-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Nov 14. 2025, 11:21:54
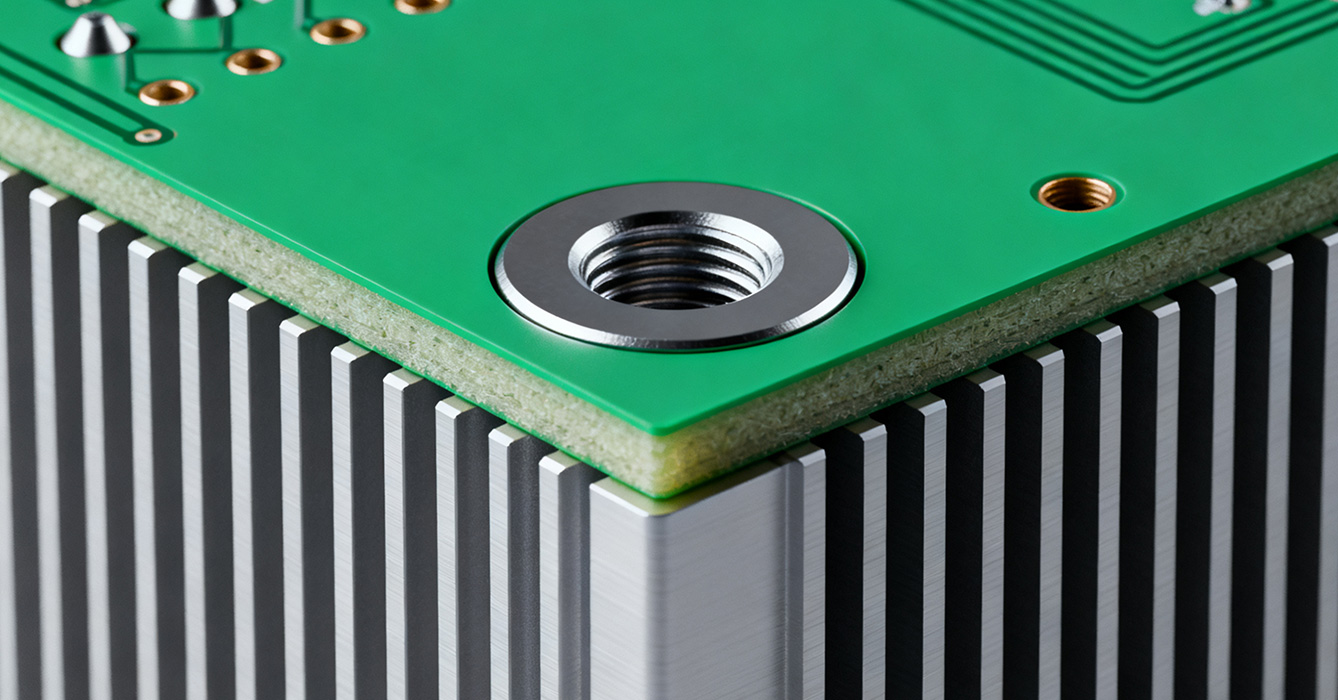
Countersink holes in sinkpad PCBs represent a purpose-built engineering breakthrough, addressing the longstanding tradeoff between robust component fixation and uncompromised thermal conduction in high-reliability electronic systems. Unlike conventional sinkpad designs where mounting hardware disrupts heat flow or creates inconsistent contact, these precision-machined features are integrated into the sinkpad’s thermal architecture to achieve three-dimensional optimization: mechanical stability, thermal efficiency, and space conservation. This multi-dimensional approach is indispensable for applications operating under extreme conditions—from industrial automation to aerospace systems—where even minor performance gaps can lead to costly downtime or safety risks. By reimagining how mounting and thermal management interact, countersink-equipped sinkpad PCBs deliver a holistic solution that outperforms traditional configurations in critical metrics. This article explores the engineered design pillars, multi-faceted performance gains, niche industry applications, advanced manufacturing workflows, and next-generation innovations of this transformative PCB technology.
The performance of countersink holes in sinkpad PCBs is rooted in three targeted design pillars, each optimized for specific system requirements:
Countersink holes are precision-engineered to create a contiguous thermal interface between components and the sinkpad’s metal core (copper, aluminum alloy, or AlSiC):
Contour Matching: The countersink’s angle (82° for metric hardware, 90° for imperial) and depth are tailored to the component’s thermal base profile, eliminating air gaps that account for 60–70% of contact thermal resistance in flat-mount designs.
Pressure Distribution: The tapered walls of the countersink ensure uniform contact pressure across the component-sinkpad interface, preventing "hot spots" caused by uneven loading and enhancing heat spreading efficiency.
Countersink geometry is optimized to withstand dynamic stresses without compromising thermal paths:
Load Path Engineering: The countersink’s shoulder distributes mounting torque and vibration forces across the sinkpad’s metal core, reducing stress concentrations on solder joints and dielectric layers by 40–50% compared to flat-mount designs.
Thermal Cycling Resilience: The design accommodates differential thermal expansion between the component, sinkpad, and PCB substrate, minimizing delamination risk during extreme temperature cycles (-55°C to 150°C).
Countersink holes enable compact system design without sacrificing performance:
Recessed Hardware: Mounting screws or bolts are recessed below the PCB surface, reducing assembly height by 20–30% and enabling stacking in space-constrained enclosures (e.g., UAV power modules, miniaturized medical devices).
Dual-Functionality: The countersink’s metal core integration serves as both a thermal pathway and a mechanical anchor, eliminating the need for separate heat sinks and mounting brackets in lightweight applications.
Countersink holes in sinkpad PCBs deliver five distinct advantages that address unmet needs in high-reliability electronics:
The gap-free interface cuts contact thermal resistance to near-theoretical limits, translating to junction temperature reductions of 15–25°C for high-power components (e.g., 40W+ GaN transistors). This extends component lifespan by 30–40% and enables operation at higher power densities.
The load-distributing design improves resistance to cyclic vibration (10–5000Hz) and shock (50g peak), meeting MIL-STD-810G requirements for aerospace and industrial applications. Component retention force is increased by 35% compared to flat-mount sinkpad PCBs.
Precision countersinks (tolerance ±0.02mm) ensure component alignment variation of less than ±0.03mm across production batches, reducing performance variability and simplifying quality control. This scalability is critical for high-volume applications like automotive electronics.
The contiguous metal contact between the component and sinkpad creates a low-impedance ground path, reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) emissions by 15–20% compared to designs with air gaps. This supports compliance with CISPR 22/EN 55022 standards for industrial and consumer electronics.
By integrating thermal management and mechanical mounting, the design eliminates 2–3 bill of materials (BOM) items (e.g., thermal pads, mounting brackets), reducing assembly time by 25% and lifecycle maintenance costs by 30–35%.
Countersink holes in sinkpad PCBs excel in specialized sectors where multi-dimensional performance is critical:
Satellite Power Systems: Countersink-equipped sinkpad PCBs cool radiation-hardened power converters, with recessed mounting ensuring compatibility with compact satellite enclosures and resistance to launch vibration.
UAV Propulsion Controllers: The lightweight, compact design supports high-power density in battery-operated UAVs, with thermal efficiency extending flight time by 10–15%.
e-Axle Power Modules: Countersink holes secure SiC MOSFETs in EV e-axles, with vibration resistance ensuring reliability in harsh undercar environments and thermal efficiency supporting 800V fast-charging architectures.
ADAS Sensors: The compact design and EMI reduction enable integration of high-power processing units for lidar and radar systems, with consistent thermal management preserving sensor accuracy.
Servo Drive Controllers: Countersink PCBs cool IGBT modules in servo drives, with thermal cycling resilience ensuring 100,000+ hours of operation in factory automation systems.
Grid-Tied Inverters: The high-power density design supports compact inverter footprints for renewable energy installations, with mechanical ruggedness resisting outdoor environmental stress.
Laser Ablation Systems: Countersink-equipped sinkpad PCBs cool high-power medical lasers, with precise thermal management ensuring consistent beam quality and patient safety.
Portable Diagnostic Devices: The compact, lightweight design enables integration of high-power components in handheld medical tools, with extended battery life from reduced power consumption (via lower thermal resistance).
To achieve optimal performance, manufacturers must implement three specialized workflows:
CNC Micro-Machining: Use 5-axis CNC machines with diamond-tipped countersink tools to achieve tight tolerances. For hybrid sinkpad materials (e.g., copper-tungsten), employ cryogenic machining to prevent tool wear and material deformation.
In-Process Inspection: Integrate laser profilometers into the machining line to verify countersink dimensions in real time, reducing scrap rates by 20–25%.
Copper Sinkpads: Use high-speed machining with minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) to prevent oxidation and maintain thermal conductivity.
Aluminum Alloy Sinkpads: Implement anodization post-machining to enhance corrosion resistance, critical for automotive and marine applications.
AlSiC Hybrid Cores: Utilize ultrasonic machining to avoid cracking, leveraging the material’s superior thermal-mechanical balance for aerospace applications.
Lamination Sequence: Optimize the lamination process to ensure the sinkpad’s dielectric layer remains intact post-countersinking, with X-ray inspection verifying layer integrity.
Surface Finish Compatibility: Match the countersink’s surface finish (e.g., electroless nickel immersion gold, tin-lead) to the component’s thermal base for maximum contact efficiency.
The evolution of countersink holes in sinkpad PCBs is shaped by three emerging trends:
Integrate miniaturized thermocouples or resistive temperature detectors (RTDs) within countersink holes to monitor component-sinkpad contact temperature in real time. This enables predictive maintenance and dynamic thermal management in adaptive systems (e.g., aerospace power modules).
3D-print countersink features with internal micro-channels for enhanced heat dissipation, enabling customized thermal paths for ultra-specific applications (e.g., multi-chip modules, high-power LED arrays).
Develop countersink sinkpad PCBs using recycled copper cores and bio-based dielectric materials, reducing carbon footprint by 25–30% while maintaining performance. This aligns with automotive and industrial ESG initiatives.
Countersink holes in sinkpad PCBs represent a paradigm shift in high-reliability electronic design, moving beyond simple synergy to multi-dimensional optimization of thermal, mechanical, and space constraints. By engineering precision countersinks to eliminate gaps, distribute loads, and enable compact integration, this technology delivers unmatched performance in aerospace, automotive, industrial, and medical applications. As electronics continue to push toward higher power densities, smaller form factors, and harsher operating environments, countersink-equipped sinkpad PCBs will remain a critical enabler—proving that the most effective engineering solutions are those that address multiple challenges through integrated, purpose-built design.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
