-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
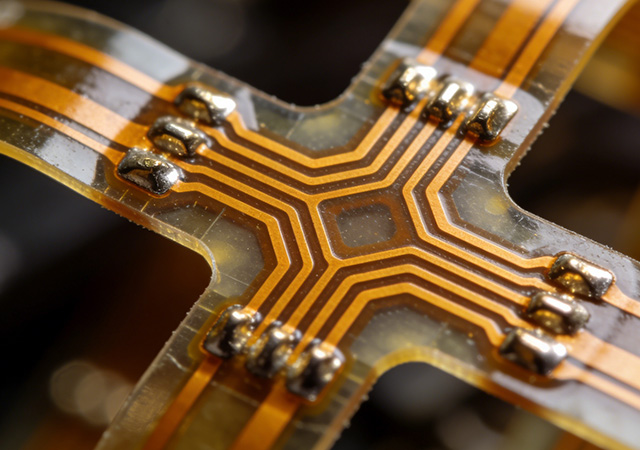
As global electronics industries march toward miniaturization, intelligence, and diversification, Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCB) have emerged as a pivotal component reshaping the design and performance of electronic products. Unlike rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs) that constrain product form factors and application scenarios, FPCB combines exceptional flexibility, lightweight construction, high-density integration, and reliable electrical performance. This versatile component breaks through the physical limitations of traditional electronics, enabling innovative designs in fields ranging from consumer electronics and medical devices to new energy vehicles and aerospace. For electronic product designers, engineering teams, and industry manufacturers, understanding the comprehensive value and application potential of FPCB is crucial to gaining a competitive edge in the fast-evolving market. This article explores the core advantages of FPCB, its diversified cross-industry appl
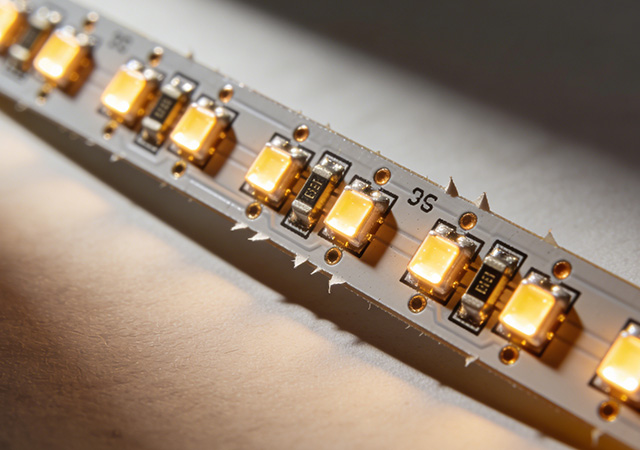
As the global lighting industry shifts toward intelligence, energy efficiency, and miniaturization, LED Lighting FPCB (Flexible Printed Circuit Board) has emerged as a core component driving innovation in lighting design and performance. Unlike rigid printed circuit boards that limit lighting form factors, LED Lighting FPCB combines flexibility, lightweight design, and excellent thermal conductivity, making it adaptable to a wide range of lighting applications—from compact smart home fixtures to large-scale urban landscape projects. This versatile component not only optimizes the structural design of LED lighting products but also enhances energy efficiency and service life, becoming an indispensable part of modern lighting ecosystems. For lighting designers, product developers, and facility operators, understanding the value and application of LED Lighting FPCB is key to creating competitive lighting solutions. This article explores the core advantages, diversified application scenari
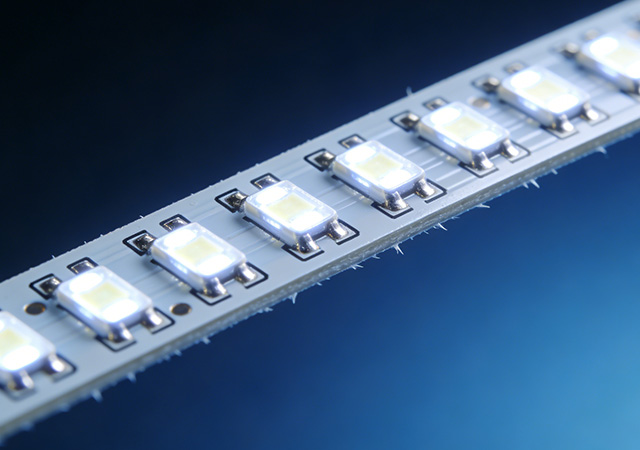

With the rapid expansion of high-performance lighting applications—from large-scale sports venues and new energy vehicle lighting to high-end commercial displays and medical surgical lighting—the demand for high brightness LED FPCB (Flexible Printed Circuit Board) has surged. A reliable High Brightness LED FPCB Manufacturer plays a pivotal role in this ecosystem, as it is not only a producer of core components but also a co-innovator that empowers downstream industries to achieve breakthroughs in lighting performance, design flexibility, and energy efficiency. Unlike ordinary LED FPCB manufacturers that focus solely on basic functionality, a professional High Brightness LED FPCB Manufacturer integrates advanced material technology, precision manufacturing processes, and customized solution capabilities to meet the stringent requirements of high-luminance, high-stability lighting scenarios. For enterprises engaged in lighting system design, automotive electronics, and display technology
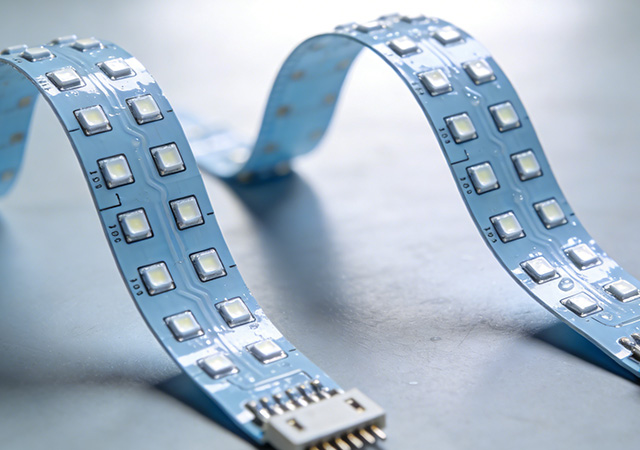
In lighting applications across harsh and humid environments—from outdoor landscapes and marine engineering to underground corridors and agricultural greenhouses—reliability and durability are critical requirements. The Waterproof LED FPCB Lighting Board has emerged as a game-changing solution, combining the flexibility of flexible printed circuit boards (FPCB) with advanced waterproof technology. Unlike traditional rigid PCB lighting boards that are prone to failure in humid conditions and lack adaptability to irregular surfaces, this innovative lighting board delivers stable performance in moisture-rich environments while fitting complex shapes. For engineers, project managers, and facility operators, the Waterproof LED FPCB Lighting Board is a core component to ensure long-term lighting stability, reduce maintenance costs, and expand the application scope of LED lighting. This article explores the core value, scenario-specific applications, implementation guidelines, and future tren
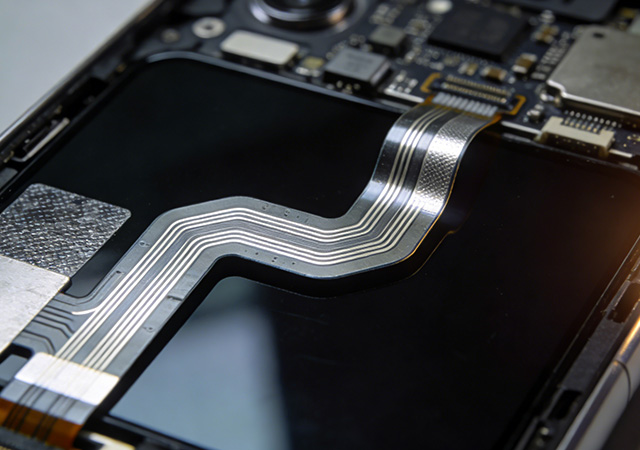

The relentless pursuit of smarter, more adaptive electronic devices has made Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPCB) a transformative force in the electronics industry. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs that constrain device design to fixed shapes and sizes, FPCB introduces unprecedented flexibility, enabling engineers to reimagine product forms while enhancing performance and user experience. From ultra-thin wearables that conform to the human body to curved automotive interfaces that blend seamlessly with interior designs, FPCB has become the backbone of innovative electronic products across sectors. As consumer demand for portability, ergonomics, and multi-functionality grows, the role of FPCB in shaping the future of electronics continues to expand.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
