent short - circuits or signal degradation. In complex PCB designs, computer - aided design (CAD) software is often employed to optimize the placement and layout of countersink holes, ensuring that they meet both mechanical and electrical requirements.

Manufacturing Processes for Countersink Holes in Aluminum PCBs
Drilling
The manufacturing of countersink holes begins with the drilling of the initial hole in the aluminum PCB. High - precision drilling machines are used for this task, capable of creating holes with precise diameters and locations. These machines can operate at high speeds and are equipped with advanced control systems to ensure accuracy.
When drilling aluminum PCBs, specialized drill bits are required. These bits are typically made of high - speed steel or carbide, which can withstand the high temperatures generated during the drilling process and provide clean, burr - free holes. The choice of drill bit depends on factors such as the thickness of the PCB, the material composition, and the desired hole diameter.
Countersinking
After the initial hole is drilled, the countersinking process is carried out. There are several methods available for countersinking in aluminum PCBs.
Mechanical countersinking is the most common method. It involves using a countersinking tool, which is a conical - shaped bit with cutting edges. This tool is mounted on a drilling machine or a specialized countersinking device. As the tool rotates, it removes material from the drilled hole, creating the conical countersink. The speed and feed rate of the tool are carefully controlled to ensure a smooth and accurate countersink with the desired depth and angle.
In some cases, laser - based countersinking may be employed. Laser technology offers high precision and the ability to create complex shapes and patterns. It can be used to create countersink holes with very tight tolerances, making it suitable for applications where high accuracy is required. However, laser countersinking is generally more expensive and may not be as suitable for high - volume production compared to mechanical methods.
Post - Processing and Quality Assurance
After the countersinking process, post - processing steps may be necessary to ensure the quality of the holes. This can include deburring, which involves removing any burrs or rough edges that may have been created during drilling and countersinking. Deburring is important as burrs can interfere with the proper seating of the fastener and may also pose a risk to the electrical insulation of the PCB.
Quality assurance is an integral part of the manufacturing process. Inspections are carried out to check the dimensions, shape, and surface finish of the countersink holes. Visual inspections, dimensional measurements using precision instruments such as calipers or micrometers, and in some cases, non - destructive testing methods may be employed to ensure that the holes meet the specified requirements.
Quality Control of Countersink Holes in Aluminum PCBs
Dimensional Inspection
Dimensional inspection is a key quality control measure for countersink holes. Precision measuring tools are used to check the diameter of the drilled hole, the depth of the countersink, and the angle of the conical depression. Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) can provide highly accurate measurements, allowing manufacturers to verify that the holes meet the design specifications within the required tolerances.
Any deviation from the specified dimensions can have a significant impact on the performance of the PCB assembly. For example, an incorrectly sized hole may result in a loose or tight fit for the fastener, affecting the mechanical and electrical integrity of the connection.
Visual Inspection
Visual inspection is another important aspect of quality control. Trained inspectors carefully examine the countersink holes for any visible defects, such as burrs, cracks, or uneven surfaces. Burrs can not only interfere with the proper installation of the fastener but can also cause electrical shorts if they come into contact with nearby traces. Cracks in the PCB around the countersink hole can weaken the structural integrity of the board, potentially leading to failure under stress.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems can also be used to perform more efficient and accurate visual inspections. These systems use cameras and image - processing algorithms to detect even the smallest defects, ensuring that only high - quality PCBs with properly formed countersink holes are passed on to the next stage of production.
Functional Testing
In addition to dimensional and visual inspections, functional testing may be conducted to ensure that the countersink holes do not negatively impact the electrical and mechanical functionality of the PCB. Mechanical functional tests can involve applying simulated forces to the mounted components to check the strength and stability of the connection provided by the countersink holes.
Electrical functional tests can include continuity testing, insulation resistance testing, and signal integrity testing. These tests help to verify that the countersink holes have not caused any electrical problems, such as short - circuits or increased electrical resistance, and that the PCB can operate reliably in its intended application.

Applications of Countersink Holes in Aluminum PCBs
Aerospace and Defense
In the aerospace and defense industries, where reliability and performance are paramount, countersink holes in aluminum PCBs play a vital role. In avionics systems, which are used for navigation, communication, and control in aircraft, components need to be mounted securely to withstand extreme conditions, including high altitudes, rapid temperature changes, and intense vibrations.
Precision - made countersink holes ensure that components remain firmly in place, preventing any movement that could disrupt the operation of these critical systems. In defense applications, such as missile guidance systems and radar systems, the use of countersink holes helps to maintain the integrity of the PCB assembly, enabling accurate and reliable performance in harsh and demanding environments.
Automotive Electronics
The automotive industry also relies on countersink holes in aluminum PCBs for various applications. In engine control units (ECUs), infotainment systems, and lighting systems, these holes are used to mount components securely. The automotive environment is filled with vibrations, temperature fluctuations, and electrical noise, and a robust connection provided by countersink holes is essential for the long - term reliability of the electronic components.
For example, in LED headlights, the PCB that holds the LEDs may use countersink holes to attach the light - emitting components to the heat sink. This not only ensures a stable mechanical connection but also facilitates efficient heat transfer, which is crucial for the performance and lifespan of the LEDs.
Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, countersink holes in aluminum PCBs contribute to both the functionality and aesthetics of the products. In smartphones, tablets, and laptops, these holes are used to mount internal components, such as batteries, circuit boards, and display modules. A flush - mounted connection provided by countersink holes allows for a more compact and sleek design, as it prevents the fasteners from protruding and taking up unnecessary space.
The smooth surface finish achieved with properly formed countersink holes also enhances the overall visual appeal of the product, which is an important factor in the highly competitive consumer electronics market. Additionally, the secure mechanical connection ensures that the components remain in place during normal use and handling, reducing the risk of damage to the device.
Future Trends and Challenges
Miniaturization
As the electronics industry continues to trend towards miniaturization, the demand for smaller and more precisely manufactured countersink holes in aluminum PCBs is increasing. With components becoming smaller and more densely packed, the size and tolerance requirements for these holes are becoming more stringent.
Manufacturers will need to develop new and improved manufacturing techniques and tools to achieve the required levels of precision. This may involve the use of advanced micro - machining technologies and the development of specialized drill bits and countersinking tools that can work with extremely small dimensions.
Integration of New Materials and Technologies
The integration of new materials, such as advanced composites and nanomaterials, into aluminum PCBs may present new challenges and opportunities for the design and manufacturing of countersink holes. These materials may have different mechanical and electrical properties, requiring adjustments to the traditional methods of creating and using countersink holes.
Emerging technologies, such as 3D printing for PCBs, could also revolutionize the way countersink holes are fabricated. 3D - printed PCBs may offer greater design flexibility, but they will also require the development of new techniques for creating accurate and reliable countersink holes.
Environmental Sustainability
Increasing concerns about environmental sustainability are driving the electronics manufacturing industry to adopt more eco - friendly practices. This includes the development of manufacturing processes for countersink holes in aluminum PCBs that reduce the use of hazardous chemicals and minimize waste generation.
Manufacturers will need to explore alternative materials and processes that are more environmentally friendly while still maintaining the quality and performance of the countersink holes. Recycling and proper disposal of PCBs at the end of their life cycle will also become increasingly important considerations.
Conclusion
Countersink holes in aluminum PCBs are a fundamental yet highly significant feature in modern electronics manufacturing. They play a crucial role in ensuring the secure mounting of components, optimizing electrical performance, and enhancing the overall durability and aesthetic appeal of PCB assemblies.
Through careful design, precise manufacturing, and rigorous quality control, these holes are tailored to meet the diverse requirements of various industries. As the electronics industry continues to evolve, countersink holes in aluminum PCBs will face new challenges and opportunities, driven by trends such as miniaturization, the integration of new materials and technologies, and the push for environmental sustainability. By addressing these challenges and embracing new opportunities, the role of countersink holes in aluminum PCBs will continue to be essential in the creation of advanced and reliable electronic devices.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
