-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Sep 08. 2025, 14:21:06
A China-based PCB giant represents the apex of scale, innovation, and global reach in the printed circuit board industry, accounting for a significant portion of the world’s PCB production and driving technological advancements across electronics sectors. These industrial leaders transcend traditional manufacturing roles, functioning as ecosystem architects that shape supply chains, set technical standards, and enable transformative technologies from 5G networks to renewable energy systems.
With decades of industrial development, China’s PCB giants have evolved from contract manufacturers to R&D powerhouses, leveraging massive production capacity, vertical integration, and strategic investments to dominate global markets. Their influence extends beyond production volumes—they dictate material trends, accelerate adoption of advanced manufacturing techniques, and partner with multinational corporations to co-develop next-generation solutions. This article explores the defining traits of these giants, their impact on global electronics, technological milestones, and strategies for maintaining leadership in a dynamic industry.
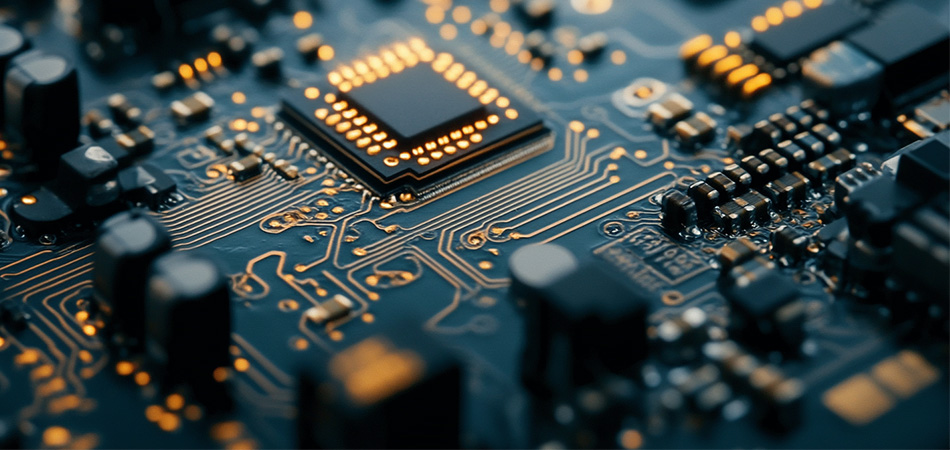
China’s PCB giants distinguish themselves through a unique blend of scale, integration, and innovation that positions them as irreplaceable players in the global electronics landscape.
Global Market Share: Collectively, China’s top PCB giants control over 50% of the global PCB market, with individual companies producing billions of square meters annually. This scale enables economies of scale that lower costs while ensuring consistent supply for high-volume clients, from smartphone manufacturers to automotive OEMs.
Multi-Site Manufacturing Networks: Operating dozens of factories across China—strategically located near raw material hubs, ports, and tech clusters—these giants can ramp production within weeks to meet surges in demand, such as seasonal spikes for consumer electronics or rapid scaling of EV PCB orders.
Diversified Product Portfolios: Offering a full spectrum of PCB types, from basic single-layer boards to ultra-complex HDI (High-Density Interconnect) designs, rigid-flex configurations, and high-frequency substrates, allowing them to serve every major electronics sector under one umbrella.
Upstream Integration: Many giants own or control key suppliers of raw materials, including copper foil, glass fiber, and resin, reducing dependency on external vendors and mitigating price volatility. For example, some integrate copper smelting operations to secure stable, cost-effective copper supplies for high-current PCBs.
In-House Component Manufacturing: Expanding into related fields such as PCB assembly (PCBA), connectors, and thermal management solutions, enabling one-stop-shop services that simplify client supply chains and reduce lead times.
Logistics and Distribution Networks: Operating global logistics arms with warehouses in key markets (e.g., Europe, North America, Southeast Asia) to ensure just-in-time delivery, critical for industries like automotive where production line disruptions are costly.
Massive R&D Investments: Allocating billions annually to research, with dedicated centers focused on advanced materials, manufacturing processes, and application-specific PCB designs. R&D teams often include thousands of engineers, collaborating with universities and research institutions worldwide.
Patent Dominance: Holding the majority of global patents in key areas such as HDI fabrication, flexible PCB materials, and thermal management technologies. This intellectual property portfolio strengthens their competitive edge and enables licensing partnerships with smaller manufacturers.
Early Adoption of Emerging Technologies: Pioneering the use of AI in quality control, 3D printing for prototyping, and digital twins for production optimization, setting benchmarks for efficiency and precision in the industry.

China-based PCB giants play a pivotal role in enabling technological progress across industries, acting as enablers of innovation rather than mere suppliers.
EV and Battery Technology: Supplying high-performance PCBs for electric vehicle powertrains, battery management systems (BMS), and charging infrastructure. Giants have developed specialized PCBs with thick copper layers (4oz+) and heat-resistant substrates to handle the high currents and temperatures of EV systems, reducing charging times and extending battery life.
Solar and Wind Energy: Producing ruggedized PCBs for solar inverters and wind turbine controllers that withstand extreme weather conditions. These PCBs incorporate conformal coatings and anti-corrosion materials to ensure 20+ year lifespans, aligning with the long operational cycles of renewable energy assets.
Case Study: A leading China-based PCB giant partnered with a global EV manufacturer to develop a 16-layer PCB for a next-gen BMS. The design integrated thermal vias and high-Tg substrates, enabling the BMS to operate at 125°C while reducing size by 30%. This collaboration accelerated the EV’s time-to-market by six months.
Network Infrastructure: Producing high-frequency PCBs for 5G base stations, small cells, and core network equipment. These PCBs use low-loss PTFE-based substrates and precise impedance control to maintain signal integrity at frequencies up to 60GHz, critical for 5G’s ultra-fast data transmission.
IoT and Smart Devices: Supplying miniaturized, energy-efficient PCBs for IoT sensors, wearables, and smart home devices. Giants leverage their HDI capabilities to pack more functionality into smaller form factors, supporting the proliferation of connected devices.
Aerospace-Grade PCBs: Manufacturing PCBs that meet strict aerospace standards (e.g., AS9100), with features like radiation hardening, vibration resistance, and lightweight materials. These PCBs power avionics systems, satellite communications, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
Defense Applications: Producing secure, tamper-resistant PCBs for military communication systems and radar equipment, with enhanced cybersecurity features to prevent unauthorized access or interference.
Example: A China-based PCB giant developed a 24-layer rigid-flex PCB for a satellite manufacturer. The PCB featured hermetic sealing and radiation-resistant materials, enabling reliable operation in low-Earth orbit for 15+ years. This solution reduced the satellite’s weight by 15kg, lowering launch costs significantly.

To solidify their dominance, China-based PCB giants are expanding beyond domestic borders through strategic investments, acquisitions, and partnerships that enhance their global footprint.
Acquiring Global Players: Purchasing established PCB manufacturers in Europe, North America, and Japan to gain access to advanced technologies, client networks, and regional market expertise. These acquisitions often focus on niche segments like aerospace PCBs or high-frequency designs.
Building Regional Hubs: Constructing mega-factories in Southeast Asia, Mexico, and Eastern Europe to bypass trade barriers, reduce logistics costs, and serve regional markets more efficiently. These facilities replicate the parent company’s quality standards and are staffed by local and Chinese engineers.
Joint R&D Labs: Partnering with semiconductor companies, electronics OEMs, and research institutions to develop PCB solutions for emerging technologies. For example, a giant might collaborate with a chipmaker to co-design PCBs optimized for next-gen processors, ensuring seamless integration and maximum performance.
Long-Term Supply Agreements: Securing multi-year contracts with global brands (e.g., Apple, Samsung, Tesla) to become their sole or primary PCB supplier. These agreements often include clauses for joint technology development and volume commitments, creating mutual dependency.
Shaping Global Standards: Participating in international organizations like IPC (Association Connecting Electronics Industries) to influence PCB design and manufacturing standards, ensuring their technologies align with global norms.
Industry Advocacy: Leading initiatives to promote sustainability, digitalization, and workforce development in the PCB sector, positioning themselves as responsible industry stewards.

China-based PCB giants are increasingly prioritizing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives to align with global sustainability goals and meet client demands for responsible sourcing.
Renewable Energy Adoption: Transitioning factories to 100% renewable energy, with large-scale solar farms and wind turbines powering production. One giant achieved 80% renewable energy usage across its Chinese facilities by 2024, with a goal of full carbon neutrality by 2035.
Circular Economy Practices: Implementing closed-loop systems for water, chemicals, and metal recycling. For example, etching chemicals are filtered and reused, while scrap copper is smelted and recast into new foil, reducing waste by 70% and lowering raw material costs.
Employee Welfare: Investing in safe working conditions, competitive salaries, and training programs to develop skilled workers. Some giants operate technical schools to train engineers and technicians, addressing the industry’s talent gap.
Community Engagement: Funding education, healthcare, and environmental projects in communities near their factories, building goodwill and ensuring social license to operate.
Public Sustainability Disclosures: Publishing detailed ESG reports aligned with global frameworks (e.g., GRI, TCFD), providing clients and investors with data on carbon emissions, water usage, and labor practices. This transparency helps clients meet their own ESG reporting requirements.

Despite their dominance, China-based PCB giants face challenges that require strategic adaptation to maintain leadership.
Diversifying Production Bases: Expanding overseas manufacturing to reduce reliance on China-centric supply chains, mitigating risks from tariffs or geopolitical tensions.
Localizing Supply Chains: Building regional supplier networks in target markets to comply with “local content” regulations, particularly in automotive and aerospace sectors.
Investing in Future Technologies: Allocating R&D budgets to emerging areas like 6G-compatible PCBs, quantum computing substrates, and biodegradable electronics, ensuring readiness for next-gen applications.
Agile Manufacturing: Implementing flexible production lines that can quickly switch between PCB types, enabling rapid response to shifts in demand (e.g., from consumer electronics to AI servers).
Global Talent Recruitment: Hiring engineers and researchers from around the world, establishing R&D centers in tech hubs like Silicon Valley and Berlin to access top talent.
Collaborative Education Programs: Partnering with universities to develop PCB-specific curricula, nourish a pipeline of skilled workers familiar with the latest technologies.
China-based PCB giants are not merely manufacturers—they are drivers of global technological progress, shaping the electronics industry through their scale, innovation, and strategic vision. Their ability to combine massive production capacity with cutting-edge R&D has made them indispensable partners for industries ranging from automotive electrification to 5G deployment.
By expanding globally, prioritizing sustainability, and investing in future technologies, these giants are well-positioned to lead the next wave of electronics innovation. For businesses seeking reliable, high-performance PCB solutions, partnering with a China-based giant offers access to unparalleled resources, technical expertise, and supply chain resilience.
As the world becomes increasingly dependent on advanced electronics, the role of these giants will only grow, underscoring their status as cornerstones of the global technology ecosystem. Their continued evolution will shape not just the PCB industry, but the future of connected, sustainable, and intelligent technologies worldwide.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
