-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Sep 04. 2025, 19:46:36
A PCB manufacturer acts as the backbone of the global electronics supply chain, transforming design concepts into physical circuit boards that power devices across industries—from smartphones and medical equipment to industrial machinery and renewable energy systems. Beyond basic fabrication, modern PCB manufacturers function as strategic partners, integrating design expertise, advanced manufacturing technologies, and quality assurance to meet diverse industry needs. In an era of miniaturization, high-performance electronics, and strict regulations, their role extends beyond production: they enable innovation by bridging engineering design and scalable, reliable manufacturing.
Today’s electronics market demands more than generic circuit boards. Manufacturers must adapt to shrinking product lifecycles, evolving material requirements, and complex industry-specific standards. A competent PCB manufacturer distinguishes itself by offering end-to-end support—from design for manufacturability (DFM) feedback to post-production testing—ensuring each PCB meets performance targets and cost constraints. Whether collaborating on prototypes for startups or mass-producing for multinational corporations, these manufacturers accelerate time-to-market and ensure product success.
This article explores the core capabilities of leading PCB manufacturers, their industry-specific adaptations, sustainable practices, emerging technologies, and key criteria for selecting a partner. It guides engineers, procurement managers, and product developers in navigating PCB production and building successful manufacturing partnerships.
Top PCB manufacturers differentiate themselves through integrated capabilities spanning design collaboration, advanced manufacturing, and rigorous quality control—ensuring PCBs are efficient, high-performing, reliable, and scalable.
Leading manufacturers engage early in product development, offering design support to optimize PCBs for manufacturability and performance:
DFM Analysis: Engineers review designs to identify production challenges (e.g., tight component spacing, suboptimal routing) and recommend adjustments. For instance, widening narrow traces improves solderability, reducing defects.
Material and Technology Recommendations: Based on the PCB’s use, manufacturers advise on substrates (e.g., high-Tg FR-4 for high temperatures, flexible polyimide for wearables) and technologies (e.g., HDI for compact designs). This prevents over-engineering and ensures cost-effectiveness.
Investment in cutting-edge equipment enables manufacturers to handle diverse, complex PCB requirements:
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) Production: HDI capabilities—including laser-drilled micro-vias and sequential lamination—support compact, high-performance PCBs for smartphones, IoT devices, and medical wearables, enabling greater component density without sacrificing signal integrity.
Flexible and Rigid-Flex Fabrication: Specialized equipment for polyimide substrates and precision folding produces flexible PCBs (e.g., foldable phones) and rigid-flex designs (ideal for aerospace and automotive applications with space constraints).
Reliable manufacturing depends on robust quality systems ensuring consistency and adherence to standards:
In-Process Inspection: Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and X-ray systems check for defects (solder bridges, missing components) at every stage. Real-time data analysis enables immediate adjustments, reducing scrap rates.
Material Traceability: Detailed records of material sources, production dates, and test results support industries like automotive and medical, where recalls or failure analysis may be necessary.

Different industries demand unique PCB characteristics, and leading manufacturers tailor processes to meet these needs, ensuring reliability in intended environments.
Automotive PCB manufacturing focuses on durability, temperature resistance, and functional safety:
Extreme Environment Testing: PCBs for ECUs, ADAS sensors, and infotainment systems undergo thermal cycling, vibration testing (ISO 16750), and chemical exposure tests. High-Tg substrates and lead-free solder ensure longevity.
Functional Safety Compliance: Production aligns with ISO 26262 (ASIL B-D) for safety-critical systems, including redundant circuitry, rigorous inspection, and detailed documentation.
High-Volume Efficiency: Automated lines and statistical process control (SPC) maintain consistency for large-scale production (100,000+ units/month), meeting tight delivery schedules.
Medical PCB manufacturing prioritizes precision, biocompatibility, and regulatory compliance:
Cleanroom Production: PCBs for implantables, diagnostics, and surgical tools are produced in Class 8+ cleanrooms to prevent contamination, reducing risks in sensitive applications.
Low-Noise Design Support: Collaboration to minimize EMI in devices like MRI machines and ECG monitors includes shielded enclosures, grounded planes, and low-noise component placement.
Regulatory Documentation: Comprehensive records support FDA and CE submissions. Manufacturers assist in validation testing to meet ISO 13485 and IEC 60601.
Industrial PCB manufacturing emphasizes ruggedness, reliability, and resistance to harsh conditions:
Ruggedization Techniques: Conformal coatings resist dust, moisture, and chemicals. Thick copper traces (2oz–4oz) handle high currents, while reinforced edges prevent vibration damage.
Long-Term Availability: Manufacturers ensure access to legacy components and maintain production processes for 10+ years, avoiding costly redesigns due to obsolescence.
High-Temperature Performance: High-Tg substrates and heat-resistant solder masks prevent delamination in factory environments (temperatures exceeding 85°C).

As environmental regulations tighten, PCB manufacturers adopt eco-friendly practices to reduce their carbon footprint and waste.
1. Green Materials and Processes
Recycled and Low-Impact Materials: Recycled copper foil, bio-based resins, and halogen-free substrates reduce reliance on virgin materials while meeting performance standards.
Lead-Free and RoHS Compliance: Eliminating lead-based solder and using water-based solder masks minimize toxic waste, aligning with global environmental regulations.
Energy-Efficient Equipment: Investment in energy-efficient ovens, laser drills, and renewable energy (solar panels) reduces electricity consumption.
2. Waste Reduction and Recycling
Chemical Recycling: Etching chemicals (e.g., copper chloride) are recycled, reducing hazardous waste. Wastewater is treated and repurposed to minimize discharge.
Scrap Reduction: Advanced AOI and process optimization lower scrap rates from 5–8% to 1–2%. Scrap materials (copper, glass fiber) are recycled, with copper recovery exceeding 95%.
Lean Manufacturing: Principles like 5S and just-in-time production reduce overproduction, inventory waste, and energy use, improving efficiency and lowering environmental impact.
3. Carbon Footprint Reduction
Supply Chain Optimization: Local sourcing and optimized delivery routes reduce transportation emissions.
Carbon Offsetting: Investments in reforestation or renewable energy offset unavoidable production emissions.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): LCAs identify high-impact stages (e.g., lamination, plating) for targeted improvements, supporting client sustainability reporting.

Technological advancements reshape production, enabling higher precision, faster turnaround, and greater flexibility. Leading manufacturers adopt these innovations to stay competitive.
Automated Production Lines: Robotic arms handle loading, placement, and inspection, reducing human error and increasing throughput. Lines reconfigure quickly for low-volume, high-mix production.
AI-Powered Quality Control: Machine learning analyzes AOI and X-ray data to detect defects more accurately than manual inspection, improving over time and reducing false positives.
Predictive Maintenance: Sensors collect equipment data (drill speed, oven temperature), with AI models predicting maintenance needs to minimize downtime and extend equipment life.
3D-Printed PCBs: Emerging technologies print conductive traces and dielectric layers, enabling complex geometries (curved, hollow) impossible with traditional methods—ideal for aerospace and wearables.
Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing reduces prototype lead times from days to hours, accelerating design iterations and product development.
Graphene and Nanocomposites: Graphene-enhanced substrates improve thermal conductivity and strength, suitable for high-power applications (e.g., EV chargers). Nanocomposites reduce weight, benefiting aerospace and portables.
Self-Healing Substrates: Research into self-healing polymers shows promise for PCBs that repair small cracks, extending lifespan in harsh environments (industrial, automotive).
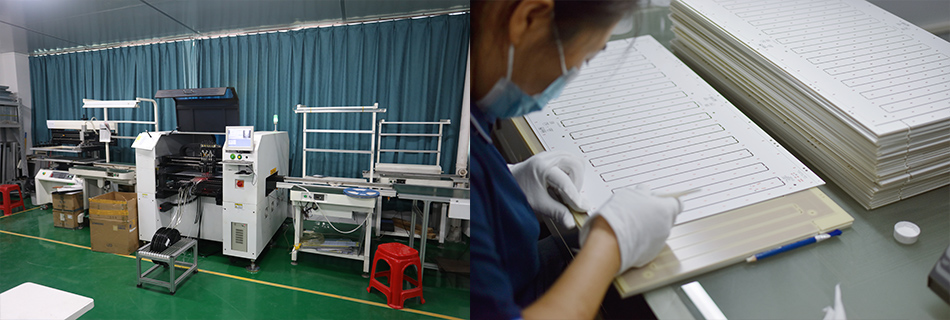
Choosing the right manufacturer ensures quality, on-time delivery, and partnership success. Evaluate potential partners based on these factors:
Service Range: Verify ability to handle specific requirements (HDI, flexible PCBs, high-volume production) and experience with similar projects/industries.
Design Support: Assess DFM feedback quality and engineering collaboration—strong support optimizes PCBs for performance and cost.
Equipment and Technology: Inquire about manufacturing equipment, inspection systems, and material handling—modern, well-maintained tools produce higher-quality PCBs.
Certifications: Check for relevant certifications (ISO 9001, IATF 16949, ISO 13485) and compliance with standards (RoHS, UL). Request audit reports or references.
Quality Processes: Understand inspection protocols, defect rates, and corrective actions—transparent systems indicate reliability commitment.
Traceability: Ensure detailed records of materials, production steps, and testing—critical for regulated industries.
Production Capacity: Evaluate scalability from prototypes to mass production and lead times for different volumes.
Supply Chain Resilience: Inquire about strategies for shortages, delays, or disruptions—diverse supplier networks reduce production risks.
On-Time Delivery: Request past performance data—consistent deadlines indicate reliable planning and execution.
Account Management: Look for dedicated managers/teams to ensure clear communication and rapid issue resolution.
Transparency: Assess how progress, delays, or quality issues are communicated—regular updates build trust.
Cultural Fit: Align values and work styles—collaborative partners invest in your success.
A PCB manufacturer is more than a production facility—it is a strategic partner enabling innovation, ensuring quality, and supporting the entire product lifecycle. Leading manufacturers excel in technical capabilities, industry expertise, sustainability, and collaboration. As electronics evolve—becoming smaller, more powerful, and integrated—their role grows increasingly vital.
Selecting a manufacturer with the right technical skills, quality standards, and reliability accelerates time-to-market, reduces costs, and ensures products meet competitive demands. Whether for automotive safety systems, medical devices, or consumer electronics, the right partner drives success.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
