-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Dec 16. 2025, 12:00:21
As the global electronics industry marches toward miniaturization, intelligence, and eco-friendliness, flexible PCB has evolved from a supporting component to a core enabler of technological innovation. Beyond its traditional advantages of thinness, light weight, and bendability, modern flexible PCB is driving breakthroughs in material science, sustainable manufacturing, and niche high-end applications. Unlike conventional rigid PCBs and early flexible circuits, today’s advanced flexible PCB integrates novel materials such as liquid metals and recyclable polymers, addressing critical challenges in stretchability, durability, and environmental impact. For electronics manufacturers and designers, understanding these emerging trends in flexible PCB is essential to unlocking new product possibilities and gaining a competitive edge in fast-evolving markets.
Recent advancements in material science have revolutionized the performance capabilities of flexible PCB, enabling functionalities that were once unattainable:
- Liquid Metal for Stretchable & Self-Healing Circuits: A groundbreaking development in flexible PCB technology is the integration of liquid metals into circuit designs. Unlike traditional copper conductors, liquid metals (such as gallium-based alloys) offer exceptional stretchability—up to 300% elongation—while maintaining stable electrical conductivity. Advanced designs incorporate multi-level conductive networks and "core-shell" self-healing technologies, allowing flexible PCB to autonomously repair micro-damage caused by repeated bending or stretching. This innovation is particularly transformative for stretchable OLED displays, wearable health monitors, and flexible robotic components, where durability and adaptability are paramount.
- Recyclable Polymers for Sustainable Electronics: Addressing the environmental challenges of electronic waste, researchers have developed flexible PCB using vitrimer-based epoxy resins. These materials retain the mechanical and electrical performance of traditional flexible PCB substrates but can be efficiently recycled by immersing them in low-boiling-point organic solvents. The recycling process separates the polymer matrix from glass fibers and electronic components without causing damage, enabling reuse of over 90% of materials. This breakthrough aligns flexible PCB production with global sustainability goals, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and toxic waste compared to conventional manufacturing.
Innovations in manufacturing processes are optimizing the production of flexible PCB, making advanced functionalities more accessible for mass and custom applications:
- Laser Welding for High-Precision Assembly: Traditional soldering techniques often cause thermal deformation or mechanical damage to delicate flexible PCB substrates. Laser welding has emerged as a superior alternative, offering non-contact operation, micro-scale positioning accuracy, and minimal heat input. This process ensures clean, residue-free connections between flexible PCB and components, even for ultra-thin (0.05mm) circuits and high-density pads. It significantly improves assembly yield and reliability, making it ideal for high-end applications such as medical devices and automotive electronics.
- Roll-to-Roll Production for Customized Scale: For applications requiring long-length flexible PCB, such as LED light strips, roll-to-roll manufacturing has replaced traditional sheet-by-sheet processes. This continuous production method reduces the number of manufacturing steps from over 10 to just 4-5, cutting labor costs by 50% and material waste by 30-50%. It enables the production of "infinitely long" flexible PCB tailored to customer specifications, supporting the growing demand for customized lighting and linear electronic systems.
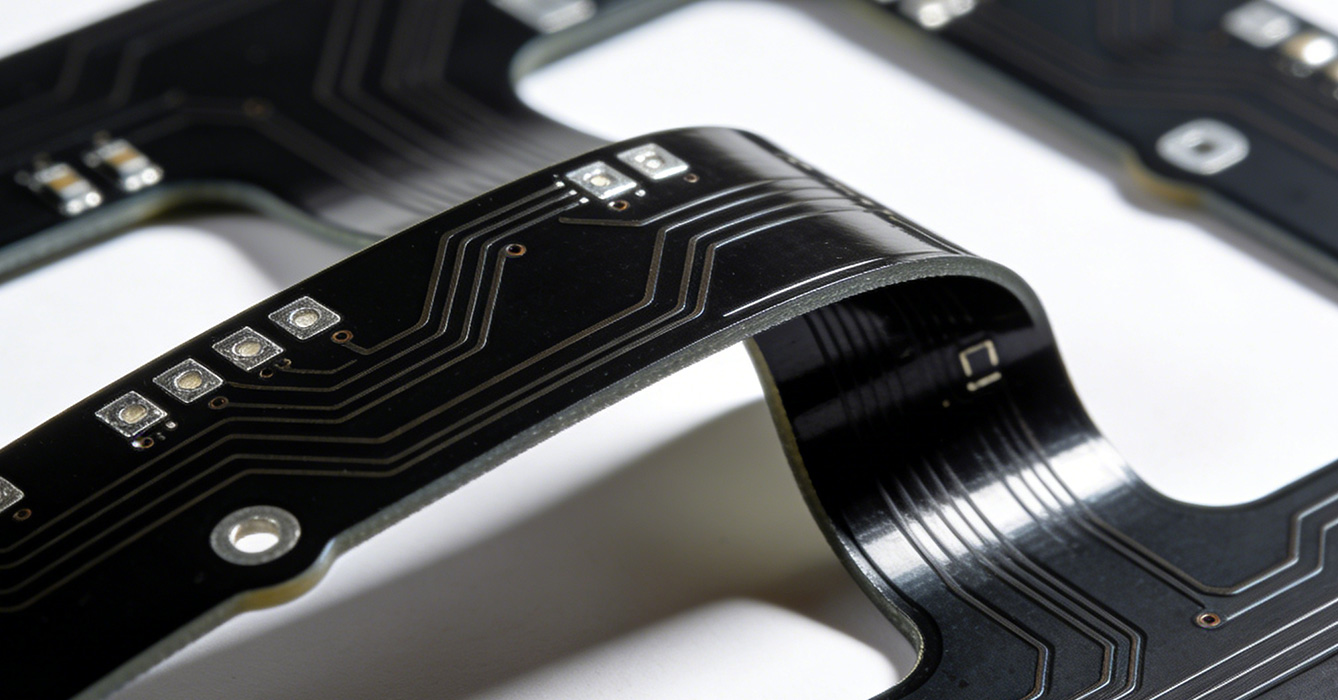

The expanded capabilities of modern flexible PCB are opening up new application areas beyond consumer electronics and automotive systems:
- Stretchable OLED Displays: Flexible PCB with liquid metal conductors is a critical component in stretchable OLED technology, enabling displays that can fold, curl, and stretch without performance degradation. This application is driving innovation in next-generation smartphones, smart wearables, and curved automotive displays, where form factor flexibility directly enhances user experience.
- Customized LED Lighting Systems: Roll-to-roll manufactured flexible PCB has become the preferred solution for custom LED light strips. Its ability to be produced in variable lengths and integrated with complex circuit designs allows for versatile lighting installations in architecture, automotive interiors, and consumer electronics, while maintaining energy efficiency and reliability.
- Environmentally Friendly Electronics: Recyclable flexible PCB is gaining traction in eco-conscious industries, including renewable energy and consumer electronics. It supports the development of sustainable products with reduced environmental footprints, meeting the growing demand for green electronics from both consumers and regulatory bodies.
The future development of flexible PCB will focus on integrating smart functionalities and expanding industrial applicability:
- Multifunctional Smart Circuits: Future flexible PCB will integrate sensing, energy harvesting, and data processing capabilities into a single flexible platform. This will enable the development of "all-in-one" solutions for wearable health monitors, environmental sensors, and IoT devices, reducing component count and improving system efficiency.
- Cost Reduction for Mass Adoption: As material and manufacturing technologies mature, the cost of advanced flexible PCB (such as liquid metal and recyclable variants) will decrease, enabling widespread adoption beyond high-end applications. This will drive growth in emerging markets such as smart textiles and low-cost wearable devices.
- Standardization for Sustainability: The industry will move toward unified standards for recyclable flexible PCB materials and manufacturing processes. This will ensure consistent quality, facilitate material recycling, and accelerate the adoption of sustainable practices across the electronics supply chain.
In conclusion, flexible PCB is undergoing a transformative evolution driven by material innovation and sustainability requirements. The integration of liquid metals and recyclable polymers, combined with advanced manufacturing processes, is expanding its performance capabilities and application boundaries. As the electronics industry continues to prioritize flexibility, durability, and environmental responsibility, flexible PCB will play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of smart, sustainable electronic products. For businesses looking to innovate, embracing these emerging trends in flexible PCB is key to staying ahead in a rapidly changing market.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
