-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Dec 18. 2025, 16:25:57
The global electronics industry is experiencing a paradigm shift toward interconnected, adaptable, and eco-conscious systems, and flexible PCB has emerged as a cornerstone technology enabling this transformation. Beyond its traditional role in consumer electronics, flexible PCB now serves as a critical enabler for emerging ecosystems including smart textiles, batteryless IoT devices, and extreme-environment electronics. By virtue of its inherent mechanical compliance, lightweight design, and compatibility with multifunctional integration, flexible PCB is breaking down the barriers between electronic components and everyday objects. For manufacturers and innovators, leveraging the latest advancements in flexible PCB technology is essential to unlocking new product possibilities and capturing opportunities in high-growth emerging markets.
Flexible PCB’s unique characteristics are driving its adoption in groundbreaking application areas that demand seamless integration of electronics with dynamic or unconventional form factors:
- Smart Textile Displays: A revolutionary application of flexible PCB lies in the development of full-flexible display textiles. By integrating flexible PCB technology with textile weaving processes, researchers have created fabrics that can emit light, display patterns, and even transmit information. These smart textiles use ultra-thin, flexible circuit traces woven into fabric fibers, enabling garments that function as wearable displays for navigation, communication, or health monitoring. The flexible PCB components maintain the fabric’s softness, breathability, and durability, withstanding repeated bending, stretching, and even washing—critical for practical wearable applications.
- Batteryless IoT Systems: Flexible PCB is pivotal to the advancement of batteryless IoT devices, addressing the sustainability and maintenance challenges of traditional battery-powered sensors. Flexible extension boards integrate energy-harvesting modules (solar, thermal, or kinetic) with configurable power management systems, enabling IoT devices to operate solely on ambient energy. This technology is transforming applications in smart agriculture, industrial monitoring, and smart cities, where devices can be deployed in remote or hard-to-reach locations without the need for battery replacement.
- Extreme-Environment Electronics: In aerospace, deep-sea exploration, and implantable medical devices, flexible PCB is engineered to withstand harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures, pressure, and corrosive environments. Advanced material formulations and circuit designs enhance reliability by mitigating issues like dielectric drift, interfacial delamination, and metal electromigration. For example, flexible PCB used in implantable medical devices combines biocompatibility with stable electrical performance, enabling long-term monitoring of vital signs without causing tissue irritation.
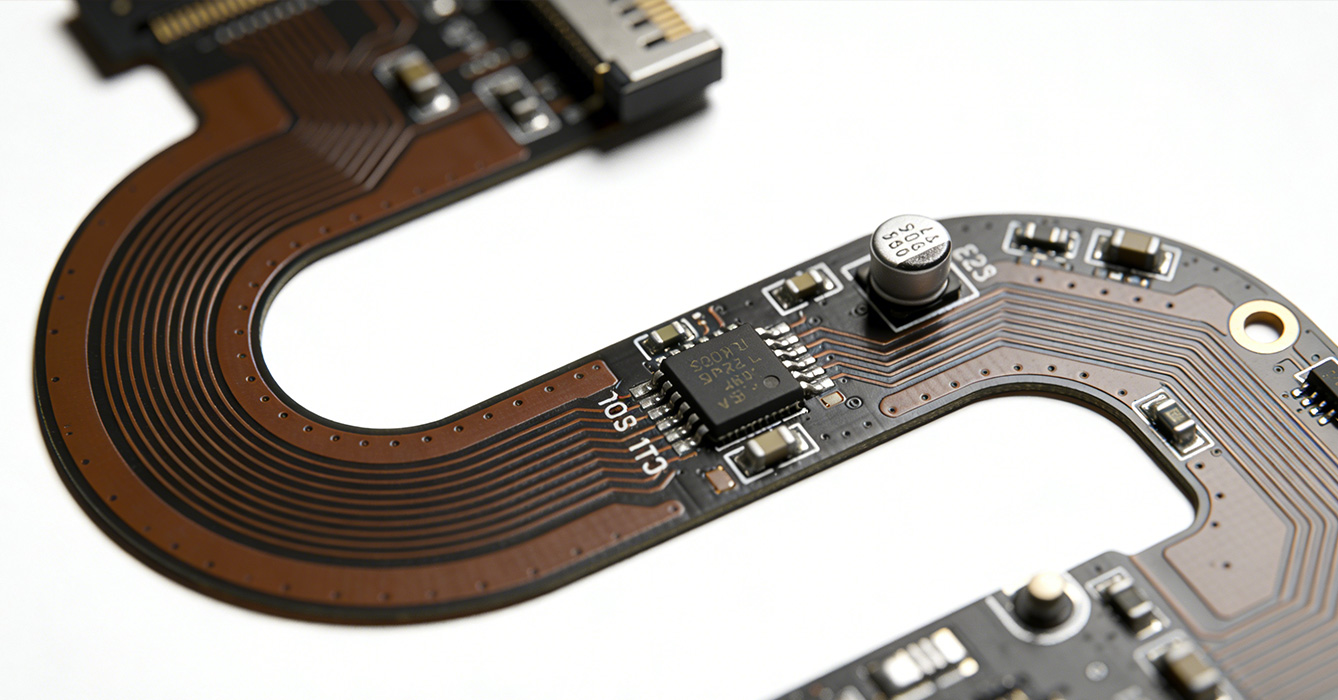
Recent advancements in materials and manufacturing processes are expanding the capabilities of flexible PCB, making it suitable for increasingly demanding applications:
- Multiscale Composite Conductive Networks: To enhance mechanical robustness and environmental resistance, flexible PCB now incorporates multiscale composite conductive materials. These materials feature a hierarchical structure that improves interfacial bonding strength, reducing the risk of circuit failure under dynamic stress. The composite networks also exhibit superior electrical conductivity and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-performance applications in extreme environments.
- Additive Manufacturing for Heterogeneous Integration: Additive manufacturing (3D printing) techniques are revolutionizing flexible PCB production by enabling the integration of heterogeneous materials—such as conductive inks, insulating polymers, and functional sensors—into a single, seamless circuit. This approach allows for the creation of complex 3D flexible structures that conform to irregular surfaces, expanding the design possibilities for smart devices. Additive manufacturing also reduces material waste, aligning with sustainable manufacturing goals.
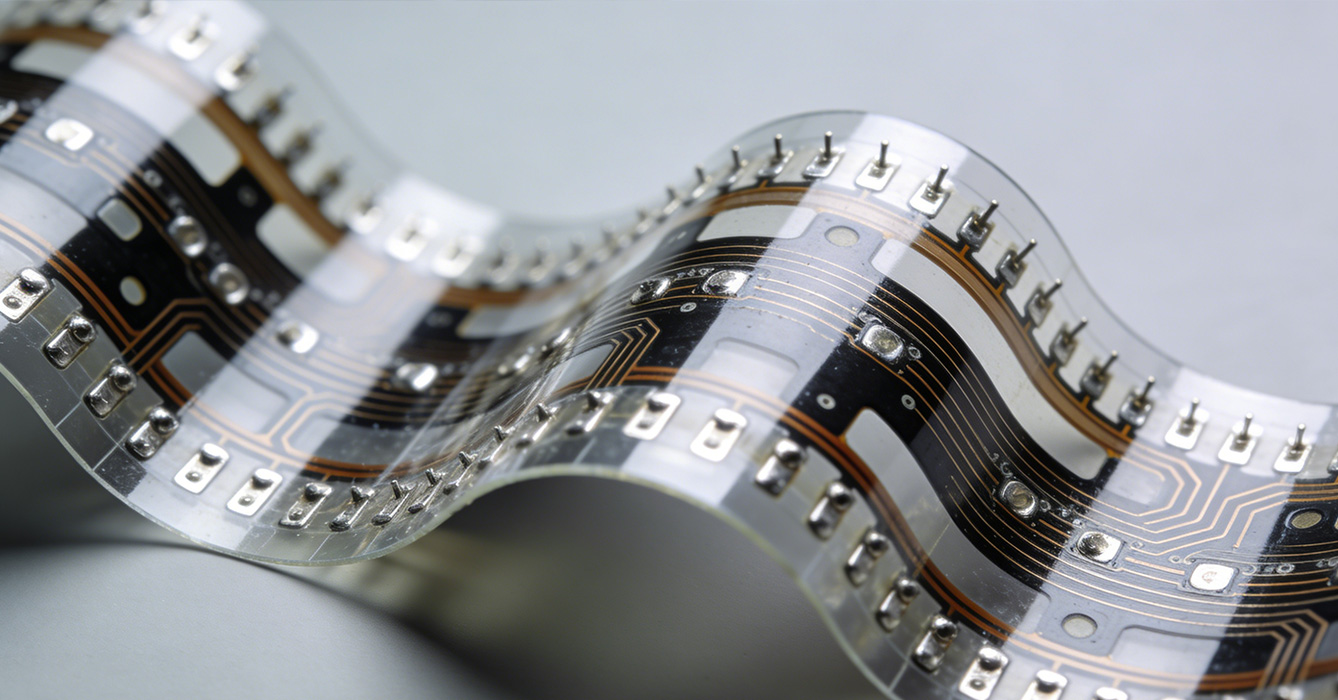
As global environmental regulations tighten and sustainability becomes a key market differentiator, flexible PCB technology is evolving to embrace greener practices:
- Recyclable and Bio-Based Materials: Manufacturers are increasingly adopting recyclable substrates and bio-based polymers for flexible PCB production. These materials maintain the mechanical and electrical performance of traditional polyimide substrates while enabling end-of-life recycling. For example, bio-based polyimides derived from renewable resources reduce the carbon footprint of flexible PCB manufacturing, supporting the circular economy in the electronics industry.
- Energy-Efficient Manufacturing Processes: Innovations in manufacturing, such as low-temperature processing and dry etching techniques, reduce energy consumption and hazardous emissions. Additionally, the integration of energy-harvesting components into flexible PCB designs enables self-powered electronic systems, further enhancing the sustainability of end products.
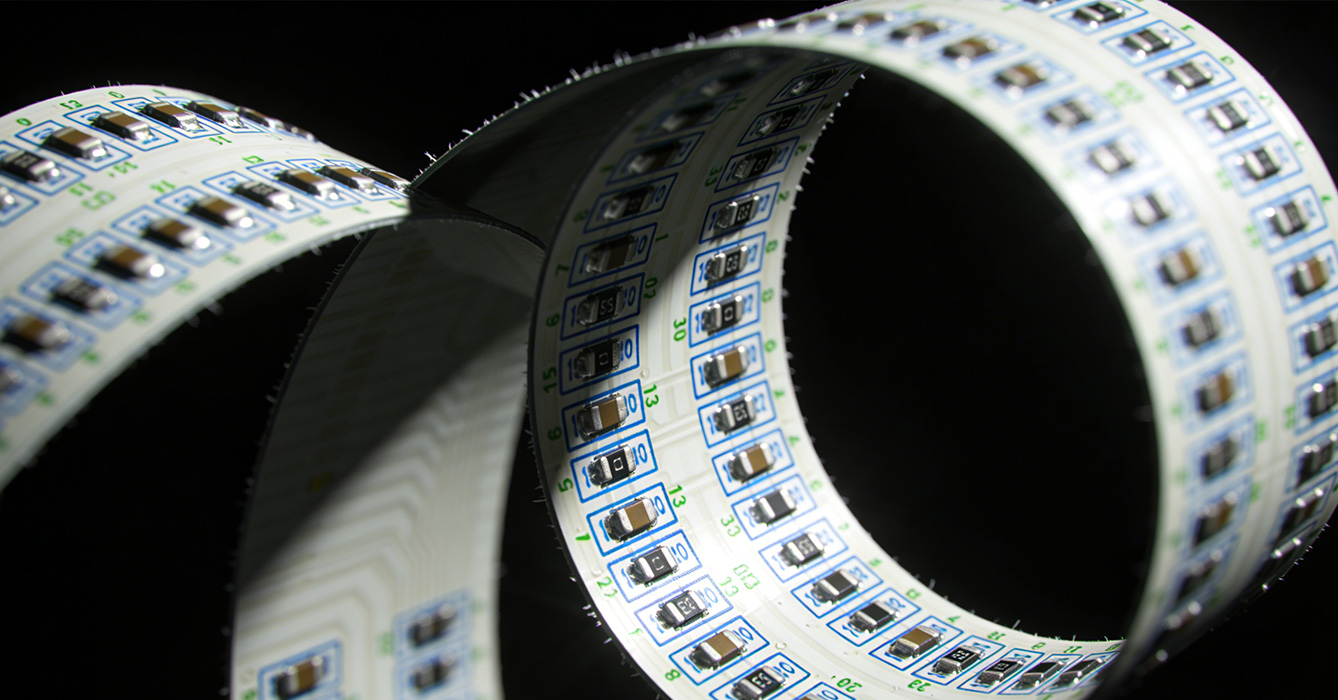

The future of flexible PCB lies in the development of active, reconfigurable electronic systems that can adapt to changing environments and user needs:
- Active Structural Reconfiguration: Research is focused on developing flexible PCB with shape-memory materials and adaptive circuits, enabling devices to change form and function in response to external stimuli. This technology will enable applications such as self-deploying aerospace sensors and adaptive wearable devices that adjust to the user’s body movements.
- Hybrid Integration with Photonics: The convergence of flexible PCB with photonics technology will enable high-speed, low-power data transmission in flexible electronic systems. This integration is critical for next-generation applications such as flexible optical communication devices and high-resolution display systems.
In conclusion, flexible PCB is no longer just a component for miniaturizing electronics but a catalyst for innovation in emerging electronic ecosystems. Its ability to integrate with diverse materials, adapt to extreme conditions, and support sustainable practices makes it indispensable for the next generation of smart textiles, IoT devices, and medical technologies. As research continues to push the boundaries of material science and manufacturing, flexible PCB will play an increasingly central role in shaping a more connected, adaptable, and sustainable electronic future.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
