-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Oct 31. 2025, 15:07:15
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of most electronic devices we use today. From your smartphone to complex industrial machines, PCBs are everywhere. Understanding the PCB assembly process is crucial whether you're an electronics hobbyist, a startup founder, or part of a large manufacturing company. This article will guide you through the key steps involved in PCB assembly, from design to manufacturing.
PCB assembly is the process of connecting electronic components to a printed circuit board to create a fully functional circuit. This process involves several steps, including designing, manufacturing, and assembling the PCB.
The quality and reliability of the final electronic product heavily depend on the precision of the PCB assembly process. Thus, understanding each step is essential for ensuring that the end product meets the required standards.
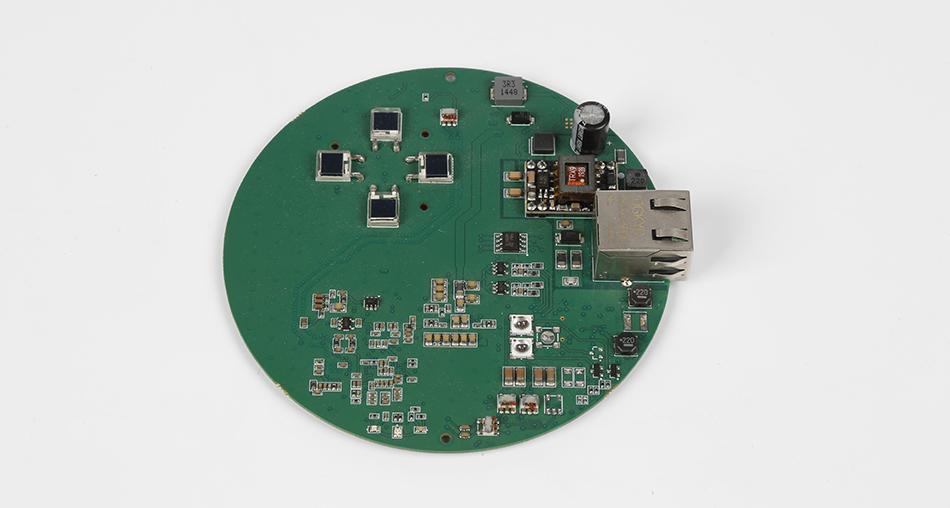
Before you can assemble a PCB, you need a design. The design process is the first and arguably one of the most critical steps in PCB assembly. It involves creating a schematic diagram that outlines the electronic circuit. This diagram serves as a blueprint for the PCB.
Several software tools are available for PCB design. These tools help in creating schematic diagrams and layout designs. Popular PCB design software includes:
Eagle: Known for its ease of use and extensive library of components.
KiCad: An open-source alternative with powerful design features.
Altium Designer: A professional-grade tool with advanced features for complex PCB designs.
While designing a PCB, consider the following factors:
Component Placement: Proper placement of components ensures efficient signal flow and heat dissipation.
Trace Routing: Traces are the copper pathways that connect components. Proper routing prevents signal interference.
Layer Configuration: Multilayer PCBs allow for complex designs and can save space.
Thermal Management: Effective heat management prevents overheating and ensures longevity.

Once the design is finalized, the next step is manufacturing. PCB manufacturing involves creating the physical board on which components will be assembled. This process includes several key stages:
Fabrication is the process of turning the design into a physical board. It involves:
Substrate Preparation: The base material, usually fiberglass, is prepared to form the board's structure.
Copper Cladding: The board is coated with a thin layer of copper, which will form the traces.
Etching: Unwanted copper is removed to reveal the designed traces.
Drilling: Holes are drilled for component leads and vias.
Solder Mask Application: A protective layer is applied to prevent solder bridges.
Silkscreen Printing: Labels and markings are printed for easy identification.
Quality control is a crucial part of PCB manufacturing. It involves testing the board for defects such as shorts, opens, or incorrect connections. Automated optical inspection (AOI) and X-ray inspection are common techniques used to ensure quality.
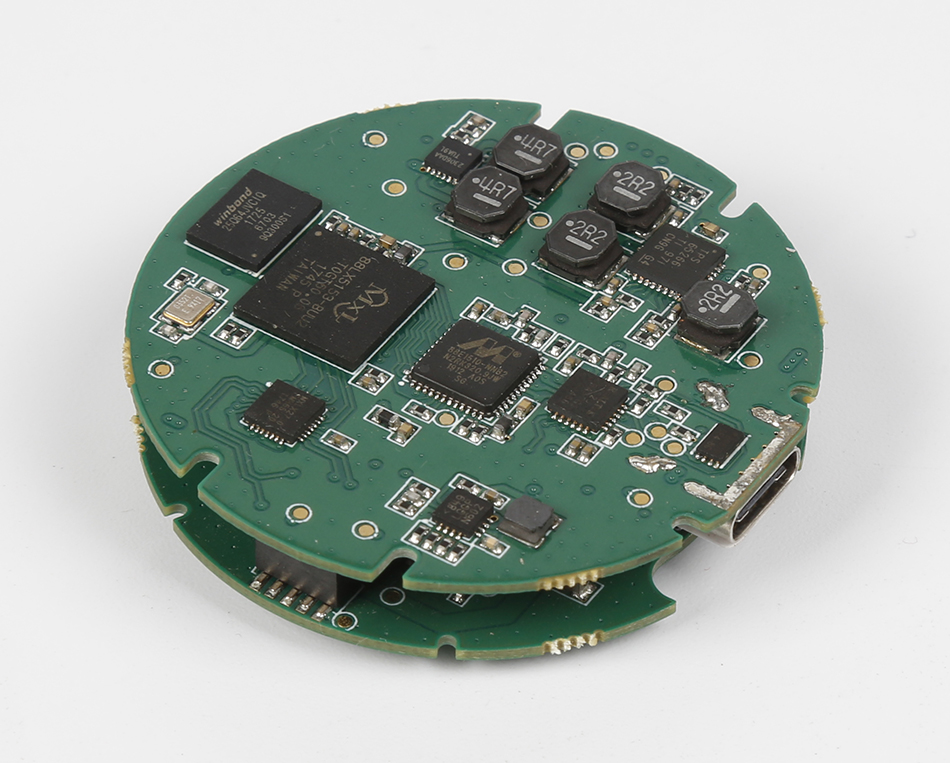
PCB assembly is where components are placed and soldered onto the manufactured board. This process involves several steps:
SMT is the most common method of mounting components on a PCB. It involves:
Solder Paste Application: Solder paste is applied to the board using a stencil.
Component Placement: Components are placed on the board using a pick-and-place machine.
Reflow Soldering: The board is heated to melt the solder paste, creating electrical connections.
THT involves inserting component leads through holes in the board and soldering them on the opposite side. This method is used for components that require strong mechanical support.
After assembly, the board undergoes inspection and testing to ensure functionality. This includes:
Visual Inspection: Checking for soldering defects or misplaced components.
In-Circuit Testing (ICT): Testing individual components for functionality.
Functional Testing: Ensuring the entire circuit works as intended.
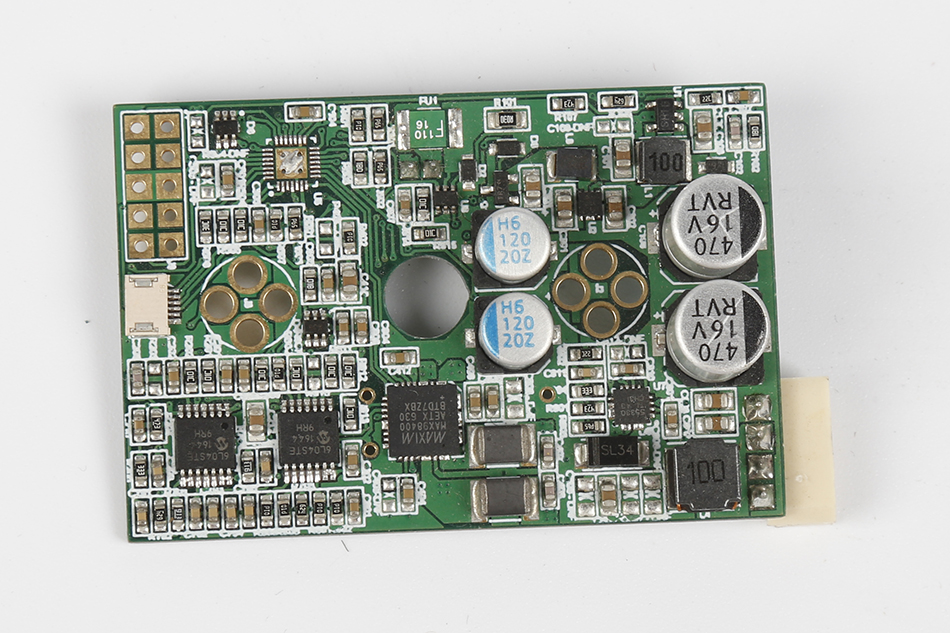
PCB assembly is not without its challenges. Common issues include:
Component Misalignment: Misplaced components can lead to faulty connections.
Soldering Defects: Poor soldering can cause shorts or open circuits.
Thermal Issues: Improper heat management can damage components.
Understanding the PCB assembly process is essential for anyone involved in electronics design and manufacturing. By mastering the steps from design to assembly, you can ensure the production of high-quality, reliable electronic devices. Whether you're a hobbyist or a professional, this knowledge can help you bring your electronic projects to life with precision and efficiency.
In this article, we've explored the critical aspects of PCB assembly, including design considerations, manufacturing processes, and assembly techniques. With this understanding, you're better equipped to tackle the challenges of PCB assembly and produce effective electronic solutions.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
