-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Nov 17. 2025, 12:42:54
Tapped Counterbore Sinkpad Design redefines secure mounting for high-power electronics by integrating precision-threaded cylindrical recesses with the thermal efficiency of sinkpad technology. Unlike standard counterbore sinkpads that rely on external nuts or adhesive fixation, tapped counterbores feature internal threads (typically M2-M3 for compact applications) directly machined into the sinkpad’s metal core—enabling direct, nut-free fastening of components. This innovative design resolves a critical pain point in compact high-power systems: achieving vibration-resistant component retention without compromising thermal conductivity or increasing assembly volume. By unifying threaded mechanical fixation and contiguous thermal transfer, tapped counterbore sinkpads excel in applications demanding repeated assembly/disassembly, space constraints, and rugged operating conditions—from portable industrial tools to aerospace microsystems. This article explores the core design synergies, performance enhancements, application-specific optimizations, manufacturing criticalities, and advanced innovations of tapped counterbore sinkpad technology.
Tapped counterbore sinkpad performance hinges on three integrated design pillars that balance mechanical security and thermal management:
Contiguous Contact Preservation: The flat-bottomed counterbore geometry maintains full contact between the component’s thermal base and the sinkpad’s metal core (copper, 6061-T6 aluminum, or CuW), while internal threads (tolerance class 6H for internal threads, 6g for external fasteners) are machined to avoid disrupting the thermal path . Thread roots are positioned 0.3–0.5mm above the dielectric layer to prevent electrical shorting while maximizing heat transfer area.
Torque-Driven Thermal Coupling: Threaded fastening applies uniform clamp load (1.5–3N·m for M2-M3 threads) across the component-sinkpad interface, eliminating micro-gaps caused by uneven pressure. This reduces contact thermal resistance by 20–30% compared to non-threaded counterbores, with junction temperature reductions of 8–12°C for 30–60W components.
Fastener-Thread Compatibility: Counterbore diameter (3–4mm typical) and thread pitch are calibrated to industry-standard fasteners: M2 (pitch 0.4mm) for lightweight components, M2.5 (pitch 0.45mm) for medium-load applications, and M3 (pitch 0.5mm) for high-vibration environments . Thread depth (1.2–2.0mm) is optimized to balance pull-out strength (>500N for M3 threads in aluminum) and material conservation.
Structural Integrity Optimization: The counterbore’s cylindrical wall thickness (minimum 0.8mm) is maintained to prevent thread stripping, while the threaded section is isolated from thermal channels in the sinkpad core. This ensures mechanical stability without degrading heat spreading efficiency.
Thread Compatibility by Material:
Aluminum (6061-T6): Ideal for tapped designs, enabling high-precision threads with Ra 1.2–1.6μm surface finish via rigid 攻丝 (rigid tapping) .
Copper: Requires coated tap and reduced cutting speeds (150–200 rpm) to prevent thread galling.
CuW (copper-tungsten): Utilizes cryogenic machining and diamond-tipped tap for thread integrity .
Dielectric Layer Protection: Thread depth is strictly controlled to stop 0.2–0.3mm above the dielectric layer, verified via X-ray inspection post-machining.
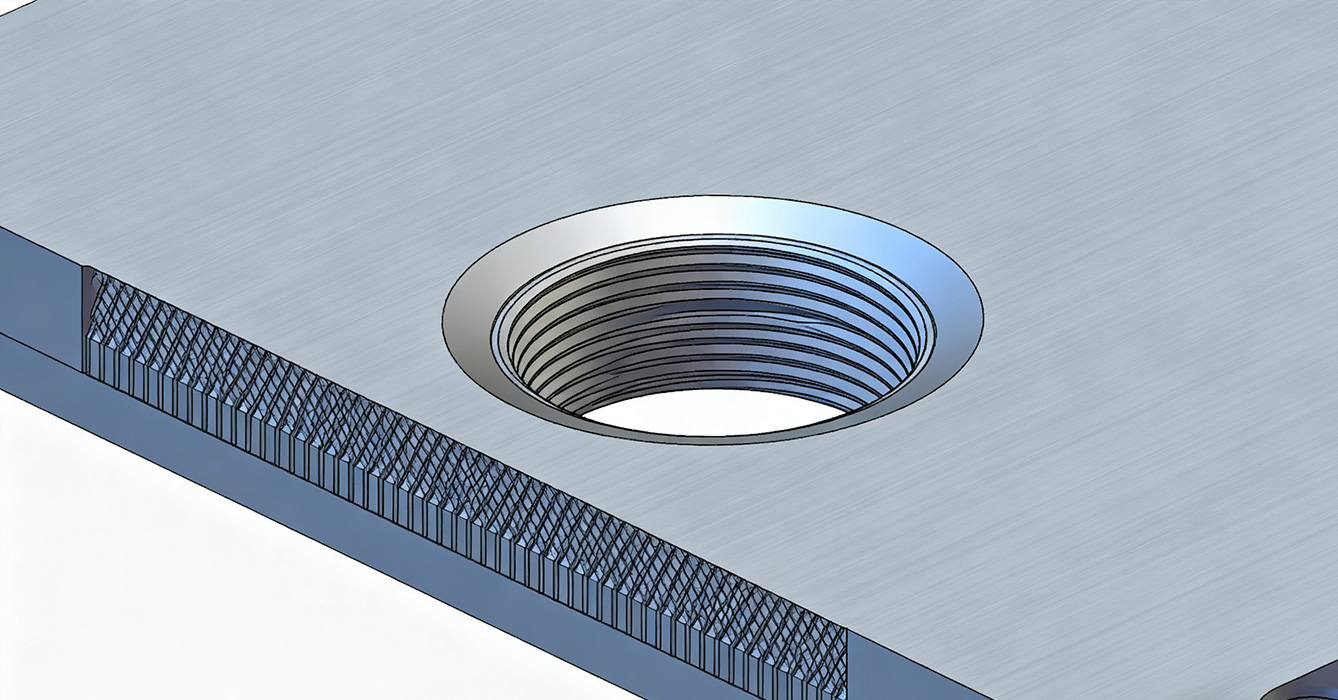
Tapped counterbore sinkpads deliver five distinct advantages over non-threaded and countersink designs:
Threaded fixation provides 40–50% greater resistance to vibration-induced loosening compared to non-threaded counterbores, meeting MIL-STD-810G random vibration standards (10–2000Hz, 15g rms). This is critical for automotive electronics, UAV power modules, and industrial sensors.
Direct threaded fastening eliminates the need for nuts, washers, or adhesive, reducing assembly time by 30–40% and enabling field serviceability. This is pivotal for portable medical devices and modular industrial controllers.
Uniform clamp load from threaded fastening minimizes thermal cycling-induced delamination (≤0.1% failure rate after 1000 cycles of -40°C to 125°C) by maintaining consistent component-sinkpad contact.
Nut-free design reduces assembly height by 25–30% compared to non-threaded counterbores with external fasteners, enabling integration in ultra-compact enclosures (e.g., wearable medical devices, miniaturized LED projectors).
Precision rigid tapping (spindle-feed synchronization ±0.01mm) achieves thread dimensional tolerances of ±0.02mm, ensuring uniform fastener fit across production batches . This reduces performance variability in high-volume applications (e.g., consumer electronics, automotive sensors).
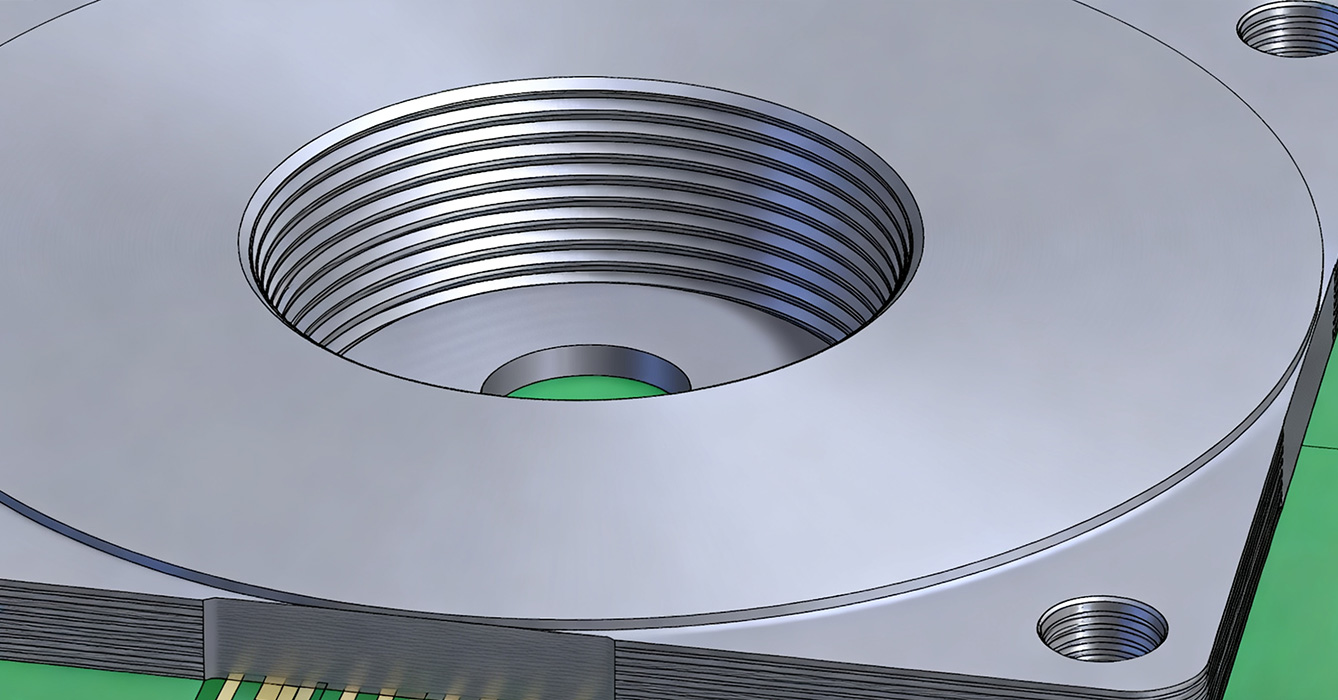
Tapped counterbore sinkpads are tailored to four high-demand sectors with targeted configurations:
e-Axle Power Modules: M3 threads in aluminum sinkpads secure SiC MOSFETs, with MQL (minimum quantity lubrication) during machining to prevent thread oxidation . Vibration resistance ensures reliability in undercar environments (10–500Hz vibration).
ADAS Sensors: M2.5 threads for compact lidar/radar modules, balancing lightweight design and secure fixation.
Handheld Laser Therapy Tools: Biocompatible 316L stainless steel sinkpads with M2 threads, featuring passivated threads for corrosion resistance. Threaded design enables sterile assembly/disassembly for maintenance.
Diagnostic Equipment: M2 threads in copper sinkpads for high-thermal-load components (e.g., laser diodes), ensuring precise thermal management and tool-free servicing.
UAV Propulsion Controllers: Lightweight aluminum sinkpads with M3 threads, optimized for pull-out strength (>600N) and weight reduction (15–20% lighter than nut-fastened designs).
Satellite Power Systems: Radiation-hardened CuW sinkpads with M2.5 threads, machined via cryogenic processes to withstand space thermal cycling (-100°C to 120°C).
Servo Drive Controllers: M3 threads in aluminum sinkpads for IGBT modules, enabling rapid field replacement (tool-free disassembly in <2 minutes).
Grid-Tied Inverters: Weather-sealed tapped counterbores with PTFE-coated threads, resisting corrosion in outdoor environments.
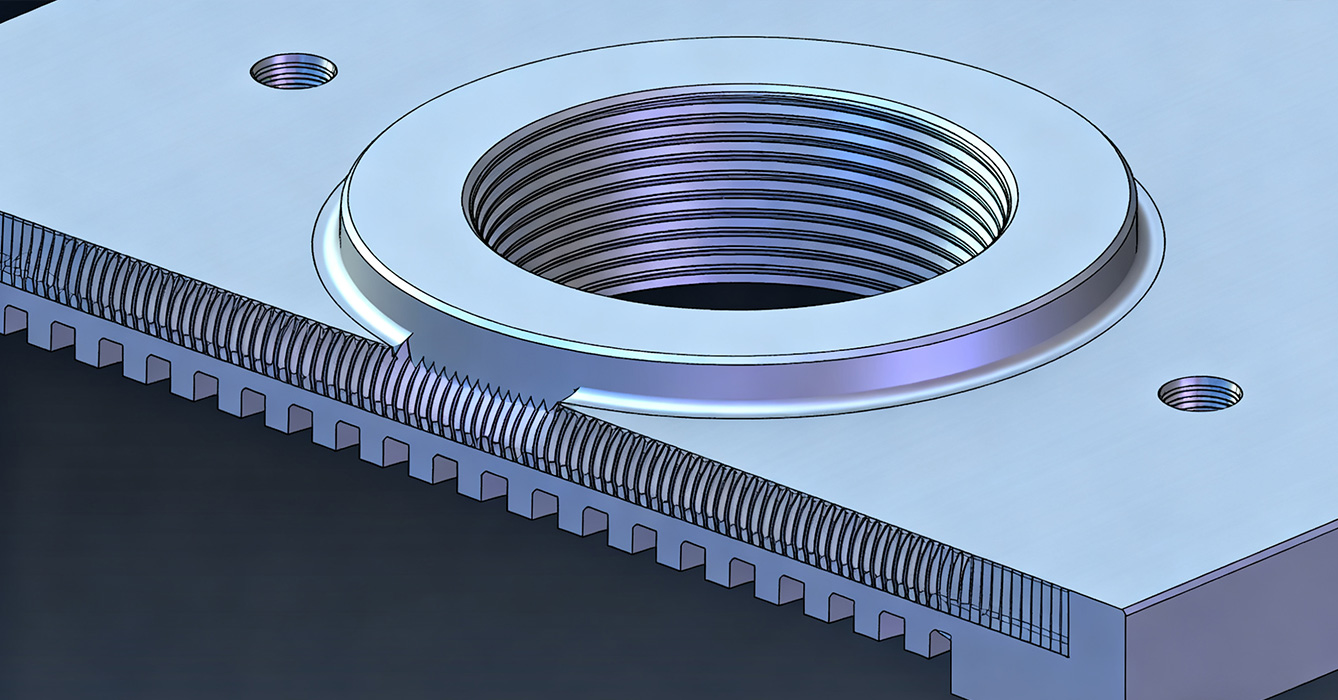
Tapping Technology Selection:
Rigid tapping for high-precision threads (±0.01mm pitch accuracy) in aluminum and copper .
Flexible tapping with elastic clamp for CuW and stainless steel to prevent tap breakage .
Machining Parameters:
Aluminum: Spindle speed 500 rpm, feed rate = pitch × speed (e.g., 250 mm/min for M2.5×0.45) .
Copper: Spindle speed 200 rpm, feed rate 90 mm/min (M2.5×0.45).
MQL (17–19 bar pressure, 19 ml/h flow) for thread surface quality and tool life extension .
Thread Inspection: Optical thread gauges (6H class) and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) verify pitch diameter, lead, and flank angle.
Thermal Path Validation: X-ray inspection confirms thread depth does not penetrate the dielectric layer.
Pull-Out Testing: Destructive testing of sample units to ensure minimum pull-out strength (≥400N for M2, ≥600N for M3).
3. Post-Machining Treatments
Corrosion Protection: Zinc-nickel plating (8–12μm) for steel threads, anodization for aluminum threads.
Thread Lubrication: Dry film lubricants (e.g., molybdenum disulfide) for high-vibration applications to reduce friction and wear.
Embedded strain gauges within the counterbore wall monitor clamp load in real time, enabling predictive maintenance for critical applications (e.g., aerospace power modules).
3D-printed hybrid sinkpads (aluminum-copper composite) with conformal threads, optimizing thermal paths and thread placement for custom component footprints.
Integrated nylon inserts or deformed thread sections for vibration-proof fastening, eliminating the need for thread lockers while maintaining thermal conductivity.
Sub-2mm counterbores with M1.6 threads for ultra-compact IoT sensors and wearable electronics, leveraging micro-rigid tapping for precision.
Tapped Counterbore Sinkpad Design represents a paradigm shift in high-power electronic mounting, unifying the mechanical security of threaded fixation with the thermal efficiency of sinkpad technology. By optimizing thread-sinkpad dimensional synergy, material machinability, and manufacturing precision, this design delivers unmatched vibration resistance, assembly efficiency, and space conservation. From automotive electrification to aerospace microsystems, tapped counterbore sinkpads address the growing demand for secure, thermally efficient, and serviceable high-power integration in compact form factors. As electronics continue to push toward higher power densities and smaller footprints, tapped counterbore sinkpads will remain a critical enabler—proving that threaded precision is the key to balancing reliability, performance, and usability in next-generation electronic systems.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
