-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Nov 17. 2025, 12:45:21
Counterbore holes stand as a foundational element in sinkpad PCB design, enabling the critical balance between mechanical stability and thermal efficiency required for high-power electronic systems. Unlike traditional through-holes or countersunk designs, counterbore holes feature a flat-bottomed cylindrical recess that accommodates fastener heads while preserving the integrity of the sinkpad’s metal core. This design is indispensable in applications where component mounting must not compromise heat dissipation—from industrial power converters to advanced medical devices. By addressing the dual challenges of secure fixation and unobstructed thermal transfer, counterbore holes have become a staple in modern PCB engineering, particularly as electronics trend toward higher power densities and compact form factors. This article explores the core design principles, manufacturing considerations, performance optimization strategies, and emerging trends of counterbore holes in sinkpad PCBs.
The effectiveness of counterbore holes in sinkpad PCBs hinges on integrating mechanical requirements with thermal management goals, avoiding trade-offs between the two.
A primary objective in counterbore design is maintaining the sinkpad’s ability to conduct heat away from high-power components. The flat-bottomed profile of counterbore holes ensures maximum contact area between the component’s thermal base and the sinkpad’s metal core, minimizing air gaps that act as thermal barriers. Designers must prioritize contiguous material continuity around the counterbore, avoiding excessive material removal that could disrupt heat spreading. Additionally, the interface between the component and counterbore bottom often benefits from thermal interface materials (TIMs), which fill micro-irregularities and enhance heat transfer efficiency. This thermal continuity is especially critical in applications operating at elevated temperatures, where even minor disruptions can lead to component degradation or failure.
Counterbore holes must provide robust mechanical fixation to withstand operational stresses, including vibration, thermal cycling, and physical handling. The recessed design allows fasteners to sit flush with the PCB surface, reducing leverage forces that could loosen connections over time. Key design considerations include wall thickness around the counterbore to prevent structural weakening and ensure resistance to fastener torque. Proper spacing between counterbore holes and PCB edges or adjacent components is also essential to avoid stress concentration, which can lead to cracking or delamination. In high-vibration environments, such as automotive or aerospace systems, counterbore designs often incorporate additional features like chamfered edges to distribute load and enhance fastening reliability.
Sinkpad materials—ranging from aluminum and copper to specialized alloys like copper-tungsten—exhibit unique characteristics that influence counterbore design and performance. Aluminum, prized for its balance of thermal conductivity and machinability, is well-suited for most counterbore applications, while copper offers superior heat transfer but requires careful machining to prevent galling. Harder materials like copper-tungsten demand specialized cutting tools and processes to achieve precise counterbore profiles without compromising surface quality. The choice of material directly impacts machining strategies, thermal performance, and mechanical strength, requiring designers to align counterbore specifications with the sinkpad’s material properties.
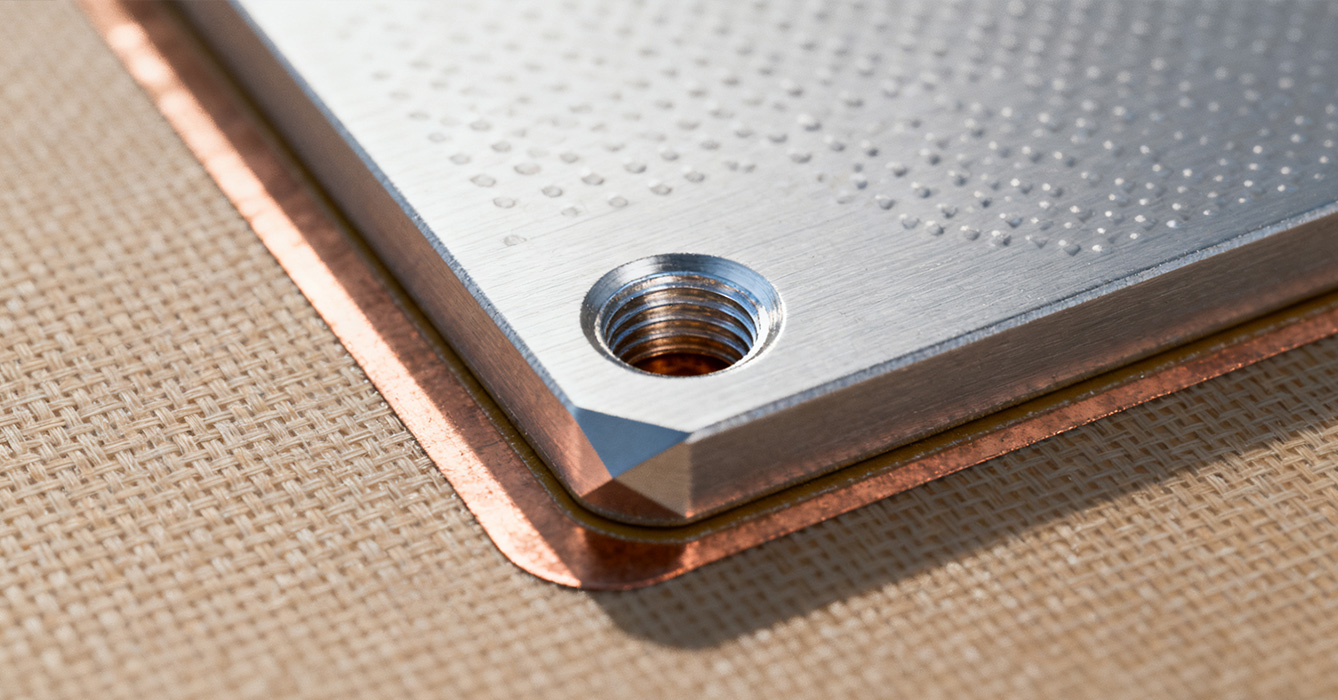

Producing high-quality counterbore holes in sinkpad PCBs requires addressing unique machining and quality control challenges, particularly as designs become more compact and precise.
Counterbore machining demands tight tolerances to ensure proper fastener fit and thermal contact. The process typically involves sequential drilling and milling operations, with careful control of depth and diameter to avoid damaging the dielectric layer beneath the sinkpad. Machining challenges include maintaining straight walls and flat bottoms, especially in small-diameter counterbores, where tool deflection can cause dimensional inaccuracies. Advanced machining techniques, such as rigid tapping and high-speed milling, help achieve the required precision, while specialized tooling—including diamond-coated cutters for hard materials—extends tool life and improves surface finish. Cooling and lubrication during machining are also critical to prevent material deformation and remove chips effectively, which can cause surface defects if not properly managed.
Rigorous quality control is essential to verify counterbore dimensions, surface quality, and structural integrity. Non-destructive testing methods like X-ray inspection ensure that counterbore depth does not penetrate the dielectric layer, preventing electrical short circuits. Optical measurement tools, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), confirm dimensional accuracy, including diameter, depth, and concentricity with guide holes. Surface finish inspections, often using profilometers, ensure the counterbore bottom is smooth enough to maximize thermal contact. These quality checks not only ensure compliance with design specifications but also support adherence to industry standards for reliability and performance.
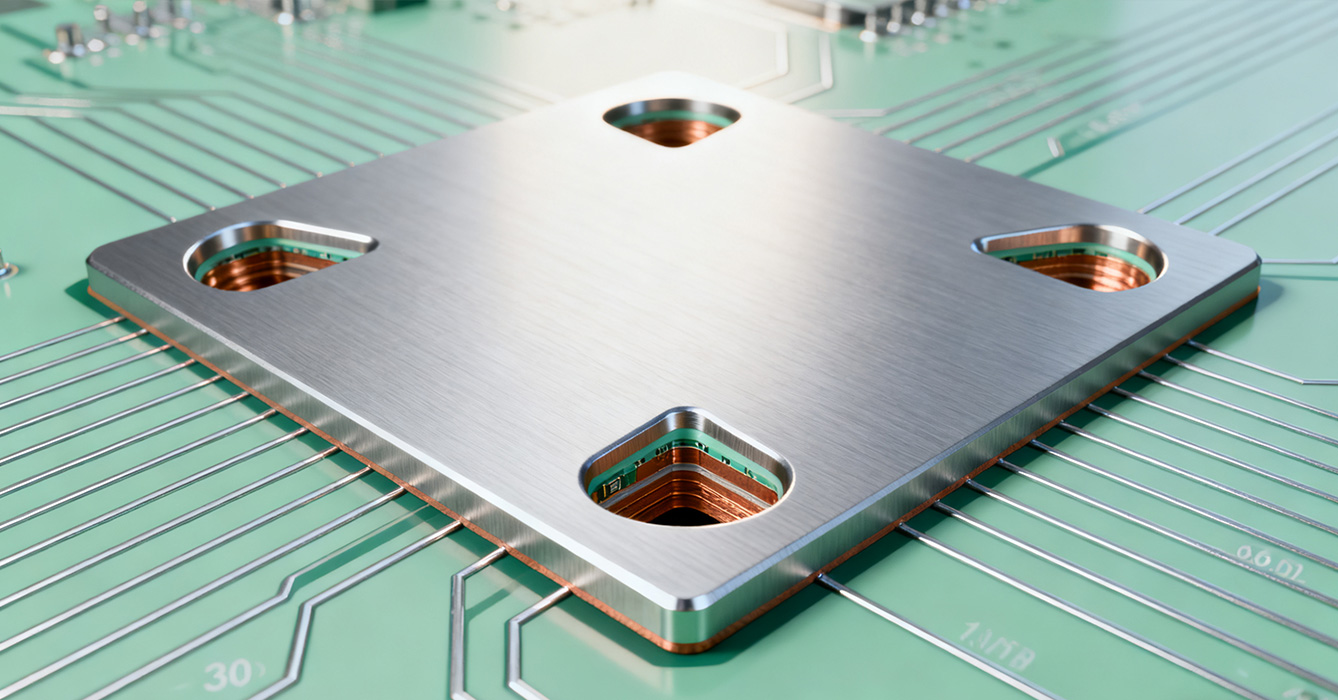
Optimizing counterbore hole performance involves balancing thermal, mechanical, and manufacturing requirements to meet application-specific needs.
In high-frequency applications, counterbore holes can impact signal integrity if not properly designed. The metal-to-dielectric transition around the counterbore can create impedance discontinuities, leading to signal reflection or attenuation. To mitigate this, designers often incorporate grounding strategies, such as annular rings or ground planes, to shield the counterbore area from signal interference. Additionally, minimizing the counterbore’s impact on signal traces—through careful routing and spacing—helps maintain signal quality, especially in high-speed digital or RF systems. This integration of counterbore design with signal integrity considerations is critical in modern electronics, where performance depends on both thermal management and signal reliability.
Counterbore holes must be tailored to withstand the operating environment, whether it involves extreme temperatures, humidity, corrosion, or chemical exposure. In harsh environments, such as industrial or marine settings, counterbore surfaces may require protective coatings—such as anodization for aluminum or passivation for stainless steel—to prevent corrosion. In high-temperature applications, material selection becomes even more critical, with heat-resistant alloys and specialized coatings ensuring long-term performance. These environmental adaptations extend the lifespan of sinkpad PCBs and maintain counterbore functionality under challenging conditions.
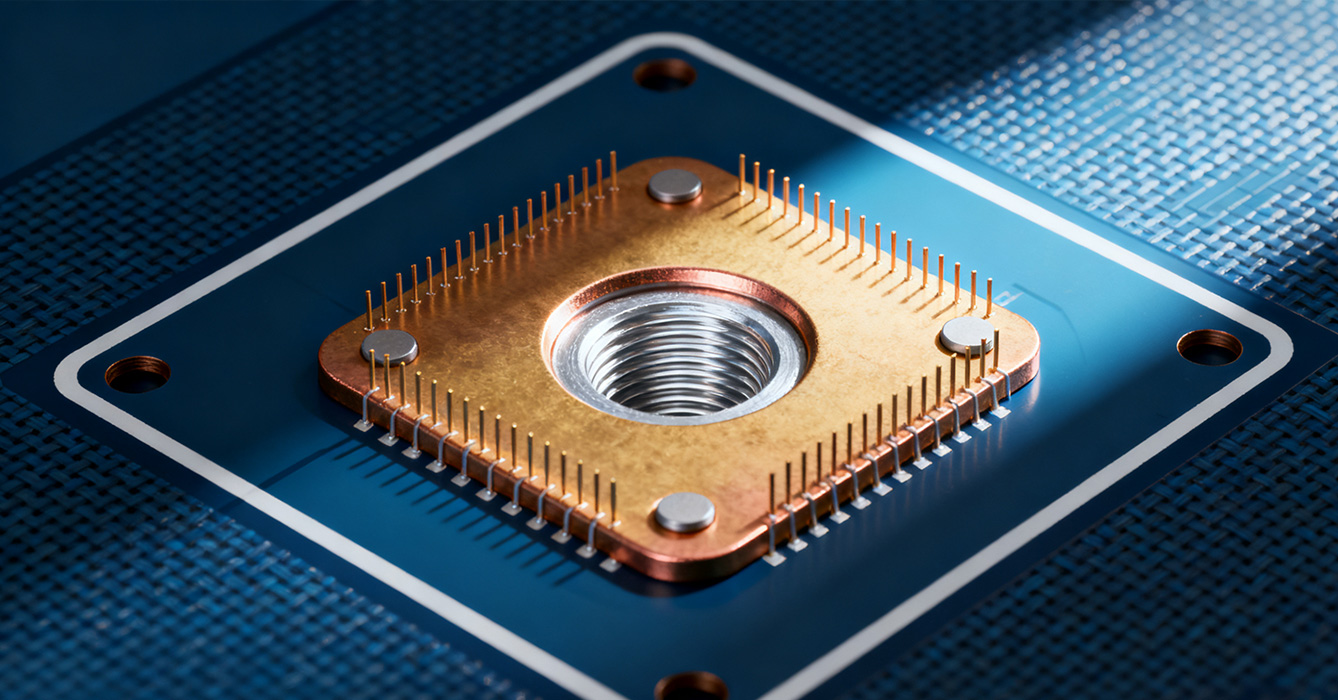
As electronic systems evolve, counterbore hole design in sinkpad PCBs is adapting to meet new demands for miniaturization, efficiency, and smart functionality.
The trend toward smaller, more powerful electronics is driving the development of micro-counterbore holes, which enable high-density component mounting without sacrificing thermal or mechanical performance. These tiny counterbores, often with diameters less than 2mm, require advanced machining technologies and ultra-precise tooling to maintain tolerances. High-density designs also benefit from optimized counterbore spacing and arrangement, allowing more components to be packed into limited PCB real estate while ensuring adequate heat dissipation and mechanical stability.
Emerging trends include integrating sensing capabilities into counterbore designs, such as embedded temperature or strain sensors that monitor thermal and mechanical conditions in real time. These smart counterbores enable predictive maintenance, alerting users to potential issues like loosening fasteners or excessive heating before they lead to failure. Additionally, additive manufacturing technologies are opening new possibilities for complex counterbore geometries, including conformal profiles that optimize thermal and mechanical performance for specific components.
Environmental considerations are shaping counterbore manufacturing, with a focus on reducing waste, energy consumption, and harmful emissions. Sustainable practices include using eco-friendly cutting fluids, optimizing machining processes to minimize material waste, and selecting recyclable sinkpad materials. These efforts align with industry-wide sustainability goals while maintaining the high performance required for counterbore holes in sinkpad PCBs.
Counterbore holes in sinkpad PCBs play a pivotal role in balancing thermal efficiency and mechanical stability, making them indispensable in modern high-power electronic systems. By adhering to design principles that prioritize thermal path continuity, mechanical strength, and material compatibility, engineers can create counterbore solutions tailored to diverse application needs. Addressing manufacturing challenges through precision machining and rigorous quality control ensures consistent performance and reliability. As electronics continue to advance toward miniaturization, higher power densities, and smart functionality, counterbore hole design will evolve to meet these demands, incorporating new materials, technologies, and sustainability practices. For engineers and manufacturers, understanding the nuances of counterbore design and implementation is key to unlocking the full potential of sinkpad PCBs in next-generation electronic systems.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
