-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Nov 24. 2025, 11:05:03
High Conductivity Thermal Pad MCPCB (Metal Core PCB) has emerged as a pivotal thermal management solution for high-power electronic systems, addressing the critical challenge of efficient heat transfer in compact, power-dense designs. Unlike standard MCPCBs that rely on basic thermal layers, this specialized variant integrates high-performance thermal pads—engineered to minimize thermal resistance—with robust metal cores (aluminum, copper, or composite substrates). As electronic devices from high-power LEDs to industrial semiconductors push toward higher power densities and smaller form factors, High Conductivity Thermal Pad MCPCB bridges the gap between heat dissipation efficiency and structural reliability. This article explores the core synergies of thermal pads and MCPCBs, material innovations, design optimizations, targeted applications, and industry trends, highlighting their role in enabling next-generation high-performance electronics.
The performance of High Conductivity Thermal Pad MCPCB stems from the seamless integration of thermal pads with MCPCB’s metal core structure, resolving key thermal bottlenecks in traditional designs.
Traditional MCPCBs often suffer from thermal resistance at the interface between components and the metal core, caused by micro-irregularities and air gaps. High conductivity thermal pads—formulated with advanced thermally conductive materials—fill these gaps, creating a continuous heat transfer path from the component junction to the MCPCB’s metal core. This interface optimization eliminates a major thermal barrier, ensuring rapid heat dissipation that prevents junction temperature spikes. Unlike generic thermal interfaces, these pads are tailored to MCPCB’s metal core properties, maintaining structural compatibility while maximizing thermal conductivity.
MCPCB’s metal core acts as a natural heat spreader, but its effectiveness depends on uniform heat distribution from the component. High conductivity thermal pads amplify this capability by distributing concentrated heat across a larger surface area before it reaches the metal core. This prevents hotspots—common in high-power applications like LED arrays or power semiconductors—that degrade performance and shorten component lifespans. The combination of the thermal pad’s heat-spreading ability and the MCPCB’s metal core’s thermal conductivity ensures consistent temperature distribution across the board.
High Conductivity Thermal Pad MCPCB maintains MCPCB’s inherent structural rigidity while adding thermal functionality. The thermal pad is engineered to withstand the mechanical stress of component mounting and thermal cycling, avoiding delamination or degradation over time. Additionally, the pad’s dielectric properties ensure electrical isolation between the component and the metal core, preventing short circuits while preserving thermal continuity. This dual compatibility—mechanical and electrical—makes the design suitable for rugged environments where reliability is non-negotiable.
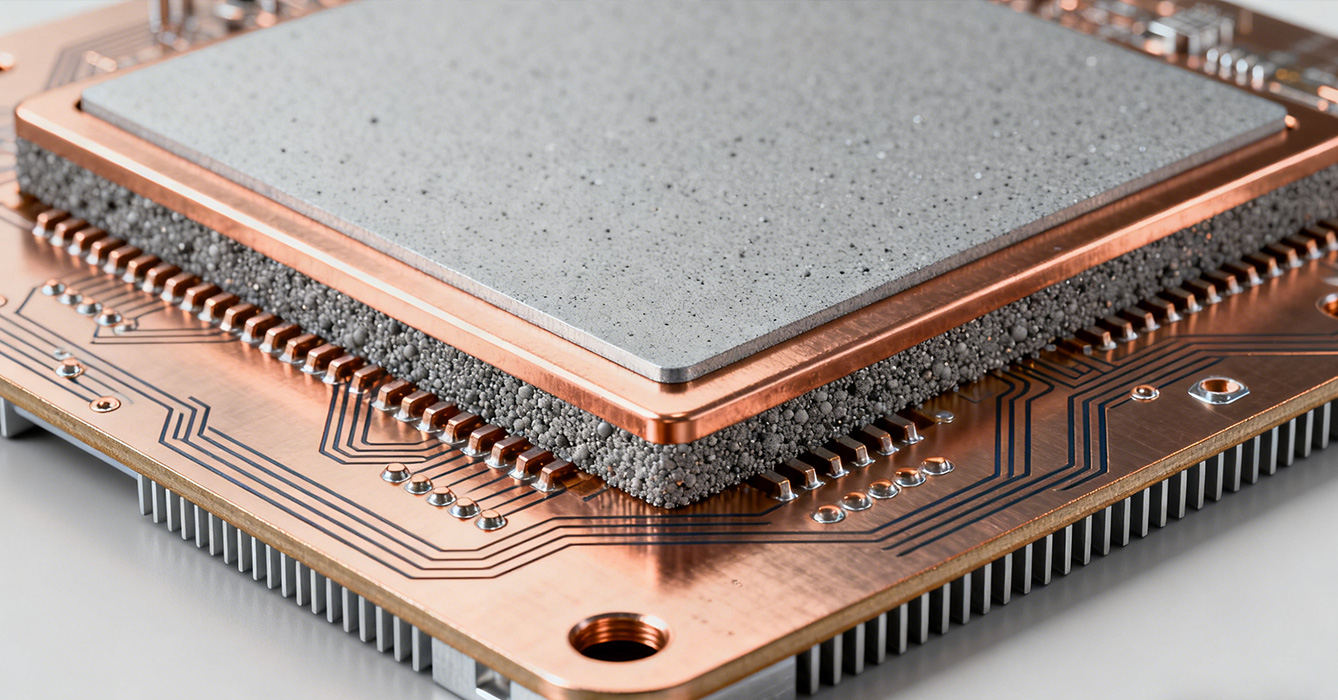

The performance of High Conductivity Thermal Pad MCPCB is defined by the thermal pad’s material composition, which balances conductivity, flexibility, and compatibility with MCPCB substrates.
Graphite-Enhanced Polymers: These pads combine the high thermal conductivity of graphite with the flexibility of polymer matrices, offering superior heat transfer while conforming to surface irregularities. Ideal for low-profile MCPCB designs (e.g., slim LED fixtures), they maintain conductivity even under compression.
Metal Particle Composites: Thermal pads infused with copper or aluminum particles deliver exceptional conductivity, bridging the gap between organic pads and solid metal interfaces. They are particularly effective for high-power MCPCBs (e.g., industrial power supplies) where maximum heat transfer is critical.
Phase-Change Materials (PCMs): These pads melt at operational temperatures, filling micro-gaps completely to minimize thermal resistance. They are well-suited for MCPCBs in temperature-variable environments (e.g., automotive electronics), as they adapt to thermal cycling without losing performance.
The thermal pad’s material is matched to the MCPCB’s metal core to optimize performance:
Aluminum Core MCPCBs: Paired with graphite or polymer-based thermal pads, aluminum core designs offer a cost-effective balance of conductivity and weight, ideal for mass-produced applications like LED lighting.
Copper Core MCPCBs: Combined with metal-particle thermal pads, copper core MCPCBs deliver maximum thermal performance for ultra-high-power systems (e.g., industrial inverters), leveraging copper’s superior heat transfer capabilities.
Composite Core MCPCBs: Ceramic-copper hybrid cores use specialized thermal pads to manage thermal expansion mismatches, ensuring reliability in extreme-temperature applications (e.g., aerospace electronics).
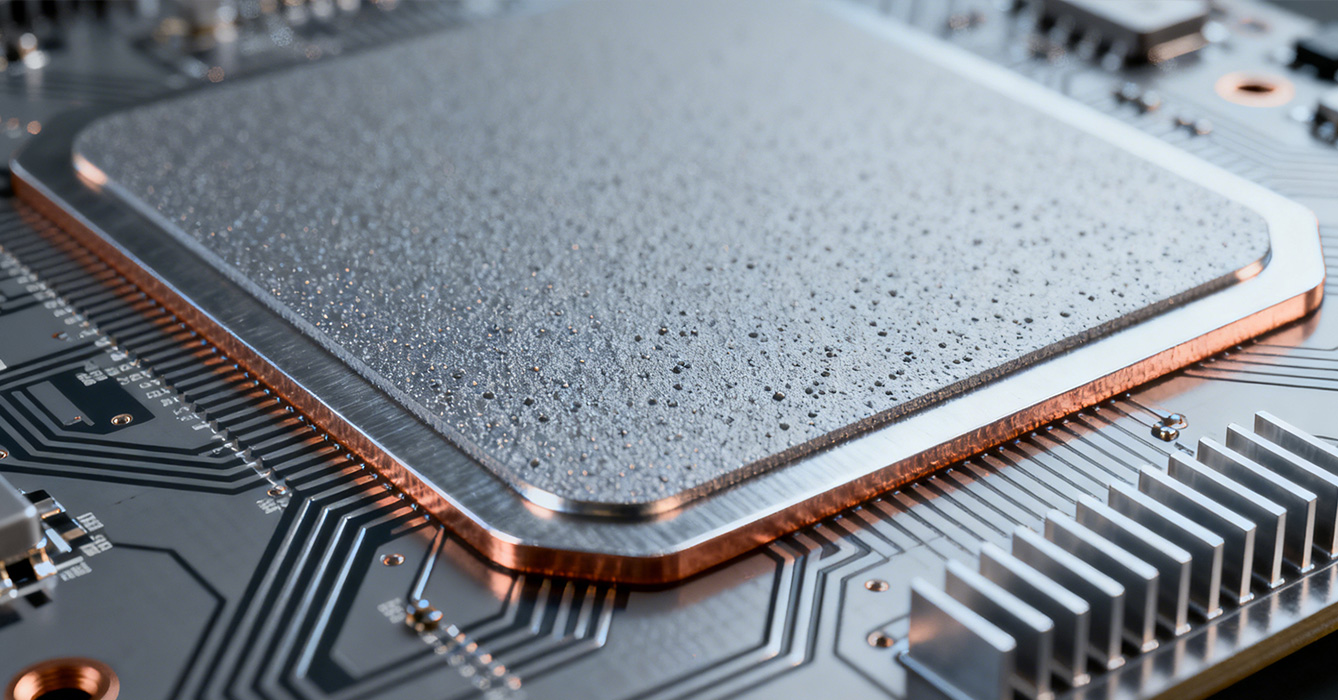
High Conductivity Thermal Pad MCPCB requires targeted design strategies to maximize thermal efficiency while accommodating application-specific constraints.
The thermal pad is precision-sized to match the component’s thermal footprint, ensuring full contact without excess material that could increase thermal mass. For arrayed components (e.g., LED modules), individual thermal pads are aligned with each chip to maintain uniform heat transfer. In high-density MCPCBs, thermal pads are strategically placed to avoid overlapping with signal traces, preserving electrical performance while prioritizing thermal paths.
Surface finish optimization is critical for minimizing contact resistance: MCPCB metal cores are precision-ground to reduce roughness, while thermal pads feature a low-tack surface that adheres without compromising heat transfer. For demanding applications, thermal pads are pre-cut to exact dimensions, eliminating gaps caused by improper fitting. Additionally, the pad’s thickness is calibrated to balance gap-filling capability and mechanical stability, ensuring it remains intact during assembly and operation.
High Conductivity Thermal Pad MCPCB is designed to complement external cooling solutions:
Passive Cooling: The MCPCB’s metal core is paired with the thermal pad to enhance heat spreading to heat sinks or fixture housings, eliminating the need for active cooling in mid-power applications (e.g., residential LED lighting).
Active Cooling: For ultra-high-power systems (e.g., AI server components), the thermal pad-MCPCB combination works with fans or liquid cooling systems, ensuring efficient heat transfer from the component to the cooling medium.
High Conductivity Thermal Pad MCPCB is tailored to industries where thermal management directly impacts performance and reliability.
Industrial High-Bays & Floodlights: Copper core MCPCBs with metal-particle thermal pads cool 100W+ LED arrays, maintaining lumen output and extending lifespan by preventing overheating.
Automotive Headlights: Aluminum core MCPCBs paired with phase-change thermal pads withstand under-hood temperature fluctuations, ensuring consistent performance in LED headlight modules.
Power Inverters & Converters: Composite core MCPCBs with high-conductivity thermal pads manage heat from IGBTs and SiC semiconductors, enabling 24/7 operation in industrial automation systems.
Fast-Charging Modules: Compact MCPCBs with graphite-enhanced thermal pads dissipate heat from high-current charging circuits, supporting 65W+ fast chargers for consumer electronics and electric vehicles.
Avionics Systems: Radiation-resistant MCPCBs with ceramic-copper cores and specialized thermal pads cool power-dense avionics components, withstanding extreme temperature ranges (-55°C to 125°C) and vibration.
Radar Systems: Low-loss MCPCBs with high-conductivity thermal pads maintain signal integrity while dissipating heat from high-frequency radar modules, ensuring reliable performance in defense applications.
Advancements in material science are enabling thinner thermal pads (≤0.1mm) with maintained conductivity, supporting ultra-compact MCPCB designs for wearable electronics and miniaturized industrial sensors.
Next-generation thermal pads will integrate EMI shielding or moisture resistance, reducing component count and simplifying MCPCB design for high-frequency or harsh-environment applications.
The industry is shifting toward recycled metal particles and bio-based polymers in thermal pads, aligning with MCPCB manufacturers’ sustainability goals while preserving thermal performance.
High Conductivity Thermal Pad MCPCB represents a significant advancement in thermal management for high-power electronics, leveraging the synergy of advanced thermal pads and robust MCPCB architecture to resolve heat dissipation challenges. By minimizing thermal resistance, enhancing heat spreading, and maintaining structural compatibility, this solution enables the miniaturization and performance optimization of devices across LED lighting, industrial power electronics, and aerospace sectors. Material innovations and targeted design strategies ensure it meets the unique demands of diverse applications, while future trends promise even greater efficiency and functionality. As electronic systems continue to push the boundaries of power density, High Conductivity Thermal Pad MCPCB will remain a critical enabler, delivering reliable thermal management that unlocks the full potential of next-generation technologies.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
