-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Sep 25. 2025, 14:35:00
In the evolving world of electronics, the quest for smaller, more reliable, and efficient components never ceases. Enter the rigid-flex PCB—a hybrid solution that combines the best of both rigid and flexible circuit boards. Understanding the advantages of rigid-flex PCBs can significantly impact your approach to PCB design and manufacturing.
Rigid-flex PCBs are a type of printed circuit board that combines elements of both rigid and flexible circuitry in a single board. This integration allows for greater design versatility and improved performance in various applications. The rigid sections provide structural support, while the flexible sections allow for bending and folding, which can be crucial in compact or irregularly shaped electronic devices.
Rigid Layers: These are the solid sections of the PCB, providing support and a base for mounting components.
Flexible Layers: These layers connect the rigid parts, allowing the board to flex and adapt to different shapes.
Plated Through Holes (PTH): These holes allow electrical connections between the different layers of the PCB.
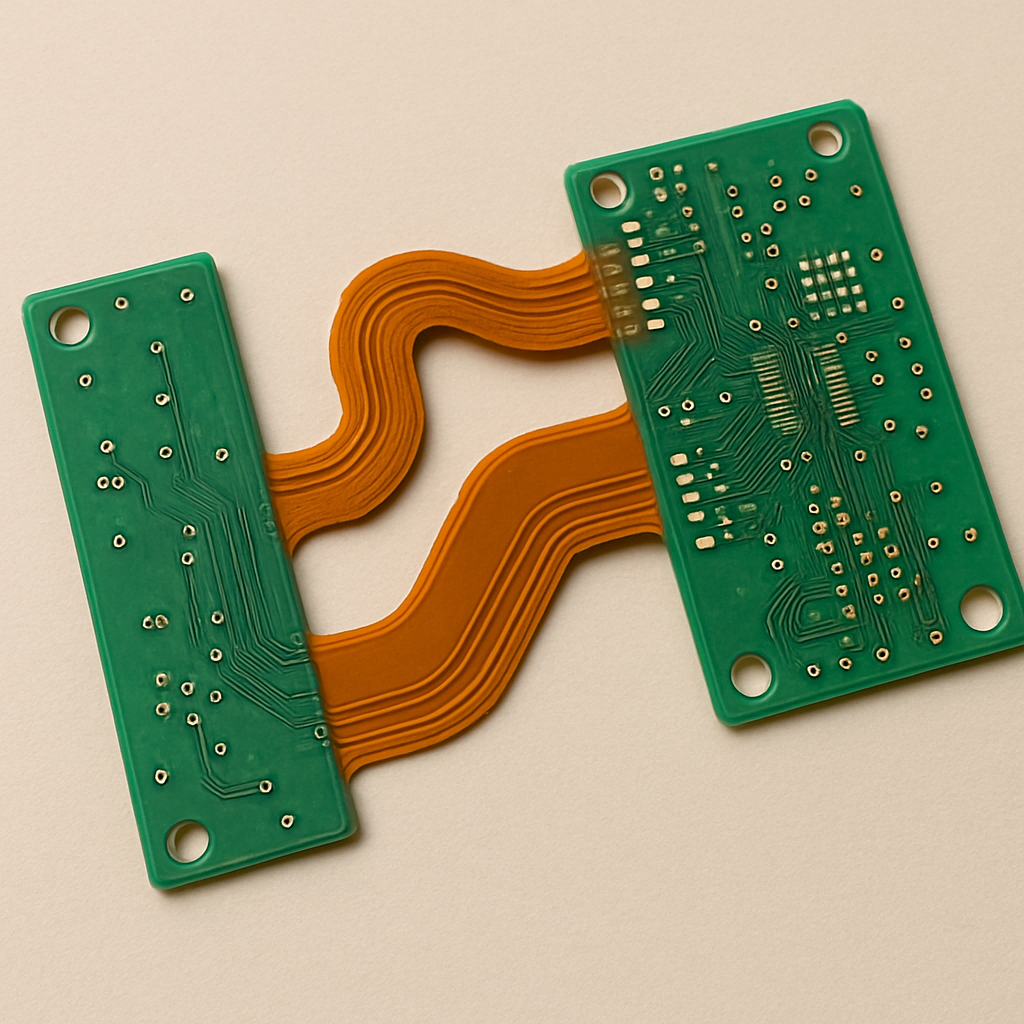
One of the most significant advantages of rigid-flex PCBs is their design versatility. By combining both rigid and flexible elements, designers can create complex geometries that would be impossible with a standard rigid PCB. This capability is particularly beneficial in applications where space is at a premium, such as in medical devices and wearable technology.
Rigid-flex PCBs can drastically reduce the size and weight of an electronic device. By integrating multiple components into a single board, the need for additional connectors is eliminated, reducing overall weight and space. This makes them ideal for aerospace and military applications where every gram counts.
The reliability of electronic devices is paramount, especially in critical applications. Rigid-flex PCBs enhance reliability by reducing the number of solder joints, which are common failure points in traditional PCBs. Additionally, the integration of rigid and flexible layers minimizes the risk of connection failure due to vibration or movement.
The combination of rigid and flexible materials in a rigid-flex PCB results in a more durable product. The flexible layers can absorb shocks and vibrations, protecting the components and maintaining performance under harsh conditions. This durability extends the life of the electronic device, making rigid-flex PCBs a cost-effective solution in the long run.
The assembly process for electronic devices using rigid-flex PCBs is simplified due to the reduced number of components and connectors. This not only speeds up manufacturing but also reduces the chance of assembly errors. A streamlined assembly process can lead to lower production costs and faster time-to-market.

In the medical field, the demand for compact, reliable devices is ever-growing. Rigid-flex PCBs are used in pacemakers, hearing aids, and medical imaging equipment due to their small size and high reliability.
Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace and defense, weight and reliability are critical. Rigid-flex PCBs are used in communication systems, navigation equipment, and missile guidance systems, where their lightweight and durable nature provide a strategic advantage.
From smartphones to wearable devices, consumer electronics benefit from the reduced size and weight of rigid-flex PCBs. The flexible nature allows for innovative product designs and improved user experiences.
While the advantages are clear, manufacturing rigid-flex PCBs presents unique challenges. The complexity of combining rigid and flexible layers requires precise engineering and advanced manufacturing techniques. Here are a few challenges:
Material Selection: Choosing materials that can withstand the bending and flexing while maintaining electrical integrity is crucial.
Design Complexity: Designing a rigid-flex PCB requires a thorough understanding of both rigid and flexible technologies.
Cost Considerations: The initial cost of manufacturing rigid-flex PCBs can be higher than traditional PCBs due to their complexity.
To successfully implement rigid-flex PCBs, collaboration between designers and manufacturers is essential. Here are some strategies:
Early Involvement: Involve manufacturers early in the design process to ensure feasibility and cost-effectiveness.
Prototyping and Testing: Extensive prototyping and testing are vital to address potential issues before mass production.
Advanced Software: Utilize advanced PCB design software capable of handling the complexities of rigid-flex designs.
Rigid-flex PCBs offer numerous advantages that can transform the way electronic devices are designed and manufactured. By understanding their benefits and addressing the challenges, companies can leverage this technology to create innovative, reliable, and efficient products.
Whether you're in the field of medical devices, aerospace, or consumer electronics, considering rigid-flex PCBs in your next project could be the key to staying ahead in an increasingly competitive market. Embrace the possibilities and take your electronic designs to new heights with rigid-flex technology.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
