-
- PCB TYPE
- PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD PROTOTYPE ALUMINUM PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD R&F PCB FPC HIGH FREQUENCY PCB HIGH-TG PCB HEAVY COPPER PCB HDI PCB PCB FOR LIGHTING METAL CORE PCB
time:Nov 21. 2025, 14:18:23
Energy-saving LED sinkpad design has become a critical focal point in the push for sustainable lighting, as it directly impacts both operational efficiency and environmental footprint. While LEDs inherently consume less power than traditional lighting technologies, their energy-saving potential is often untapped due to inadequate thermal management. Suboptimal sinkpad designs can lead to increased energy use, shortened lifespans, and compromised performance—undermining the sustainability goals of lighting systems. Unlike generic thermal solutions, energy-saving LED sinkpads require a holistic engineering approach that balances heat dissipation, material efficiency, and compliance with global energy standards. This article addresses the key engineering challenges, rigorous validation methods, industry compliance frameworks, and real-world implementation insights for energy-saving LED sinkpad design, providing a practical guide for engineers and manufacturers.
Developing effective energy-saving LED sinkpads requires overcoming interconnected challenges that span thermal, mechanical, and material engineering.
The primary challenge lies in integrating thermal management with electrical efficiency and mechanical practicality. LEDs operate most efficiently within a narrow thermal range, but sinkpad designs must also accommodate electrical traces, mounting constraints, and environmental stressors. For example, reducing sinkpad thickness to minimize material use can compromise thermal conductivity, while adding cooling features may increase weight and installation complexity. Engineers must navigate these trade-offs to create designs where thermal dissipation enhances energy efficiency without sacrificing structural integrity or electrical performance. This synergy is particularly critical in compact fixtures, where space limitations amplify the impact of every design decision.
Energy-saving LED sinkpads must perform reliably across diverse environmental conditions, from extreme temperatures in outdoor lighting to humidity in commercial spaces. Temperature fluctuations cause thermal expansion and contraction, which can degrade material bonds and create air gaps—increasing thermal resistance and forcing LEDs to consume more power to maintain brightness. For outdoor applications, sinkpads must resist corrosion, UV radiation, and moisture, as these factors reduce thermal efficiency over time. Balancing environmental durability with energy-saving goals requires selecting materials and finishes that withstand harsh conditions without adding unnecessary thermal mass or reducing heat transfer capabilities.
While advanced materials and designs can enhance energy savings, they often come with higher upfront costs. Engineers face the challenge of developing sinkpads that deliver long-term energy efficiency gains without pricing themselves out of the market. This requires prioritizing cost-effective materials (e.g., recycled aluminum over copper-graphene composites for mid-range applications) and optimizing designs to reduce manufacturing complexity. The goal is to create a total cost of ownership advantage, where lower energy bills offset any initial cost premium over standard sinkpads.
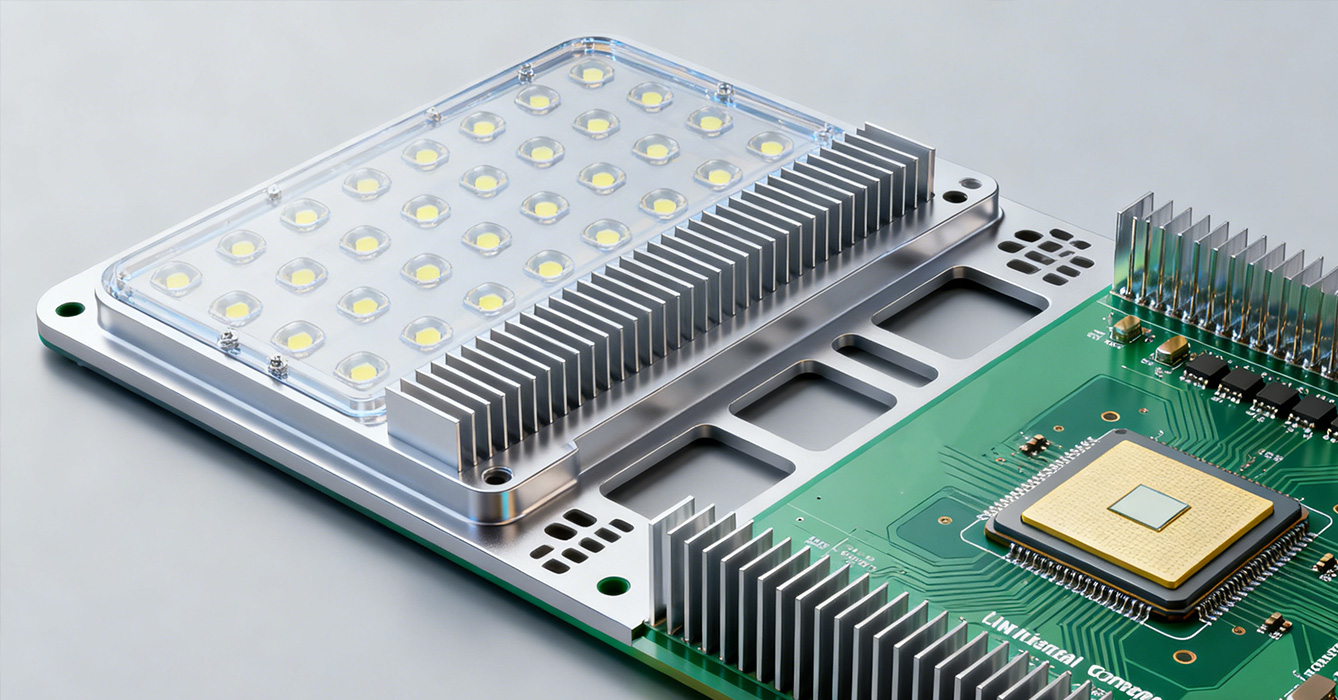
Ensuring the performance of energy-saving LED sinkpads requires specialized validation methods that measure both thermal efficiency and energy consumption.
Thermal Performance Testing
Infrared (IR) Thermography: Captures real-time temperature distribution across the sinkpad and LED junction, identifying hotspots that indicate inefficient heat transfer. This non-destructive test verifies that the sinkpad maintains uniform temperatures, a key factor in reducing energy use.
Thermal Resistance Measurement: Uses laser flash analysis (LFA) to quantify thermal resistance (Rθ) between the LED junction and sinkpad surface. Lower thermal resistance directly translates to reduced energy consumption, as LEDs operate at cooler temperatures.
Thermal Cycling Testing: Subjects sinkpads to repeated temperature cycles (-40°C to 85°C) to simulate real-world conditions, ensuring thermal efficiency remains consistent over time. This test validates that material bonds and thermal paths do not degrade, preserving energy-saving performance for the sinkpad’s lifespan.
Power Consumption Profiling: Measures LED driver power draw under different thermal conditions, comparing energy use with standard sinkpad designs. Validates that the energy-saving sinkpad reduces power consumption by 5-20% as intended, without compromising lumen output.
Lumen Maintenance Tracking: Monitors lumen output over 10,000+ hours to ensure energy savings do not come at the cost of performance. Energy-saving sinkpads should maintain ≥90% lumen output, as reduced brightness would force users to increase power to compensate.
Life-Cycle Energy Analysis: Calculates total energy use across the sinkpad’s lifespan, including manufacturing, transportation, operation, and disposal. This holistic analysis verifies that energy savings during operation outweigh any embodied energy from production.
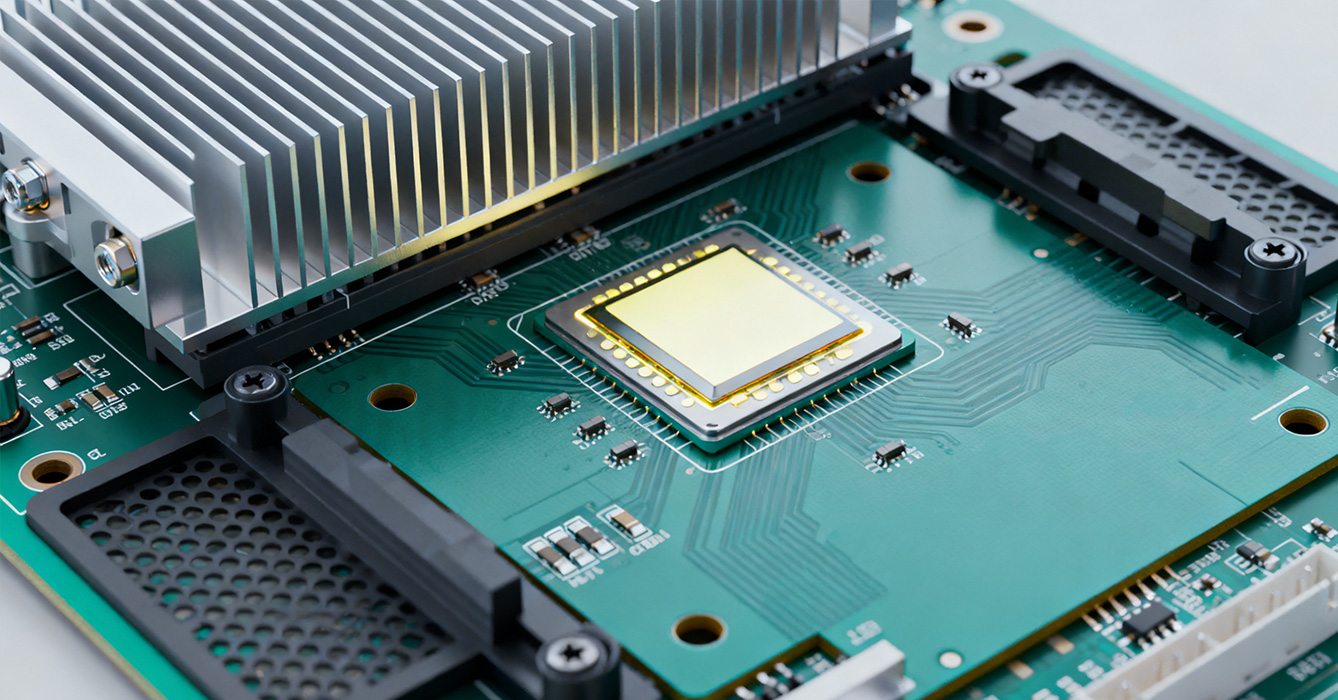

Energy-saving LED sinkpad designs must align with global standards and certifications to validate their efficiency claims and ensure market acceptance.
ENERGY STAR: Requires LED lighting systems to meet strict energy efficiency criteria, with sinkpad design playing a key role in achieving the required lumens per watt (lm/W) ratio. ENERGY STAR-certified fixtures with optimized sinkpads typically consume 75% less energy than incandescent lights.
IES LM-80: Specifies performance requirements for LED packages, modules, and arrays, including thermal management expectations. Sinkpad designs must support LM-80 compliance by maintaining junction temperatures within specified limits, ensuring consistent lumen output and energy efficiency.
EU ErP Directive: Mandates minimum energy performance standards for lighting products sold in the European Union. Energy-saving sinkpads help manufacturers meet ErP’s lm/W requirements and reduce the environmental impact of their products.
RoHS/REACH Compliance: Restricts hazardous substances in sinkpad materials, ensuring environmental safety during manufacturing and disposal. Using recycled metals and eco-friendly finishes helps meet these requirements while reducing carbon footprint.
BREEAM/LEED Integration: Supports green building certifications by contributing to energy efficiency and sustainability goals. Lighting systems with energy-saving sinkpads can earn points toward BREEAM or LEED certification, making them attractive for commercial and residential projects.
In smart office buildings, energy-saving LED sinkpads are integrated with occupancy sensors and natural light harvesting systems. For example, a 10-story office tower in Chicago used aluminum-fin sinkpads with low-loss thermal interfaces, reducing lighting energy consumption by 22% compared to standard designs. The sinkpads’ passive cooling eliminated fan energy use, while integration with smart controls adjusted power based on occupancy and ambient light—delivering annual energy savings of 30,000 kWh.
Solar street lights in rural areas rely on energy-saving sinkpads to maximize battery life. A project in Spain used corrosion-resistant sinkpads with integrated micro-channels, reducing LED power demand by 18%. This extended the lights’ runtime by 2.5 hours per night during low-sunlight months, eliminating the need for grid backup and reducing carbon emissions by 1.2 tons annually per 100 lights.
Energy-saving LED sinkpad design is a complex engineering endeavor that requires balancing thermal efficiency, environmental adaptability, and cost-effectiveness. By addressing core challenges such as thermal-electrical-mechanical synergy and environmental durability, engineers can create designs that unlock the full energy-saving potential of LED lighting. Rigorous validation methods—from thermal resistance testing to life-cycle energy analysis—ensure these designs perform as intended, while compliance with global standards like ENERGY STAR and ErP validates their efficiency claims. Real-world implementations in smart buildings and solar lighting demonstrate that energy-saving sinkpads deliver tangible benefits, reducing energy consumption, lowering costs, and supporting sustainability goals. As the lighting industry continues to prioritize efficiency and environmental responsibility, energy-saving LED sinkpad design will remain a critical technology, driving innovation and enabling a greener future.

Got project ready to assembly? Contact us: info@apollopcb.com



We're not around but we still want to hear from you! Leave us a note:

Leave Message to APOLLOPCB
