-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Sep 29. 2025, 11:35:17
In the world of electronics, RF circuits play an essential role in the wireless communication systems we rely on every day. From smartphones to satellite communications, these circuits are at the heart of transmitting and receiving signals. This article will guide you through the fundamentals of RF circuits, helping you understand how they work and their importance in modern technology.
RF stands for Radio Frequency, which refers to electromagnetic wave frequencies in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz. RF circuits are electronic circuits that operate in this frequency range, enabling the transmission and reception of radio waves. They are crucial in devices that require wireless communication, such as radios, televisions, and mobile phones.
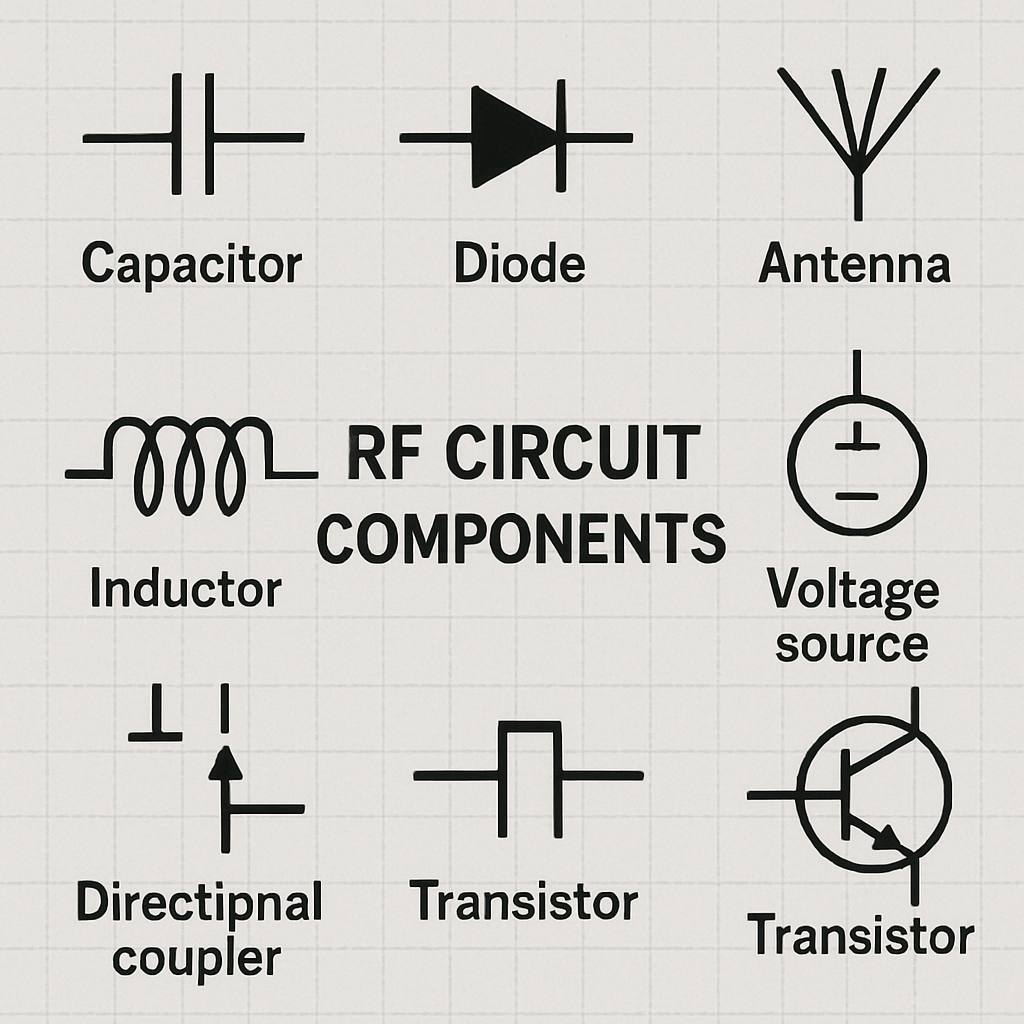
RF circuits consist of various components, each serving a specific function. Some of the key components include:
Resistors and Capacitors: These components manage the flow of electrical current and store electrical energy, respectively, within the circuit.
Inductors: Inductors store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them, which is vital for tuning and filtering signals.
Transistors and Diodes: These are active components that amplify signals and allow current to flow in one direction, respectively.
Antennas: Antennas are used to transmit and receive electromagnetic waves, converting them into electrical signals and vice versa.
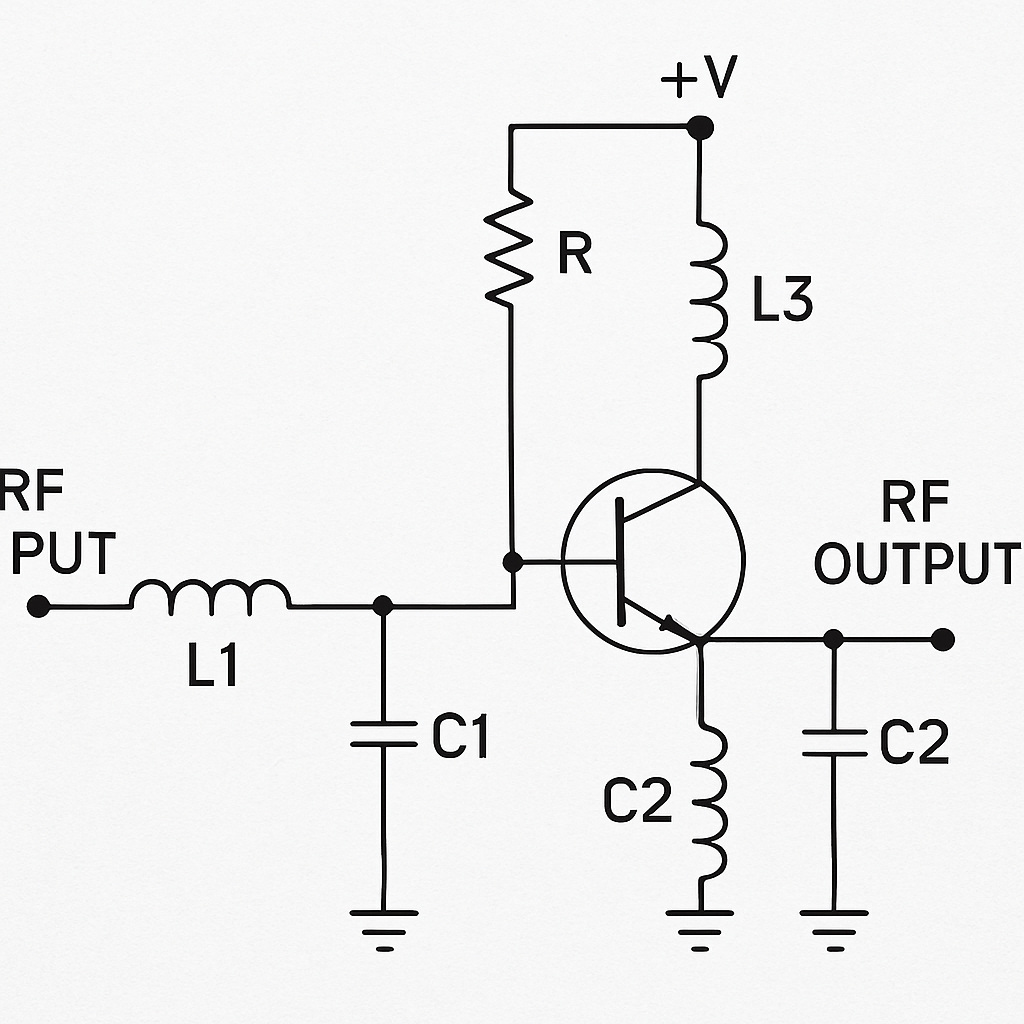
Active RF circuits use active components, such as transistors, to amplify or modify signals. These circuits are essential for boosting weak signals, making them stronger for further processing or transmission.
Active RF circuits work by using a small input signal to control a larger output signal. Transistors, the primary active components, are used to amplify the input signal. This amplification process is critical in maintaining signal strength and quality over long distances.
RF Amplifiers: These circuits amplify weak signals received by antennas, ensuring that the signal remains strong enough for processing.
Mixers: Mixers combine two or more signals to produce new frequencies, allowing for frequency conversion in communication systems.
Oscillators: Oscillators generate periodic waveforms, which are essential for producing carrier signals in communication systems.
Designing RF circuits requires a strong understanding of both the components and the signals they will process. Here are some key considerations when designing RF circuits:
The frequency range of an RF circuit determines its application. Different components and design techniques are needed for circuits operating at different frequency ranges. For example, circuits operating at higher frequencies require components with smaller physical dimensions.
Impedance matching is crucial in RF circuits to ensure maximum power transfer between components. Mismatched impedances can lead to signal reflection and loss, reducing the circuit's efficiency.
In RF circuit design, ensuring adequate signal amplification is vital. This involves selecting the right type and number of amplifiers to maintain the desired signal strength throughout the circuit.
Filtering
Filtering is used to remove unwanted frequencies from a signal. RF filters are designed to allow certain frequencies to pass while blocking others, ensuring that only the desired signals are processed.
Designing RF circuits comes with its own set of challenges. Here are some common obstacles faced by engineers:
Parasitic elements are unintended components that arise from the physical layout of the circuit. They can cause unwanted interference and signal distortion, complicating the design process.
RF circuits are susceptible to interference from other electronic devices and environmental factors. Shielding and careful layout design are necessary to minimize interference and maintain signal quality.
Heat generation is a significant concern in RF circuits, as excessive heat can damage components and degrade performance. Proper thermal management techniques, such as heat sinks and thermal pads, are essential to ensure the circuit's reliability.
RF circuits are used in a wide range of applications, from everyday consumer electronics to advanced communication systems. Some common applications include:
RF circuits are the backbone of wireless communication systems, enabling devices to transmit and receive signals over long distances. This includes mobile phones, Wi-Fi routers, and Bluetooth devices.
Radio and television broadcasting rely on RF circuits to transmit audio and video signals to receivers. These circuits ensure that signals are transmitted clearly and efficiently to reach a broad audience.
Radar systems use RF circuits to detect objects and measure their distance, speed, and direction. These systems are essential in aviation, maritime navigation, and weather forecasting.
Satellite communication systems use RF circuits to send and receive signals between Earth and satellites in orbit. These circuits enable global communication and data transmission for various applications, including GPS and satellite TV.
RF circuits are an integral part of modern technology, enabling wireless communication and signal processing across various applications. Understanding the basics of RF circuits, including their components, design considerations, and challenges, is essential for anyone interested in electronics and communication systems. With this knowledge, you'll be better equipped to appreciate the complexity and importance of RF circuits in our connected world.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
