-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Nov 24. 2025, 11:29:42
Aluminum Base Thermal Pad PCB has become a mainstream thermal management solution for mid-to-high-power electronic systems, combining the structural advantages of aluminum base PCBs (lightweight, rigid, cost-efficient) with the interface heat transfer optimization of high-conductivity thermal pads. Unlike copper base or ceramic base alternatives that prioritize extreme performance but incur higher costs, aluminum base designs strike a balance between thermal efficiency, manufacturability, and cost—making them ideal for mass-produced applications from LED lighting to consumer electronics fast chargers. As electronic devices demand smaller form factors and higher power densities while controlling production costs, Aluminum Base Thermal Pad PCB resolves the core pain point of "efficient heat dissipation at scale" by leveraging aluminum’s natural heat spreading capability and thermal pads’ gap-filling performance. This article explores the unique value proposition, material synergy, design optimizations, targeted applications, and manufacturing advantages of this specialized PCB solution.
Aluminum’s abundance and low processing cost (30-50% lower than copper or ceramic substrates) make Aluminum Base Thermal Pad PCB the most cost-effective choice for high-volume applications. For example, a 100W LED high-bay light using an aluminum base design reduces material costs by 25-30% compared to copper base alternatives, while maintaining thermal performance sufficient for 50,000+ hours of operation. This cost advantage is amplified by thermal pads’ compatibility with automated assembly processes, enabling high-speed lamination and component mounting without specialized equipment.
Aluminum’s density (2.7 g/cm³) is 35% of copper’s (8.96 g/cm³), making Aluminum Base Thermal Pad PCB ideal for weight-sensitive applications. A typical 100x100mm aluminum base PCB weighs only 15-20g (vs. 40-50g for copper base), reducing transportation costs and enabling slim fixture designs (e.g., 5mm-thick LED panel lights). Additionally, aluminum’s inherent rigidity resists warpage during thermal cycling (-40°C to 85°C), ensuring structural stability in rugged environments like automotive under-hood systems or industrial machinery.
While aluminum’s thermal conductivity (237 W/(m·K)) is lower than copper’s (401 W/(m·K)), the integration of high-conductivity thermal pads bridges this gap by minimizing interface thermal resistance. The combination delivers a total thermal resistance (Rθ) of 0.8-1.2°C/W—sufficient for 30-200W applications, which cover 80% of high-power electronic use cases. For example, a 65W fast charger using an aluminum base PCB with a graphite-enhanced thermal pad achieves a junction temperature reduction of 25-30°C compared to standard FR4 PCBs, preventing thermal throttling while keeping the charger’s weight under 100g.
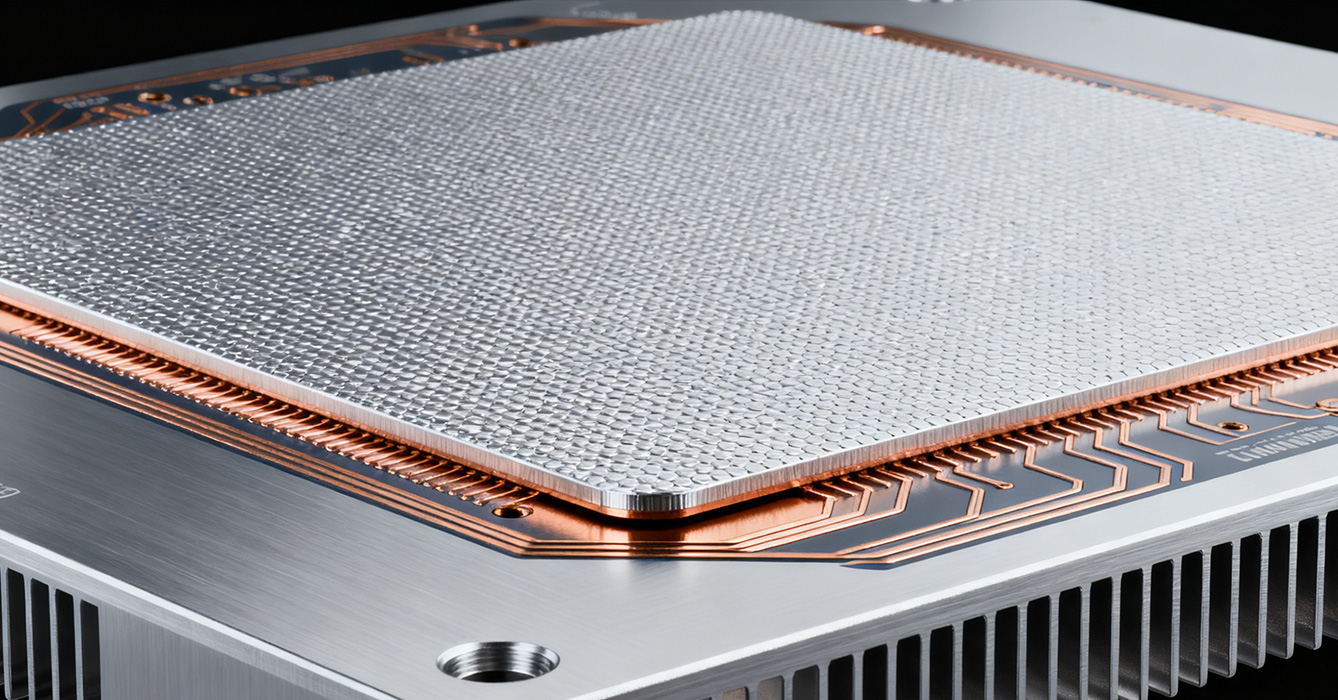

The performance of Aluminum Base Thermal Pad PCB depends on the precise matching of thermal pad materials to aluminum’s properties, ensuring interface compatibility and maximum heat transfer.
Graphite-Enhanced Polymer Pads (Thermal Conductivity: 5-15 W/(m·K)): The most common pairing for aluminum base PCBs, these pads combine flexibility (to conform to aluminum’s micro-irregularities) and cost-effectiveness. Ideal for mid-power applications (30-100W) like LED downlights, retail track lights, and 65W fast chargers, they fill air gaps (0.1-0.3mm) between components and the aluminum core, reducing interface thermal resistance by 40-50%.
Phase-Change Material (PCM) Pads (Thermal Conductivity: 8-20 W/(m·K)): Suited for temperature-variable environments (e.g., automotive interior lighting, outdoor sensors), PCM pads melt at 45-60°C to form a perfect interface with the aluminum base, maintaining low thermal resistance across thermal cycles. They are particularly effective for aluminum bases used in under-hood automotive electronics, where temperatures fluctuate between -40°C and 125°C.
Metal-Particle Composite Pads (Thermal Conductivity: 15-30 W/(m·K)): For high-power aluminum base applications (100-200W) like industrial LED floodlights or 120W EV on-board chargers, these pads (infused with aluminum or copper particles) enhance heat transfer while remaining compatible with aluminum’s thermal expansion coefficient (CTE: 23.1 ppm/K), avoiding delamination.
Core Thickness: 1.0-3.0mm (most common: 1.5mm) balances heat spreading capability and form factor. Thicker cores (2.0-3.0mm) are used for 100W+ applications, while 1.0-1.5mm cores suit compact designs like smartphone fast chargers.
Surface Finish: Anodized or sandblasted aluminum surfaces (Ra = 0.8-1.2μm) improve thermal pad adhesion, preventing slippage during assembly and operation. Anodization also adds corrosion resistance for outdoor applications.
Dielectric Layer: 50-150μm thick thermally conductive dielectric (e.g., epoxy resin with ceramic fillers) ensures electrical isolation between the aluminum core and copper traces, with breakdown voltage ≥2kV to meet safety standards.
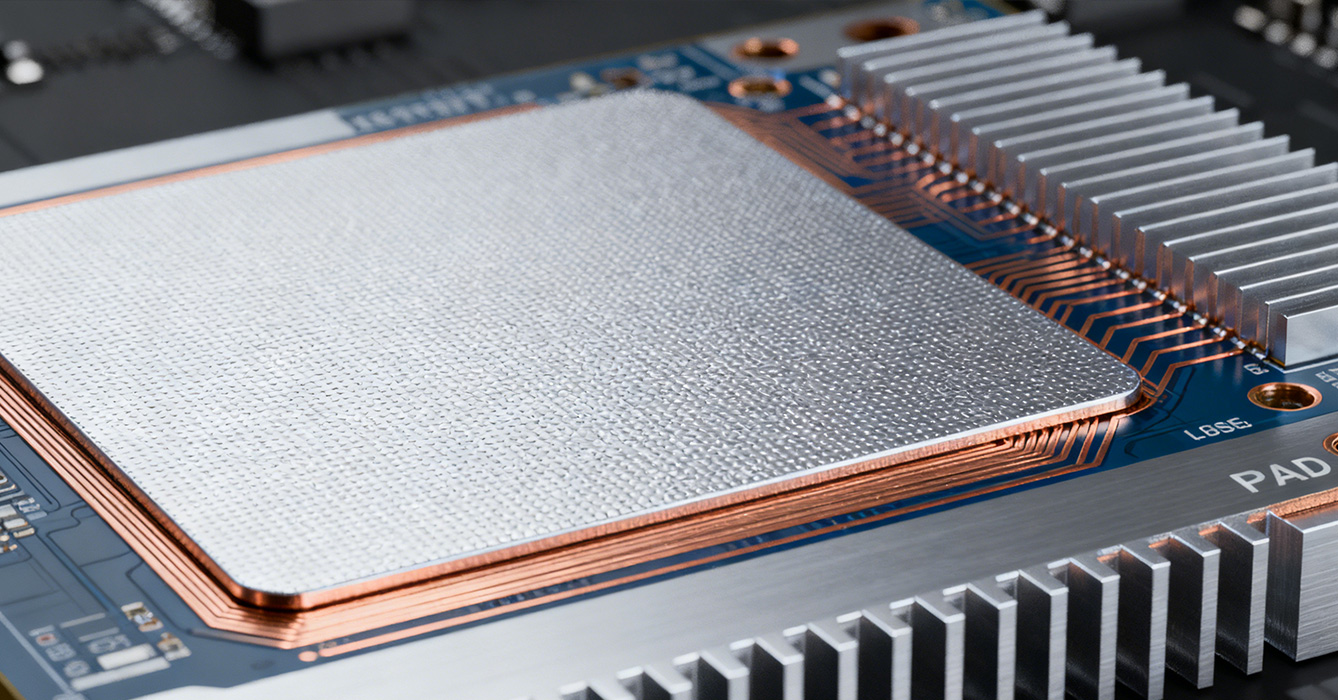

Footprint Matching: Thermal pads are sized to 1:1 with component thermal pads (e.g., LED chips, power MOSFETs) to avoid excess material that increases thermal mass. For LED arrays, individual 3x3mm thermal pads align with each 1W LED chip, ensuring uniform heat transfer to the aluminum base.
Edge Clearance: A 1-2mm clearance between thermal pads and PCB edges prevents heat accumulation at the board perimeter, enhancing overall heat spreading. In high-density designs (e.g., fast charger PCBs), thermal pads are offset from signal traces by ≥0.5mm to preserve electrical performance.
Surface Preparation: Aluminum bases undergo precision grinding to reduce surface roughness (Ra ≤1.0μm), minimizing air gaps between the base and thermal pad. Thermal pads are pre-cut to exact dimensions to avoid misalignment, which can increase thermal resistance by 30-40%.
Compression Control: During assembly, thermal pads are compressed to 70-80% of their original thickness (e.g., a 0.5mm pad compressed to 0.35-0.4mm) to maximize contact area. This compression is calibrated to avoid damaging the aluminum base or component solder joints.
Radial Copper Pour: A thin copper layer (1-2oz) on the aluminum base’s component side is designed in a radial pattern from the thermal pad, directing heat from the component to the aluminum core’s entire surface. This increases heat spreading area by 2-3x compared to no copper pour, reducing hotspots.
Integrated Fins: For ultra-high-power applications (150-200W), aluminum bases are machined with integral fins (height 5-10mm, spacing 3-5mm) to enhance passive cooling. The thermal pad transfers heat to the finned aluminum core, which dissipates heat via natural convection—eliminating the need for fans.
Residential & Commercial Lighting: 5-30W LED downlights, panel lights, and track lights use 1.0-1.5mm aluminum base PCBs with graphite-enhanced thermal pads, balancing slim design and energy efficiency (≥80 lm/W).
Industrial & Outdoor Lighting: 50-200W LED high-bays, floodlights, and street lights leverage 2.0-3.0mm aluminum bases with metal-particle thermal pads, enduring 12+ hours of daily operation while maintaining lumen output (≥90% retention after 10,000 hours).
65-120W Charger Adapters: Compact aluminum base PCBs (50x70mm) with PCM thermal pads cool high-current charging chips (e.g., GaN-based controllers), enabling slim charger designs (thickness ≤15mm) without overheating.
Power Banks & Wireless Chargers: 10-30W portable power devices use lightweight aluminum base PCBs to dissipate heat from charging circuits, extending battery life by preventing thermal degradation.
Interior Lighting: 5-20W LED ambient lighting, instrument cluster backlights, and door panel lights use aluminum base PCBs with phase-change thermal pads, withstanding cabin temperature fluctuations (-40°C to 85°C).
Sensor Modules: ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems) sensors (e.g., LiDAR, radar) use aluminum base PCBs to cool power management circuits, ensuring reliable performance in automotive environments.
Mid-Power Inverters & Motor Drives: 50-100kW industrial systems use aluminum base PCBs with metal-particle thermal pads to cool IGBTs and diodes, balancing cost and reliability for 24/7 operation.
IoT Edge Devices: Compact industrial sensors and controllers leverage aluminum base PCBs’ lightweight and thermal efficiency, operating in harsh environments (dust, humidity) without active cooling.
Aluminum base PCBs are compatible with standard PCB manufacturing equipment, enabling high-volume production (100k+ units/month) with minimal retooling. Thermal pads are applied via automated lamination machines, with cycle times as low as 10 seconds per board—far faster than manual bonding for ceramic or copper base alternatives.
Aluminum’s resistance to warpage during etching, lamination, and soldering results in a yield rate of 98-99% (vs. 92-95% for copper base PCBs). Thermal pads’ flexibility compensates for minor aluminum surface irregularities, reducing defect rates caused by interface gaps.
Aluminum Base Thermal Pad PCBs easily meet global safety and environmental standards:
Electrical Safety: Dielectric layers with breakdown voltage ≥2kV comply with IEC 61249-2-21 (PCB safety standard) and UL 94V-0 (flame retardancy).
Environmental Compliance: Recycled aluminum (99.85% purity) and RoHS/REACH-compliant thermal pads (no lead, cadmium, or mercury) align with global sustainability regulations.
Aluminum bases with graphene or carbon nanotube (CNT) coatings are emerging, boosting thermal conductivity by 20-30% (to 280-300 W/(m·K)) while maintaining cost parity with standard aluminum designs. These coated bases paired with advanced thermal pads (e.g., MXene-infused polymers) will enable aluminum base PCBs to compete with copper base in 200-300W applications.
Next-generation designs will integrate EMI shielding or moisture-resistant layers into the thermal pad-aluminum base stack, reducing component count and simplifying assembly for high-frequency applications (e.g., 5G small cells).
Increased use of 100% recycled aluminum cores and bio-based thermal pad polymers will reduce carbon footprints by 30-40%, aligning with global circular economy goals while maintaining performance.
Aluminum Base Thermal Pad PCB represents the optimal balance of thermal efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and manufacturability for mass-produced high-power electronics. By leveraging aluminum’s lightweight, structural rigidity, and low cost with thermal pads’ gap-filling and heat-transfer capabilities, this solution addresses the core need of "scalable thermal management" for LED lighting, fast chargers, automotive electronics, and industrial systems. Its compatibility with high-volume production processes, high yield rate, and compliance with global standards make it the preferred choice for manufacturers seeking to balance performance and cost. As material innovations enhance aluminum’s thermal conductivity and thermal pads’ functionality, Aluminum Base Thermal Pad PCB will continue to dominate mid-to-high-power electronic applications, enabling the next generation of compact, efficient, and affordable devices.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
