-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
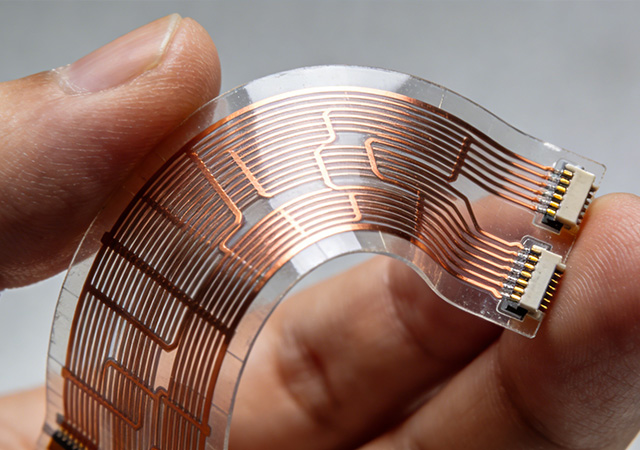
In the era of electronic miniaturization and intelligence, Flexible Circuit Assembly has evolved from a niche component process to a foundational technology that powers diverse electronic products. This assembly process leverages the inherent flexibility and compactness of flexible circuits, integrating electronic components into adaptive, space-efficient designs that overcome the limitations of rigid circuit assemblies. From everyday consumer gadgets to industrial automation systems and new energy equipment, Flexible Circuit Assembly enables seamless component integration, reliable signal transmission, and optimized product form factors. As industries pursue lighter, thinner, and more functional electronic devices, the versatility and adaptability of Flexible Circuit Assembly have made it an indispensable driver of modern electronic innovation.
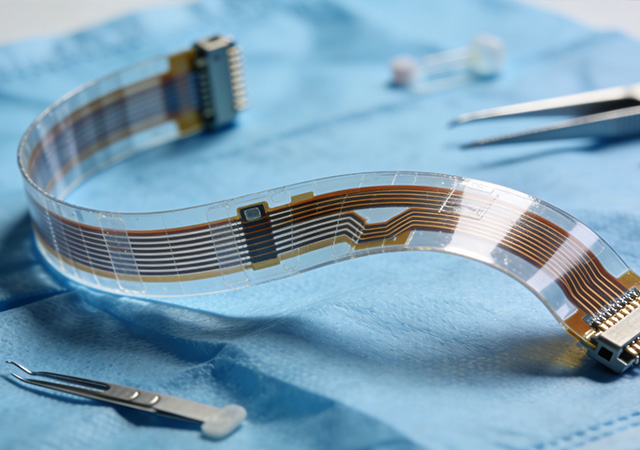
In the rapidly advancing landscape of healthcare technology, the demand for miniaturized, reliable, and biocompatible electronic components has elevated Medical Grade Flexible Circuit Assembly to a pivotal position. Unlike standard flexible circuit assembly, Medical Grade Flexible Circuit Assembly is engineered to meet the most stringent regulatory and performance requirements, as it directly impacts patient safety and treatment outcomes. This specialized assembly process integrates flexible circuit technology with medical-specific design principles, enabling the development of innovative devices ranging from implantable bioelectronics to minimally invasive surgical tools. As healthcare evolves toward personalized and precise medicine, Medical Grade Flexible Circuit Assembly has become an indispensable enabler, ensuring that life-critical devices deliver consistent performance in the complex and sensitive environment of the human body.
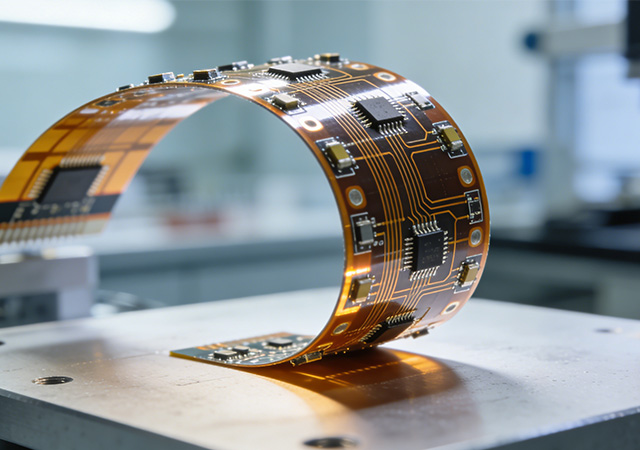
In the realm of advanced electronics, where performance margins are narrow and operational reliability is non-negotiable, High Precision Flexible Circuit Assembly has emerged as a foundational technology. This specialized assembly process combines the inherent flexibility of flexible circuits with ultra-precise manufacturing techniques, delivering interconnect solutions that meet the stringent requirements of mission-critical applications. From life-saving medical devices to high-performance aerospace systems, High Precision Flexible Circuit Assembly ensures that electronic components integrate seamlessly, transmit signals accurately, and withstand extreme operating conditions. As industries demand increasingly miniaturized, high-density, and reliable electronic systems, the role of this assembly technology in driving innovation and ensuring operational safety has become irreplaceable.
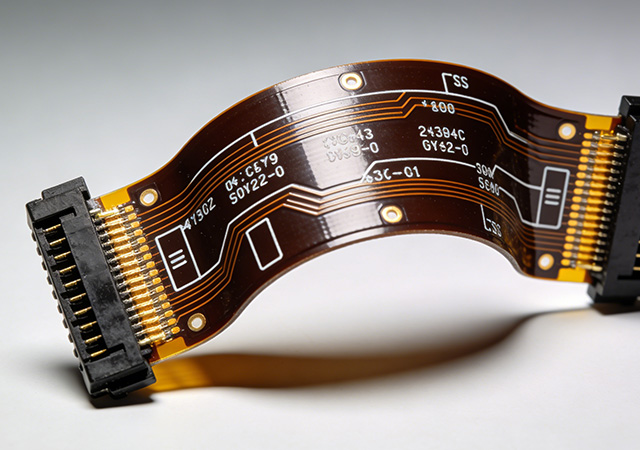
In the wave of electronic industry innovation, flexible circuit has emerged as a transformative foundational component, reshaping the design paradigm and application boundaries of electronic products. Unlike rigid printed circuit boards that restrict form and adaptability, flexible circuit features inherent flexibility, lightweight properties, and reliable electrical performance, enabling electronic devices to break free from traditional structural constraints. From daily consumer electronics to industrial automation and precision medical equipment, flexible circuit serves as the "vascular system" that connects components and transmits signals, laying a solid foundation for the development of flexible, portable, and intelligent electronic products. As global demand for high-performance and adaptive electronics continues to rise, the strategic value of flexible circuit in driving industry upgrading has become increasingly prominent.
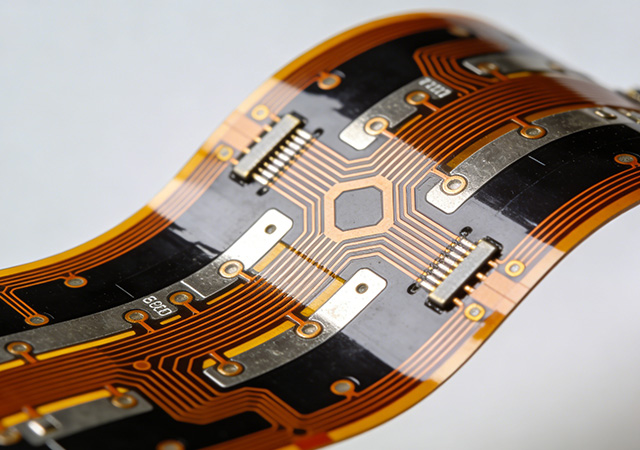
In the dynamic landscape of electronic product development, the demand for personalized, high-performance components has made customize flexible circuit a cornerstone of innovation. Unlike standard flexible circuits that offer limited adaptability, a customize flexible circuit is engineered to meet the unique spatial, functional, and environmental requirements of specific applications. From compact wearable devices to rugged industrial equipment, customize flexible circuit breaks through the design constraints of traditional electronic components, enabling engineers to translate creative concepts into practical, efficient products. As industries ranging from consumer electronics to smart manufacturing pursue greater product differentiation, the role of customize flexible circuit in delivering tailored solutions has become increasingly indispensable.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
