-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Jul 07. 2025, 10:50:36
In the dynamic realm of modern lighting technology, Surface - Mount Device (SMD) LEDs have emerged as a dominant force, revolutionizing illumination across diverse sectors. At the core of their high - performance operation lies the meticulous design of SMD LED aluminum circuits. The synergy between the unique properties of aluminum and the specific requirements of SMD LEDs creates a foundation for efficient, reliable, and compact lighting solutions. This article delves into the intricate details of SMD LED aluminum circuit design, exploring material considerations, design methodologies, manufacturing processes, quality assurance practices, real - world applications, and emerging market trends.
Material Science Underlying SMD LED Aluminum Circuit Design
Aluminum Substrate Selection
The choice of aluminum for SMD LED circuit substrates is a strategic decision driven by its remarkable thermal conductivity. SMD LEDs, despite their energy - efficiency, generate substantial heat during operation. Aluminum's ability to rapidly dissipate this heat is crucial for maintaining the optimal operating temperature of SMD LEDs, thereby preventing performance degradation, color shift, and premature failure.
Different aluminum alloys offer varying performance characteristics. Alloys with enhanced mechanical strength can withstand the mechanical stresses encountered during manufacturing, assembly, and operation, ensuring the structural integrity of the circuit. Moreover, aluminum's formability allows for the creation of custom - shaped substrates, facilitating integration into diverse lighting fixtures with complex geometries.
Dielectric Layer Considerations
The dielectric layer in SMD LED aluminum circuits serves a dual - critical function: providing electrical insulation between the conductive traces and the aluminum substrate while facilitating heat transfer. The selection of dielectric material significantly impacts the overall performance of the circuit.
High - temperature - resistant dielectrics, such as polyimide - based materials, are often preferred for high - power SMD LED applications. These materials can endure elevated temperatures without compromising electrical insulation, making them suitable for scenarios where SMD LEDs operate under heavy loads. On the other hand, ceramic - filled epoxies offer a cost - effective alternative with improved thermal conductivity. By incorporating ceramic fillers, they enhance the heat - transfer efficiency from SMD LEDs to the aluminum substrate, enabling better thermal management in a wide range of lighting products.
Copper Traces for Electrical Connectivity
Copper, renowned for its low electrical resistance, is the material of choice for the conductive traces in SMD LED aluminum circuits. This property ensures efficient power delivery to SMD LEDs, minimizing power losses and reducing the heat generated within the traces themselves. The thickness and width of copper traces are carefully calculated based on the current - carrying requirements of SMD LED arrays.
In high - density SMD LED circuits, where multiple LEDs are closely packed, proper trace routing and sizing are essential to prevent voltage drops and ensure uniform current distribution among the LEDs. Surface treatments, including electroless nickel immersion gold (ENIG), electroless nickel electroless palladium immersion gold (ENEPIG), and organic solderability preservatives (OSP), are applied to copper traces to enhance their corrosion resistance, solderability, and long - term electrical reliability.
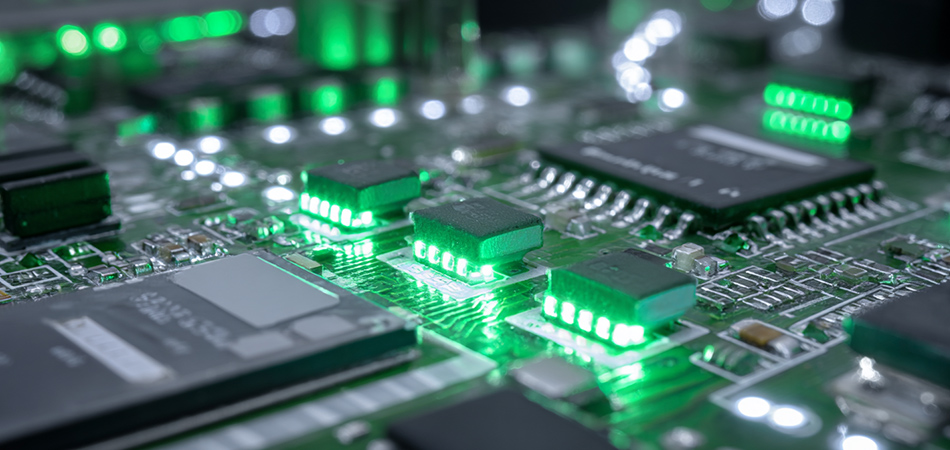
Design Methodologies for SMD LED Aluminum Circuits
Thermal Management Design
Thermal management is the cornerstone of SMD LED aluminum circuit design. Effective heat dissipation is vital for maintaining the luminous efficacy and lifespan of SMD LEDs. Thermal vias play a pivotal role in this process, acting as direct conduits for heat to transfer from the SMD LEDs to the aluminum substrate.
The design of thermal vias involves optimizing their size, number, and distribution across the circuit. A well - engineered thermal via layout can significantly enhance heat - dissipation efficiency, reducing the temperature gradient across the SMD LED array. Additionally, integrating heat sinks or heat spreaders with the aluminum circuit further improves thermal performance. These external components increase the surface area available for heat exchange with the surrounding environment, effectively preventing thermal - induced failures.
Electrical Design Considerations
Electrical design in SMD LED aluminum circuits focuses on ensuring stable and efficient power supply to SMD LEDs. This includes designing appropriate current - limiting circuits, voltage regulators, and driver circuits. In multi - LED arrays, careful consideration must be given to the electrical configuration of SMD LEDs, whether in series, parallel, or a combination, to achieve uniform brightness and avoid premature failure due to uneven current distribution.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is another critical aspect of electrical design. SMD LED drivers can generate electromagnetic interference (EMI), which may disrupt other electronic devices in the vicinity. Therefore, proper shielding, filtering, and layout techniques are employed to minimize EMI and ensure compliance with EMC standards.
Mechanical Design Elements
The mechanical design of SMD LED aluminum circuits takes into account factors such as the physical dimensions of the circuit, mounting requirements, and the mechanical stresses it may endure during operation. The size and shape of the circuit are determined by the lighting fixture design and the number and arrangement of SMD LEDs.
Mounting holes and attachment mechanisms are incorporated to securely fasten the circuit within the lighting fixture. In outdoor or harsh - environment applications, the mechanical design must also consider factors like resistance to vibration, shock, and corrosion. Reinforcement features, such as stiffeners or protective enclosures, may be added to enhance the mechanical durability of the circuit.
Optical Design Integration
Optical design is closely intertwined with SMD LED aluminum circuit design. The placement and orientation of SMD LEDs on the circuit directly affect the light distribution pattern of the lighting fixture. For applications requiring specific beam angles, color mixing, or light intensity profiles, SMD LEDs need to be precisely positioned and oriented on the circuit.
Optical components, such as lenses, reflectors, and diffusers, are often integrated with the SMD LED aluminum circuit. The circuit design must accommodate these components, ensuring proper alignment and mechanical stability. The interaction between the circuit and optical components is crucial for achieving the desired lighting performance, whether it's for general illumination, task lighting, or specialized lighting applications.
Manufacturing Processes of SMD LED Aluminum Circuits
Circuit Board Fabrication
The fabrication of SMD LED aluminum circuits begins with the production of the circuit board itself. This involves processes such as drilling, plating, and lamination. Drilling creates holes for vias, component mounting, and other purposes. Mechanical drilling is commonly used for larger holes, while laser drilling offers higher precision for small, complex holes, such as microvias.
Plating is essential for depositing a layer of copper on the drilled holes and the surface of the board to ensure electrical conductivity. It typically consists of electroless plating, which deposits a thin layer on non - conductive surfaces, followed by electrolytic plating to build up the copper layer to the desired thickness. Lamination bonds the different layers of the circuit board together, including the aluminum substrate, dielectric layer, and copper traces, using adhesive films or prepregs under high pressure and temperature.
SMD LED Placement and Soldering
The placement of SMD LEDs on the aluminum circuit is a highly precise process. Automated pick - and - place machines are used to accurately position SMD LEDs on the designated pads of the circuit board. These machines can handle a wide range of SMD LED sizes and types, ensuring consistent and repeatable placement.
After placement, SMD LEDs are soldered to the circuit board using reflow soldering or wave soldering techniques. Reflow soldering involves heating the circuit board in a reflow oven, melting the solder paste pre - applied to the pads, and creating a strong electrical and mechanical connection between the SMD LEDs and the circuit. Wave soldering, on the other hand, passes the circuit board over a wave of molten solder, soldering the components in a continuous process.
Surface Finishing
Surface finishing of SMD LED aluminum circuits is crucial for protecting the copper traces from oxidation and providing a suitable surface for soldering and component attachment. Common surface finishing techniques include hot air solder leveling (HASL), organic solderability preservatives (OSP), and electroless nickel immersion gold (ENIG).
HASL is a traditional and cost - effective method that involves immersing the circuit board in molten solder and then blowing off the excess with hot air. OSP provides a thin, transparent organic coating that protects the copper from oxidation and is suitable for fine - pitch components. ENIG offers excellent corrosion resistance and a smooth, flat surface, making it ideal for high - reliability applications.

Quality Assurance in SMD LED Aluminum Circuit Production
Incoming Material Inspection
Before production begins, all incoming materials, including the aluminum substrate, copper foil, dielectric materials, SMD LEDs, and other components, are thoroughly inspected. The aluminum substrate is checked for flatness, purity, alloy composition, and mechanical properties. Copper foil is inspected for thickness uniformity and surface quality.
Dielectric materials are tested for electrical insulation, thermal conductivity, and dielectric constant. SMD LEDs are verified for their specifications, such as luminous intensity, color temperature, and forward voltage drop. Only materials and components that meet strict quality standards are approved for use in the production process.
In - Process Quality Control
During the manufacturing process, quality control measures are implemented at various stages. After drilling, the holes are inspected for size accuracy, roundness, and the presence of burrs. In the plating process, the thickness and uniformity of the copper layer are continuously monitored.
During SMD LED placement and soldering, automated optical inspection (AOI) systems are used to detect any misaligned or missing components, as well as soldering defects such as cold joints, bridges, or insufficient solder. In - process testing of electrical parameters, such as current and voltage, may also be conducted to ensure the proper functioning of the circuit at each stage of production.
Final Testing
Once the SMD LED aluminum circuit is fully manufactured, it undergoes comprehensive final testing. Electrical tests include checking for short circuits, open circuits, and proper operation of the LED driver circuits. The luminous performance of SMD LEDs, including luminous intensity, color temperature, and color rendering index, is measured to ensure compliance with product specifications.
Thermal tests, such as thermal cycling and infrared thermography, are performed to evaluate the circuit's thermal management capabilities. These tests simulate real - world operating conditions to identify potential thermal issues. Mechanical tests may also be conducted to assess the durability of the circuit under vibration, shock, and other mechanical stresses.
Applications of SMD LED Aluminum Circuits
Residential Lighting
In residential settings, SMD LED aluminum circuits are widely used in a variety of lighting fixtures, including ceiling lights, wall sconces, table lamps, and recessed downlights. The energy - efficiency and long lifespan of SMD LEDs, combined with the effective thermal management of aluminum circuits, make them an ideal choice for homeowners.
These circuits enable the creation of aesthetically pleasing and customizable lighting solutions. With precise control over the placement and orientation of SMD LEDs, designers can achieve different light distribution patterns, color effects, and dimming capabilities, enhancing the ambiance and functionality of residential spaces.
Commercial Lighting
Commercial buildings, such as offices, shopping malls, hotels, and hospitals, benefit significantly from SMD LED aluminum circuits. In large - scale commercial applications, the energy savings and reduced maintenance costs offered by SMD LEDs are substantial.
SMD LED aluminum circuits are used in a diverse range of commercial lighting products, including linear fluorescent replacements, troffers, high - bay lights, and display lighting. The ability to provide uniform and high - quality illumination, along with advanced control features like daylight harvesting and occupancy sensing, makes them well - suited for commercial environments.
Outdoor Lighting
Outdoor lighting applications, such as streetlights, parking lot lights, landscape lighting, and floodlights, demand robust and reliable lighting solutions. SMD LED aluminum circuits are well - equipped to meet these requirements, thanks to their excellent thermal management, mechanical durability, and resistance to environmental factors.
The aluminum substrate effectively dissipates the heat generated by SMD LEDs, preventing overheating in direct sunlight or high - temperature environments. Additionally, the circuit design can be optimized to withstand rain, dust, corrosion, and mechanical impacts, ensuring long - term performance and reliability in outdoor settings.
Automotive Lighting
The automotive industry has witnessed a rapid adoption of SMD LED lighting, and aluminum circuits play a crucial role in this trend. SMD LED aluminum circuits are used in automotive headlights, taillights, interior lighting, and daytime running lights.
The compact size and high efficiency of SMD LEDs, combined with the thermal management advantages of aluminum circuits, enable the development of sleek and energy - efficient automotive lighting systems. Advanced lighting features, such as adaptive headlights, dynamic turn signals, and customizable interior lighting, are made possible by precise SMD LED circuit design.
Specialized Lighting Applications
SMD LED aluminum circuits are also widely used in specialized lighting applications, including horticultural lighting, medical lighting, and aviation lighting. In horticultural lighting, SMD LEDs are customized to emit specific wavelengths of light required for plant growth. The thermal management capabilities of aluminum circuits ensure stable operation of SMD LEDs, providing consistent light output for optimal plant development.
In medical lighting, high - quality, flicker - free, and color - accurate illumination is essential. SMD LED aluminum circuits can be designed to meet these stringent requirements, providing reliable lighting for surgical procedures, examination rooms, and other medical applications. In aviation lighting, where weight, reliability, and performance are critical, SMD LED aluminum circuits offer lightweight yet robust lighting solutions for aircraft interiors and exteriors.

Market Trends in SMD LED Aluminum Circuit Design
Miniaturization and High - Density Integration
The trend towards miniaturization in the electronics industry is driving the development of SMD LED aluminum circuits with higher density integration. As SMD LEDs become smaller and more powerful, circuit designs need to accommodate a larger number of LEDs in a compact space.
Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as high - density interconnect (HDI) technology and micro - via drilling, are being adopted to create more complex and compact SMD LED aluminum circuits. These advancements enable the development of smaller, more efficient lighting fixtures with enhanced functionality, suitable for applications like wearable lighting devices and miniature electronic gadgets.
Smart Lighting Integration
The growing popularity of smart lighting systems is influencing SMD LED aluminum circuit design. Smart lighting allows for remote control, dimming, color - changing, and integration with home automation systems. SMD LED aluminum circuits are being designed to incorporate smart lighting features, such as built - in sensors, wireless communication modules, and microcontrollers.
These circuits enable seamless integration with smart home platforms, providing users with greater control and customization options for their lighting. The ability to adjust lighting based on occupancy, ambient light levels, or user preferences enhances energy efficiency and user experience.
Sustainable Design and Manufacturing
Sustainability is becoming an increasingly important factor in SMD LED aluminum circuit design. Manufacturers are focusing on using eco - friendly materials, reducing energy consumption during production, and improving the recyclability of products.
Aluminum, being a highly recyclable material, aligns well with sustainable design principles. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop more energy - efficient manufacturing processes for SMD LED aluminum circuits, such as using low - power consumption equipment and optimizing production layouts to minimize waste.
Advanced Thermal Management Solutions
As SMD LEDs continue to increase in power density, the demand for advanced thermal management solutions in aluminum circuits is rising. New materials and technologies, such as graphite thermal interface materials, phase - change materials, and micro - channel cooling, are being explored to enhance heat dissipation.
Innovative circuit designs that optimize thermal via placement, heat sink integration, and heat - spreading mechanisms are also being developed. These advancements ensure that SMD LEDs can operate at higher power levels without sacrificing performance or lifespan, enabling the development of more powerful and efficient lighting solutions.
In conclusion, SMD LED aluminum circuit design is a complex and evolving field that combines material science, electrical engineering, mechanical design, and optical integration. The continuous advancements in this area are driving the development of more efficient, reliable, and versatile lighting solutions across various industries. As technology continues to progress, SMD LED aluminum circuits will play an even more crucial role in shaping the future of lighting, meeting the growing demands for energy - efficiency, functionality, and sustainability.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
