-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Dec 25. 2025, 12:01:24
As global electronics industries march toward miniaturization, intelligence, and diversification, Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCB) have emerged as a pivotal component reshaping the design and performance of electronic products. Unlike rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs) that constrain product form factors and application scenarios, FPCB combines exceptional flexibility, lightweight construction, high-density integration, and reliable electrical performance. This versatile component breaks through the physical limitations of traditional electronics, enabling innovative designs in fields ranging from consumer electronics and medical devices to new energy vehicles and aerospace. For electronic product designers, engineering teams, and industry manufacturers, understanding the comprehensive value and application potential of FPCB is crucial to gaining a competitive edge in the fast-evolving market. This article explores the core advantages of FPCB, its diversified cross-industry applications, key implementation and selection guidelines, and future technological trends, highlighting its irreplaceable role as a core enabler in advanced electronic systems.
Traditional rigid PCBs face inherent limitations that hinder their ability to meet the evolving demands of modern advanced electronic systems. Their rigid structure restricts product design to fixed, regular shapes, making it impossible to adapt to the curved, foldable, or irregular contours required by emerging products—such as foldable smartphones, wearable health monitors, and miniaturized medical instruments. This inflexibility not only limits creative product design but also restricts the integration of electronics into space-constrained or dynamically shaped environments.
Another critical drawback lies in the trade-off between integration density and weight. Rigid PCBs require additional connectors and wiring to connect multiple boards, increasing the overall size, weight, and complexity of electronic systems. In applications where lightweight and compact design are paramount—such as aerospace equipment, portable medical devices, and electric vehicles—this excess weight and bulk reduce operational efficiency and performance. Additionally, rigid PCBs are prone to damage under vibration, impact, or thermal expansion, compromising reliability in harsh operating environments. FPCB addresses these limitations through its unique flexible, lightweight, and integrated design, becoming a foundational component for next-generation electronic systems.
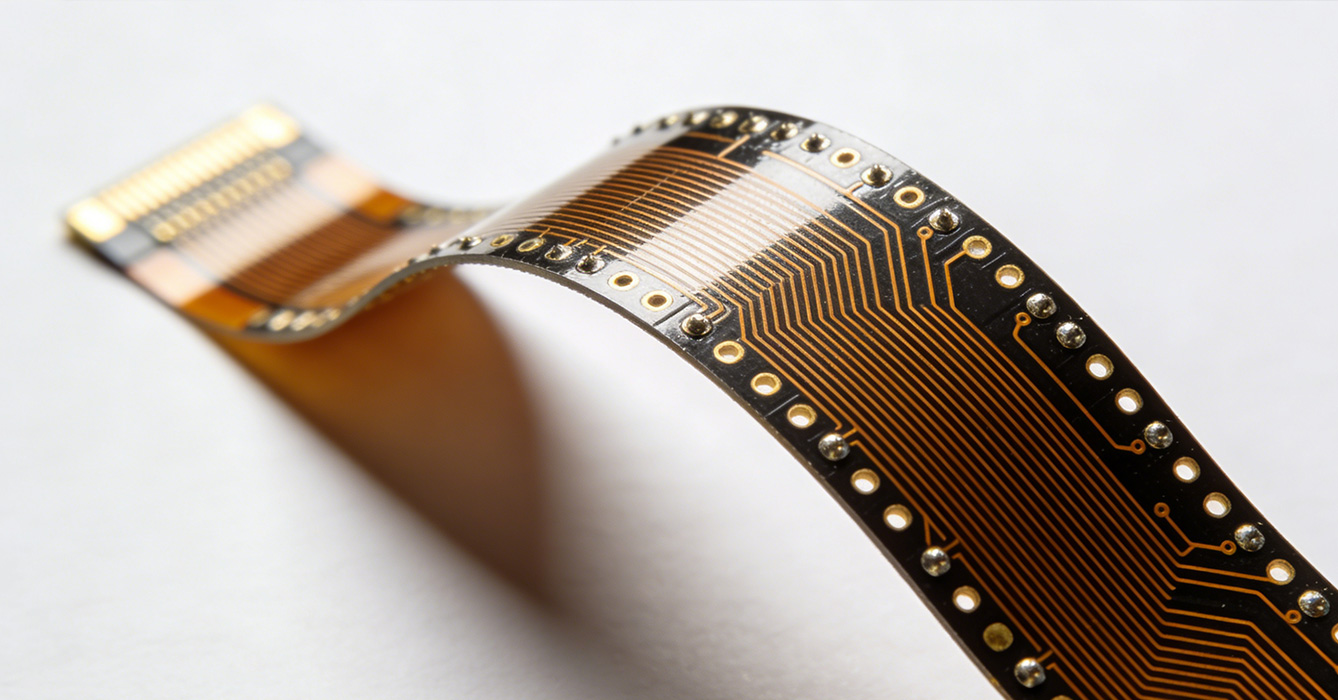
FPCB offers five distinct advantages that make it indispensable in advanced electronic applications, driving innovation across industries:
- Exceptional flexibility and design freedom: The inherent flexibility of FPCB allows it to be bent, folded, twisted, or conformed to complex 3D shapes, enabling revolutionary product designs. For example, foldable smartphone screens rely on FPCB to connect the foldable display modules, ensuring seamless electrical connectivity even during repeated folding. This flexibility also allows electronics to be integrated into tight or irregular spaces, such as the curved interiors of automotive dashboards or the compact housing of wearable devices.
- Lightweight and space-saving: FPCB is significantly thinner and lighter than rigid PCBs, with a thickness often measured in micrometers. This lightweight characteristic reduces the overall weight of electronic systems, a critical advantage in aerospace, automotive, and portable electronics. Its thin profile also enables miniaturization of products, such as slim smartwatches and compact medical sensors, without compromising functionality.
- High-density integration and reliable connectivity: FPCB supports high-density circuit routing and can integrate multiple components (such as chips, resistors, and capacitors) into a single flexible substrate. This reduces the need for additional connectors and wiring, simplifying product structure and improving electrical connectivity reliability. In high-precision electronic systems, such as semiconductor testing equipment, this high-density integration ensures stable signal transmission and reduces interference.
- Superior resistance to harsh environments: High-quality FPCB uses durable materials such as polyimide, which exhibit excellent resistance to temperature extremes, humidity, vibration, and chemical corrosion. This makes FPCB suitable for harsh operating environments, including automotive engine bays, industrial control systems, and aerospace equipment, where traditional rigid PCBs may fail due to environmental stress.
- Cost-effectiveness in mass production: For mass-produced electronic products, FPCB can be manufactured with automated processes, reducing labor costs and improving production efficiency. Its simplified design also minimizes the number of components and assembly steps, further lowering overall production costs. Additionally, FPCB’s flexibility reduces the need for custom mechanical parts to accommodate circuit boards, saving design and manufacturing time.
FPCB’s versatility enables its widespread application across multiple high-growth electronic industries, driving innovation and performance improvements:
- Consumer electronics: FPCB is a core component in modern consumer electronics, including foldable smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, and wireless earbuds. In foldable phones, FPCB enables the flexible display to bend repeatedly while maintaining electrical connectivity; in smartwatches, its lightweight and thin design allows for slim, comfortable wearables with comprehensive functionality. FPCB also powers camera modules in smartphones, enabling compact, high-performance imaging systems.
- Medical devices: The medical industry leverages FPCB for miniaturized, high-reliability devices such as minimally invasive surgical instruments, wearable health monitors, and implantable medical devices. For example, FPCB is used in endoscopes to transmit images and control signals through narrow, curved channels; in wearable glucose monitors, it enables flexible, skin-conforming sensors that continuously track health data. FPCB’s biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization processes also make it suitable for medical applications.
- New energy vehicles (NEVs): NEVs rely on FPCB for various critical systems, including battery management systems (BMS), in-vehicle infotainment systems, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). In BMS, FPCB’s high-density integration and heat resistance ensure accurate monitoring of battery cells; in ADAS, it enables the compact integration of sensors (such as cameras, lidar, and radar) into the vehicle’s design. FPCB’s lightweight design also contributes to reducing the overall weight of NEVs, improving energy efficiency and range.
- Aerospace and defense: The aerospace industry uses FPCB in lightweight electronic systems such as satellite components, aircraft avionics, and missile guidance systems. FPCB’s high reliability, resistance to extreme temperatures and vibration, and lightweight design make it ideal for these applications, where every gram of weight savings and every increase in reliability are critical. For example, FPCB is used in satellite communication systems to enable compact, high-performance signal processing modules.
To maximize the performance and reliability of FPCB in electronic systems, follow these key implementation and selection guidelines:
- Match FPCB specifications to application requirements: Select FPCB materials, thickness, and circuit configurations based on the specific needs of the application. For high-temperature environments (such as automotive engine bays), choose polyimide substrates with high thermal resistance; for flexible wearable devices, select ultra-thin, highly flexible FPCB with excellent bendability. Consider factors such as operating temperature range, flexibility requirements, and electrical performance needs.
- Optimize circuit design for flexibility and reliability: When designing FPCB circuits, avoid sharp corners and excessive trace density in areas that will be frequently bent, as this can lead to circuit fatigue and failure. Use appropriate trace widths and spacing to ensure electrical performance and mechanical durability. Incorporate reinforcement layers in areas where FPCB will be connected to other components to prevent damage from insertion and removal.
- Ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations: For applications in medical, aerospace, and automotive industries, ensure that the selected FPCB meets relevant industry standards and regulations (such as ISO 13485 for medical devices, AS9100 for aerospace). Verify that FPCB materials are compliant with environmental regulations (such as RoHS and REACH) to avoid legal and market access issues.
- Partner with reliable FPCB manufacturers: Select manufacturers with proven expertise in the target application area, strong R&D capabilities, and comprehensive quality control systems. Ensure that the manufacturer can provide technical support during the design phase, conduct rigorous testing (such as bend testing, thermal cycling, and electrical performance testing), and maintain stable production capacity to meet project timelines.
Driven by technological advancements and growing demand for advanced electronic systems, FPCB is poised to evolve toward greater integration, intelligence, and adaptability:
- Integration of flexible hybrid electronics (FHE): Future FPCB will integrate traditional electronic components with flexible sensors, actuators, and energy harvesters, creating fully flexible, self-powered electronic systems. For example, FPCB with integrated solar cells could power wearable devices, eliminating the need for frequent charging.
- Advancements in high-density and miniaturization: As electronic products continue to shrink, FPCB will develop higher circuit density, smaller line widths, and tighter component spacing. This will enable the integration of more functionality into smaller spaces, supporting the development of next-generation miniaturized devices such as micro-implantable medical devices and ultra-compact sensors.
- Enhanced performance in extreme environments: Research and development will focus on improving FPCB’s performance in extreme conditions, such as ultra-high temperatures, radiation, and deep-sea environments. This will expand FPCB’s application in aerospace, deep-sea exploration, and nuclear energy industries.
- Adoption of intelligent manufacturing technologies: FPCB manufacturers will increasingly adopt intelligent manufacturing technologies such as AI-driven quality inspection, automated circuit design, and digital twin simulation. This will improve production efficiency, reduce defects, and enable faster customization of FPCB for specific applications.
In conclusion, FPCB is a transformative component that enables the miniaturization, flexibility, and reliability of advanced electronic systems across industries. Its unique advantages over traditional rigid PCBs make it indispensable in consumer electronics, medical devices, new energy vehicles, and aerospace applications. By following sound implementation and selection guidelines, and partnering with reliable manufacturers, organizations can fully leverage the potential of FPCB to drive product innovation and gain a competitive edge. As technological trends such as flexible hybrid electronics and intelligent manufacturing advance, FPCB will continue to play an increasingly critical role in shaping the future of the global electronics industry. For anyone involved in the design, development, or manufacturing of electronic systems, understanding and embracing FPCB is essential to staying at the forefront of technological innovation.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
