-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Dec 29. 2025, 16:18:54
Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPCB) has emerged as a transformative technology that is reshaping the landscape of modern electronics. Moving beyond the limitations of rigid printed circuit boards, FPCB’s inherent flexibility, miniaturization potential, and reliable electrical performance have made it a cornerstone of innovative product development across industries. From ultra-thin wearable devices that conform to the human body to complex flexible displays that redefine user interaction, FPCB is driving a paradigm shift in how electronic devices are designed, manufactured, and experienced. As the demand for smarter, more adaptive electronics continues to surge, FPCB’s role in enabling technological advancement becomes increasingly indispensable.
The evolution of FPCB is fueled by continuous technological innovations that enhance its performance and expand its application boundaries. One key breakthrough is the development of high-performance substrate materials. Advanced polyimide and liquid crystal polymer (LCP) substrates have replaced traditional materials, offering superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and signal integrity—critical for high-frequency applications such as 5G communication devices. These materials ensure that FPCB maintains stable performance even in extreme operating conditions, from high-temperature industrial environments to low-temperature aerospace settings.
Another significant advancement is the refinement of manufacturing processes. Precision laser drilling, automated optical inspection (AOI), and additive manufacturing technologies have improved the accuracy and efficiency of FPCB production. These processes enable the creation of ultra-fine circuit traces and miniaturized vias, supporting higher component density and further reducing the size of FPCB. Additionally, the integration of flexible electronic components, such as thin-film batteries and printed sensors, into FPCB designs has transformed it from a mere interconnection component to a multi-functional system core.
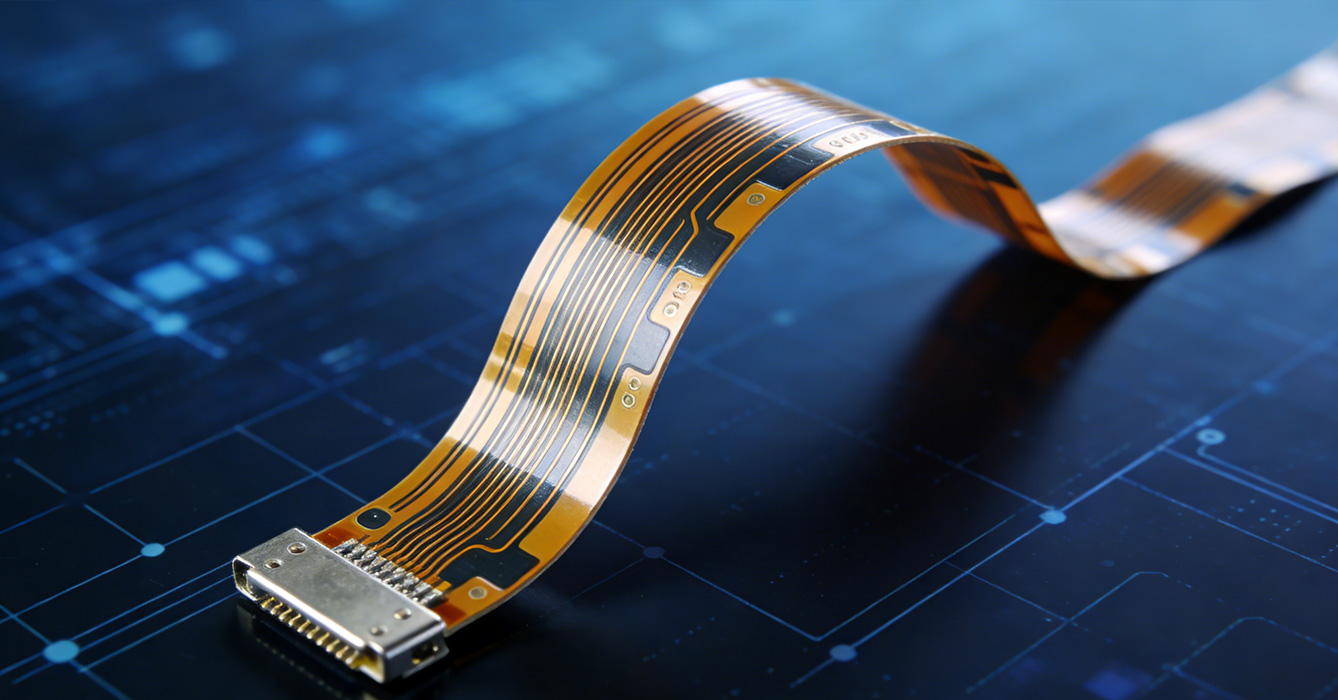
While FPCB is widely used in consumer electronics, its application is rapidly expanding into emerging high-growth sectors, unlocking new possibilities. In the field of flexible displays, FPCB is a critical enabler of foldable and rollable screens. It provides the necessary flexibility to support repeated bending without compromising the display’s electrical connections, making devices such as foldable smartphones, rollable laptops, and flexible smartwatches a reality. This application has redefined the form factor of consumer electronics, offering users enhanced portability and versatility.
In smart agriculture, FPCB is used in flexible sensor systems that monitor soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels. These sensors can be easily deployed in irregularly shaped farmland or greenhouses, providing real-time data to optimize irrigation and fertilization. The lightweight and durable nature of FPCB ensures that these sensors can withstand outdoor environmental conditions for extended periods. In the field of wearable health technology, FPCB is integrated into skin-like biosensors that continuously monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood glucose, and body temperature, enabling personalized healthcare and early disease detection.
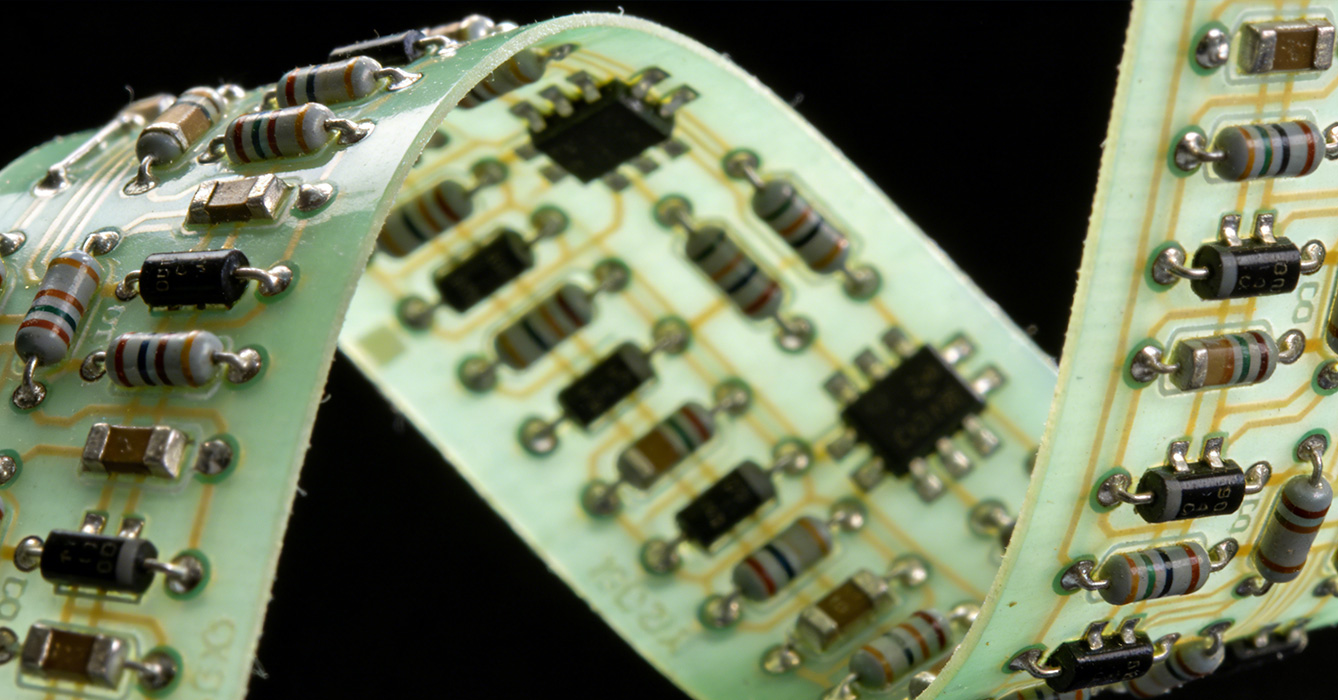
Designing high-performance FPCB requires careful consideration of several core principles to maximize its potential. First, material selection must align with the application’s requirements. For high-frequency or high-temperature applications, LCP or high-grade polyimide substrates are preferred, while cost-sensitive applications may use polyester substrates. Second, thermal management is critical. FPCB’s thin profile can lead to heat accumulation, so designers must optimize circuit layouts, incorporate heat-dissipating structures, and select thermally conductive materials to ensure stable performance.
Third, flexibility and mechanical durability must be balanced. Designers should avoid sharp bends and stress concentrations in high-flex areas, using curved traces and reinforcing materials where necessary. Additionally, design for manufacturability (DFM) is essential. Collaborating with manufacturers early in the design process ensures that the FPCB design is compatible with production processes, reducing the risk of defects and improving production efficiency. Rigorous testing, including mechanical bending tests and electrical performance validation, is also necessary to ensure the FPCB meets the application’s reliability requirements.
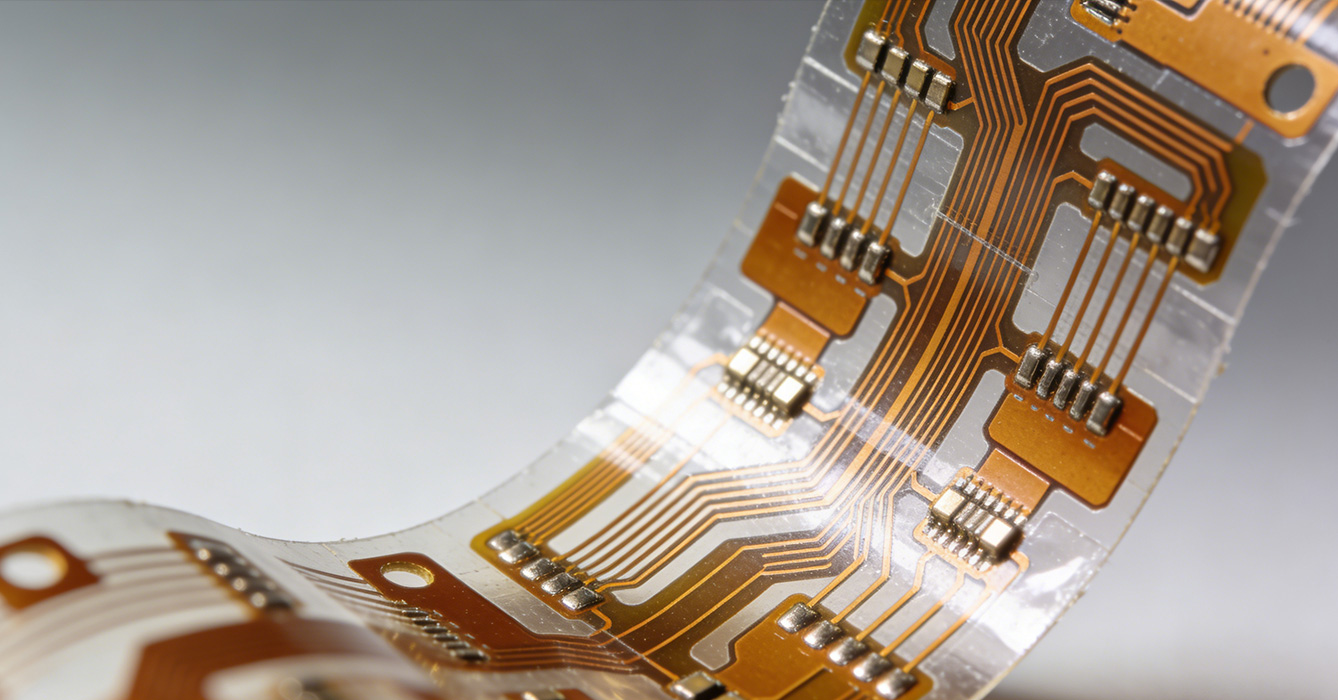
The future of FPCB is shaped by two key trends: smart integration and sustainability. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, FPCB is increasingly being integrated with smart control modules and wireless communication technologies. This enables the development of self-powered, connected devices that can transmit data wirelessly, supporting applications such as smart cities, industrial IoT, and remote monitoring systems. The integration of AI algorithms into FPCB-based systems further enhances their adaptability, enabling them to analyze data and make intelligent decisions in real time.
Sustainability is another critical trend driving FPCB innovation. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly materials, such as recyclable substrates and lead-free components, to reduce the environmental impact of FPCB production. Additionally, advancements in biodegradable FPCB materials are being explored, offering a solution to the growing electronic waste problem. The development of energy-efficient FPCB designs is also a focus, aligning with global efforts to reduce energy consumption and achieve carbon neutrality.
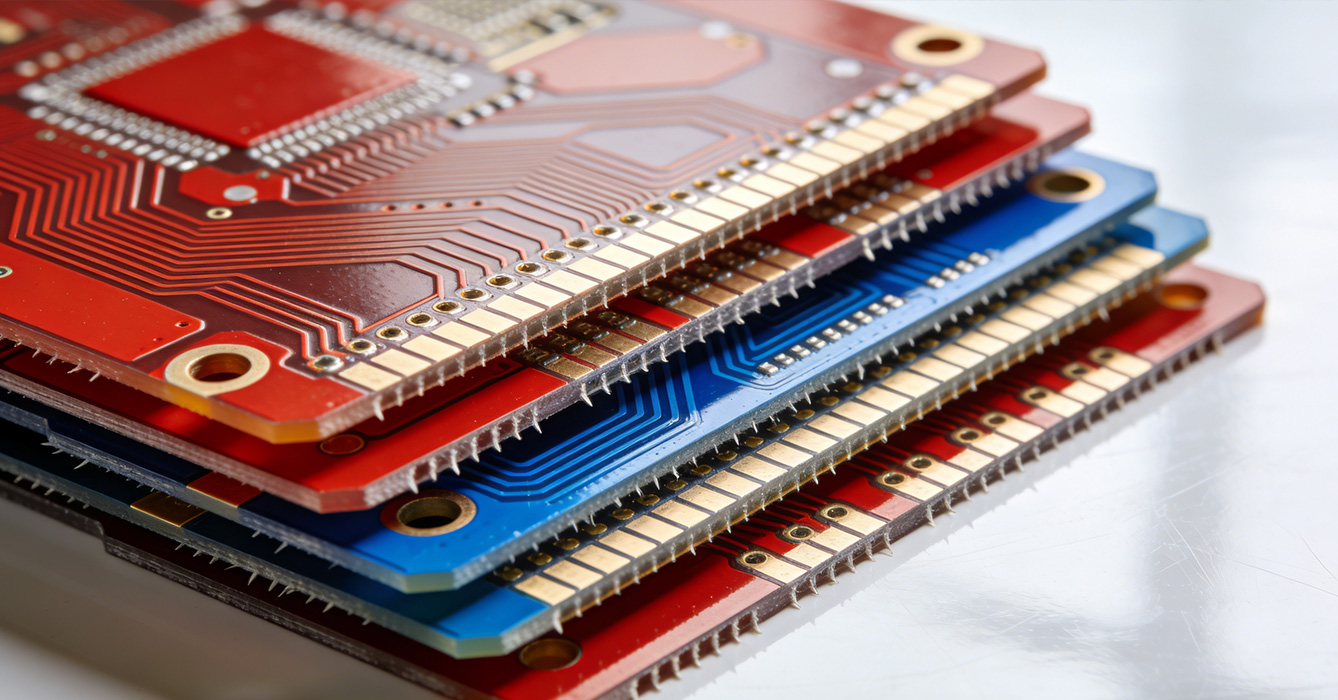

In conclusion, FPCB is at the forefront of the flexible electronics revolution, driving technological evolution through continuous innovation. Its unique combination of flexibility, miniaturization, and reliability has made it indispensable in emerging sectors such as flexible displays, smart agriculture, and wearable health technology. By adhering to sound design principles and embracing smart integration and sustainability trends, FPCB will continue to redefine the possibilities of electronic devices. As the demand for adaptive, efficient, and sustainable electronics grows, FPCB’s role in shaping the future of technology will become even more prominent.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
